
Double junction
Encyclopedia
Junction (rail)
A junction, in the context of rail transport, is a place at which two or more rail routes converge or diverge.This implies a physical connection between the tracks of the two routes , 'points' and signalling.one or two tracks each meet at a junction, a fairly simple layout of tracks suffices to...
where a double track
Double track
A double track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single track railway where trains in both directions share the same track.- Overview :...
railway splits into two double track lines. Usually, one line is the main line
Main line (railway)
The Mainline or Main line of a railway is a track that is used for through trains or is the principal artery of the system from which branch lines, yards, sidings and spurs are connected....
and carries traffic through the junction at normal speed, while the other track is a branch line
Branch line
A branch line is a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line...
that carries traffic through the junction at reduced speed.
A number of configurations are possible.
Diamond
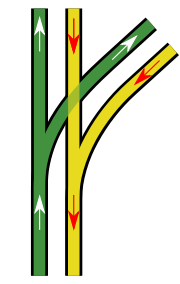
The simplest and oldest arrangement consists of two turnouts
Railroad switch
A railroad switch, turnout or [set of] points is a mechanical installation enabling railway trains to be guided from one track to another at a railway junction....
and a fixed diamond crossing. Because the diamond needs to be relatively coarse, say 1 in 8, the curve radius is necessarily small, leading to a speed of perhaps 25 km/h. This type of junction is common on street-running tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
ways, where speeds are quite low and junction must fit in to the available road space. Because the points are close together, the entire junction can be controlled by the mechanical point rodding of a single signal box
Signal box
On a rail transport system, signalling control is the process by which control is exercised over train movements by way of railway signals and block systems to ensure that trains operate safely, over the correct route and to the proper timetable...
.
Signal passed at danger
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
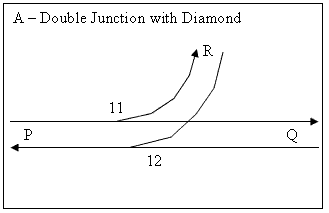
(SPAD) protection — A train from R to P with 12 points reverse is protected from a train from P doing a SPAD
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
by 11 points also lying reverse. A train from P to Q is NOT protected from a train from R doing a SPAD.
Switched diamond
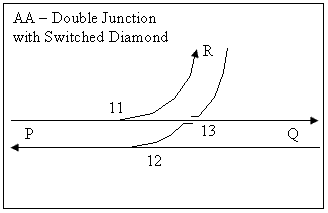
The fixed diamond can be replaced with a switched diamond, which eliminates the gap in rails at the K-crossing, which allows a higher speed if the geometry is poor. However, switched diamonds are not a perfect solution to the K-crossing problem, as the switches are very coarse compared to the finer switches of a turnout, and require high maintenance. The additional ends are also awkward to control unless power operated point machine
Point machine
A point machine is a device for operating railway turnouts especially at a distance.-Overview:In the earliest times, railway turnouts were operated manually by simple levers...
s are used.
Ladder
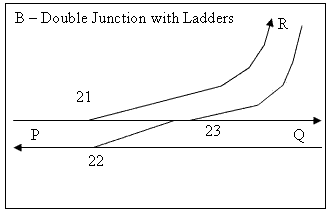
An improved junction replaces the diamond with turnouts, which can be of as fine an angle as possible, so that this junction can carry branch traffic at high speed. This configuration assumes power operation of the points, as high speed turnout are generally not suitable for mechanical operation. The high speed turnouts may require more than one point machine each. The turnouts can have no superelevation while the curve in the branch can; therefore the radius in the turnouts must be greater than the radius of the curve in the branch.
Since the ladder type junction requires much more length, diamond type junctions can only be converted into ladder types if there is room and no bridge, tunnels or platforms in the way.
SPAD protection
Essentially the same as for a double junction with diamond.
Examples include Harris Park railway station, Sydney.
Single lead Left Hand
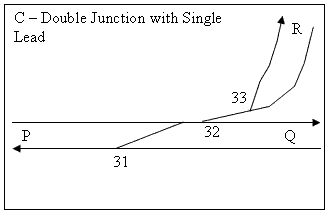
A single lead junction is used where traffic density is lower, and moves one of the turnouts on the main line onto the branch. This may reduce the number of turnouts on the main line that are subject to wear. The diamond crossing is a wearing component due to the gaps in the K-crossings, and this configuration eliminates the diamond.
Space permitting, a single lead junction may be a stage towards construction of a higher speed ladder junction.
Risk
However, unlike in the ladder, branch trains in opposite directions can collide head-onHead-on collision
A head-on collision is one where the front ends of two ships, trains, planes or vehicles hit each other, as opposed to a side collision or rear-end collision.-Rail transport:...
at 32 if either one passes a signal at danger
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
(SPAD). This has contributed to fatal accidents, e.g. in the UK at: Glasgow Bellgrove
Glasgow Bellgrove rail crash
On 6 March 1989 two Class 303 commuter trains crashed on the Springburn branch of the North Clyde Line, just east of Bellgrove station in the East End of Glasgow, Scotland...
on 6 March 1989 and Newton on 21 July 1991.

Junction (rail)
A junction, in the context of rail transport, is a place at which two or more rail routes converge or diverge.This implies a physical connection between the tracks of the two routes , 'points' and signalling.one or two tracks each meet at a junction, a fairly simple layout of tracks suffices to...
where a double track
Double track
A double track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single track railway where trains in both directions share the same track.- Overview :...
railway splits into two double track lines. Usually, one line is the main line
Main line (railway)
The Mainline or Main line of a railway is a track that is used for through trains or is the principal artery of the system from which branch lines, yards, sidings and spurs are connected....
and carries traffic through the junction at normal speed, while the other track is a branch line
Branch line
A branch line is a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line...
that carries traffic through the junction at reduced speed.
A number of configurations are possible.
Diamond

The simplest and oldest arrangement consists of two turnouts
Railroad switch
A railroad switch, turnout or [set of] points is a mechanical installation enabling railway trains to be guided from one track to another at a railway junction....
and a fixed diamond crossing. Because the diamond needs to be relatively coarse, say 1 in 8, the curve radius is necessarily small, leading to a speed of perhaps 25 km/h. This type of junction is common on street-running tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
ways, where speeds are quite low and junction must fit in to the available road space. Because the points are close together, the entire junction can be controlled by the mechanical point rodding of a single signal box
Signal box
On a rail transport system, signalling control is the process by which control is exercised over train movements by way of railway signals and block systems to ensure that trains operate safely, over the correct route and to the proper timetable...
.
Signal passed at danger
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
(SPAD) protection — A train from R to P with 12 points reverse is protected from a train from P doing a SPAD
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
by 11 points also lying reverse. A train from P to Q is NOT protected from a train from R doing a SPAD.
Switched diamond

The fixed diamond can be replaced with a switched diamond, which eliminates the gap in rails at the K-crossing, which allows a higher speed if the geometry is poor. However, switched diamonds are not a perfect solution to the K-crossing problem, as the switches are very coarse compared to the finer switches of a turnout, and require high maintenance. The additional ends are also awkward to control unless power operated point machine
Point machine
A point machine is a device for operating railway turnouts especially at a distance.-Overview:In the earliest times, railway turnouts were operated manually by simple levers...
s are used.
Ladder

An improved junction replaces the diamond with turnouts, which can be of as fine an angle as possible, so that this junction can carry branch traffic at high speed. This configuration assumes power operation of the points, as high speed turnout are generally not suitable for mechanical operation. The high speed turnouts may require more than one point machine each. The turnouts can have no superelevation while the curve in the branch can; therefore the radius in the turnouts must be greater than the radius of the curve in the branch.
Since the ladder type junction requires much more length, diamond type junctions can only be converted into ladder types if there is room and no bridge, tunnels or platforms in the way.
SPAD protection
Essentially the same as for a double junction with diamond.
Examples include Harris Park railway station, Sydney.
Single lead Left Hand

A single lead junction is used where traffic density is lower, and moves one of the turnouts on the main line onto the branch. This may reduce the number of turnouts on the main line that are subject to wear. The diamond crossing is a wearing component due to the gaps in the K-crossings, and this configuration eliminates the diamond.
Space permitting, a single lead junction may be a stage towards construction of a higher speed ladder junction.
Risk
However, unlike in the ladder, branch trains in opposite directions can collide head-onHead-on collision
A head-on collision is one where the front ends of two ships, trains, planes or vehicles hit each other, as opposed to a side collision or rear-end collision.-Rail transport:...
at 32 if either one passes a signal at danger
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
(SPAD). This has contributed to fatal accidents, e.g. in the UK at: Glasgow Bellgrove
Glasgow Bellgrove rail crash
On 6 March 1989 two Class 303 commuter trains crashed on the Springburn branch of the North Clyde Line, just east of Bellgrove station in the East End of Glasgow, Scotland...
on 6 March 1989 and Newton on 21 July 1991.

Junction (rail)
A junction, in the context of rail transport, is a place at which two or more rail routes converge or diverge.This implies a physical connection between the tracks of the two routes , 'points' and signalling.one or two tracks each meet at a junction, a fairly simple layout of tracks suffices to...
where a double track
Double track
A double track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single track railway where trains in both directions share the same track.- Overview :...
railway splits into two double track lines. Usually, one line is the main line
Main line (railway)
The Mainline or Main line of a railway is a track that is used for through trains or is the principal artery of the system from which branch lines, yards, sidings and spurs are connected....
and carries traffic through the junction at normal speed, while the other track is a branch line
Branch line
A branch line is a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line...
that carries traffic through the junction at reduced speed.
A number of configurations are possible.
Diamond

The simplest and oldest arrangement consists of two turnouts
Railroad switch
A railroad switch, turnout or [set of] points is a mechanical installation enabling railway trains to be guided from one track to another at a railway junction....
and a fixed diamond crossing. Because the diamond needs to be relatively coarse, say 1 in 8, the curve radius is necessarily small, leading to a speed of perhaps 25 km/h. This type of junction is common on street-running tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
ways, where speeds are quite low and junction must fit in to the available road space. Because the points are close together, the entire junction can be controlled by the mechanical point rodding of a single signal box
Signal box
On a rail transport system, signalling control is the process by which control is exercised over train movements by way of railway signals and block systems to ensure that trains operate safely, over the correct route and to the proper timetable...
.
Signal passed at danger
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
(SPAD) protection — A train from R to P with 12 points reverse is protected from a train from P doing a SPAD
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
by 11 points also lying reverse. A train from P to Q is NOT protected from a train from R doing a SPAD.
Switched diamond

The fixed diamond can be replaced with a switched diamond, which eliminates the gap in rails at the K-crossing, which allows a higher speed if the geometry is poor. However, switched diamonds are not a perfect solution to the K-crossing problem, as the switches are very coarse compared to the finer switches of a turnout, and require high maintenance. The additional ends are also awkward to control unless power operated point machine
Point machine
A point machine is a device for operating railway turnouts especially at a distance.-Overview:In the earliest times, railway turnouts were operated manually by simple levers...
s are used.
Ladder

An improved junction replaces the diamond with turnouts, which can be of as fine an angle as possible, so that this junction can carry branch traffic at high speed. This configuration assumes power operation of the points, as high speed turnout are generally not suitable for mechanical operation. The high speed turnouts may require more than one point machine each. The turnouts can have no superelevation while the curve in the branch can; therefore the radius in the turnouts must be greater than the radius of the curve in the branch.
Since the ladder type junction requires much more length, diamond type junctions can only be converted into ladder types if there is room and no bridge, tunnels or platforms in the way.
SPAD protection
Essentially the same as for a double junction with diamond.
Examples include Harris Park railway station, Sydney.
Single lead Left Hand

A single lead junction is used where traffic density is lower, and moves one of the turnouts on the main line onto the branch. This may reduce the number of turnouts on the main line that are subject to wear. The diamond crossing is a wearing component due to the gaps in the K-crossings, and this configuration eliminates the diamond.
Space permitting, a single lead junction may be a stage towards construction of a higher speed ladder junction.
Risk
However, unlike in the ladder, branch trains in opposite directions can collide head-onHead-on collision
A head-on collision is one where the front ends of two ships, trains, planes or vehicles hit each other, as opposed to a side collision or rear-end collision.-Rail transport:...
at 32 if either one passes a signal at danger
Signal passed at danger
A Signal passed at danger , in British railway terminology, occurs when a train passes a stop signal without authority to do so. It is a term primarily used within the British Railway Industry, although it can be applied worldwide.-Categories of SPAD:...
(SPAD). This has contributed to fatal accidents, e.g. in the UK at: Glasgow Bellgrove
Glasgow Bellgrove rail crash
On 6 March 1989 two Class 303 commuter trains crashed on the Springburn branch of the North Clyde Line, just east of Bellgrove station in the East End of Glasgow, Scotland...
on 6 March 1989 and Newton on 21 July 1991.Hall, Chapter 6: Hidden Dangers - Single Lead Junctions These risks can be reduced by trap points, ATP
Automatic Train Protection
Automatic Train Protection in Great Britain refers to either of two implementations of a train protection system installed in some trains in order to help prevent collisions through a driver's failure to observe a signal or speed restriction...
or TPWS.
Risk amelioration
The hazard of the short section of single line with the single lead junction would be reduced if there were two red signals protecting it. British practice mostly has one protecting signal. New South Wales practice mostly has two red signals protecting such a junction, albeit at the cost of some reduction in train headway. Alternatively, trap points could be installed to protect the single line. Two signal protection is a relatively easy way to reduce these risks, and would have been helpful at the Ladbroke Grove rail crashLadbroke Grove rail crash
The Ladbroke Grove Rail Crash was a rail accident which occurred on 5 October 1999 at Ladbroke Grove, London, England. Thirty-one people were killed and more than 520 injured...
. A comprehensive ATP system would also help.
Single lead Right Hand
A right hand single lead junction cannot protect against a collision should the Q-P train overrun the signal protecting the junction, and this is not ameliorated by reverting to a double junction.Diamond and wide centres
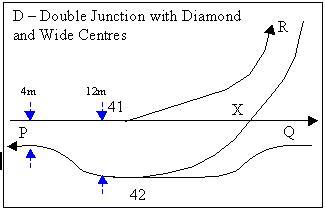
A double junction with a diamond can have its speed limit raised if the track centres are widened from say 4 m to say 12 m to allow for a fixed coarse-angled diamond crossing with fine-angled turnouts. Examples are at Cabramatta, Australia and Wootton Bassett
Wootton Bassett
Royal Wootton Bassett , informally known as Wootton Bassett, is a small market town and civil parish in Wiltshire, England, with a population of 11,043 in 2001...
, England.
If the legs of the coarse crossing X are straight, then this arrangement eliminates the need for switched diamonds and their inconvenient moving parts.
SPAD protection
Essentially the same as for a double junction with diamond.
Flyovers
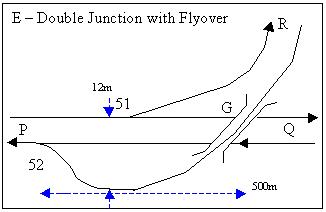
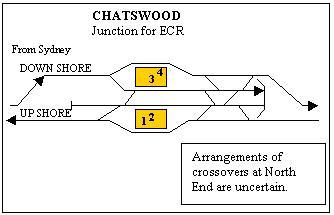
A double junction can be grade separated so that there is no flat crossing, reducing conflicts and reducing congestion. Flyovers require a lot of space both lengthwise and crosswise, and cannot always be built. Flying junction example at Aynho Junction. Diving junctions such as at Chatswood are a variant. Weaver Junction
Weaver Junction
Weaver Junction is a railway junction on the West Coast Main Line . It connects Ditton to the WCML via Runcorn Railway Bridge and opened on 1 April 1869. Trains bound for Liverpool from London diverge from the WCML at this junction. Weaver Junction is the oldest flying junction in Britain....
is the oldest flying junction in the United Kingdom and perhaps the world. See also Aynho Junction.
SPAD protection
Because the diamond crossing or equivalent is eliminated, one of the potential SPAD hazards is also eliminated, leaving just the merging junction hazard.

