
Double switching
Encyclopedia
Switch
In electronics, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another....
to close or open both the positive and negative sides of a DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
electrical circuit, or both the hot and neutral sides of an AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
circuit. This technique is used to prevent shock hazard
Electric shock
Electric Shock of a body with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin, muscles or hair. Typically, the expression is used to denote an unwanted exposure to electricity, hence the effects are considered undesirable....
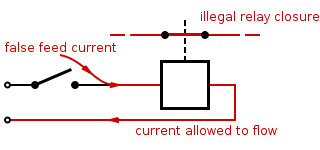
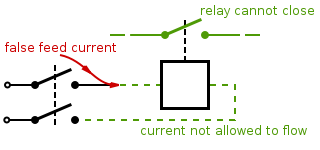
in electric devices connected with unpolarised AC power plugs and sockets. Double switching is a crucial safety engineering practice in railway signalling
Railway signalling
Railway signalling is a system used to control railway traffic safely, essentially to prevent trains from colliding. Being guided by fixed rails, trains are uniquely susceptible to collision; furthermore, trains cannot stop quickly, and frequently operate at speeds that do not enable them to stop...
, wherein it is used to ensure that a single false feed of current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
to a relay
Relay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
is unlikely to cause a wrong side failure. It is an example of using redundancy
Redundancy (engineering)
In engineering, redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system, usually in the case of a backup or fail-safe....
to increase safety and reduce the likelihood of failure, analogous to double insulation. Double switching increases the cost and complexity of systems in which it is employed, for example by extra relay contacts and extra relays, so the technique is applied selectively where it can provide a cost-effective safety improvement.
Landslip and Washaway Detectors
A landslip or washawayWashaway
A washaway is a particular kind of landslide that can affect man-made structures such as cuttings, embankments and bridges. They are thus a hazard to railways and road traffic.- Overview :...
detector is buried in the earth embankment, and opens a circuit should a landslide occur. It is not possible to guarantee that the wet earth of the embankment will not complete the circuit which is supposed to break. If the circuit is double cut with positive and negative wires, any wet conductive earth is likely to blow a fuse on the one hand, and short the detecting relay on the other hand, either of which is almost certain to apply the correct warning signal.
Clapham
The Clapham Junction rail crashClapham Junction rail crash
The Clapham Junction rail crash was a serious railway accident involving two collisions between three commuter trains at 08:10 on the morning of Monday, 12 December 1988....
of 1988 was caused in part by the lack of double switching (known as "double cutting" in the British Railway industry). The signal relay in question was switched only on the hot side, while the return current came back on an unswitched wire. A loose wire bypassed the contacts by which the train detection relays switched the signal, allowing the signal to show green when in fact there was a stationary train
Train
A train is a connected series of vehicles for rail transport that move along a track to transport cargo or passengers from one place to another place. The track usually consists of two rails, but might also be a monorail or maglev guideway.Propulsion for the train is provided by a separate...
ahead. 35 people were killed in the resultant collision.
United Flight 811
A similar accident on the United Airlines Flight 811United Airlines Flight 811
United Airlines Flight 811 experienced a cargo door failure in flight on Friday, February 24, 1989, after its stopover at Honolulu International Airport, Hawaii...
was caused in part by a single-switched safety circuit for the baggage door mechanism. Failure of the wiring insulation in that circuit allowed the baggage door to be unlocked by a false feed, leading to a catastrophic de-pressurisation, and the deaths of nine passengers.
Tri-colour LED
Some tri-colour Light Emitting Diodes for railway use were wired with four wires, one for each of the three colours, and a common wire for the return. Due to water ingress and other problems, the lamp units were displaying false greens. The solution was to change to wiring with six wires with separate positive and negative wires to the LEDs of each colour.Faulty attitude indicator
Big airplanes have three independent attitude indicatorAttitude indicator
An attitude indicator , also known as gyro horizon or artificial horizon, is an instrument used in an aircraft to inform the pilot of the orientation of the aircraft relative to earth. It indicates pitch and bank or roll and is a primary instrument for flight in instrument meteorological conditions...
s, one for the pilot, one for the co-pilot, and a third one to resolve disputes between the first two. A Peruvian airplane apparently had a faulty wire in one of the indicators. The indicators for the pilot and co-pilot were switched to common mode, so they both displayed the same wrong attitude indications. In the dark, it was not possible to tell the true horizon in any way other than the attitude indicator, and the plane crashed into the sea.
Railway couplings
Around 1994, new standards for the electrical couplings between carriages of United Kingdom passenger trains introduced the requirement for separate earth wires for critical functions such as brakes and doors. Common earths can cause interference between circuits that are otherwise independent, with unpredictable effects.A similar crosstalk problem occurred when using Phantom circuit
Phantom circuit
In telecommunication and electrical engineering, a phantom circuit is an electrical circuit derived from suitably arranged wires with one or more conductive paths being a circuit in itself and at the same time acting as one conductor of another circuit....
s to increase the number of telegraph or telephone circuits.

