
Dive computer
Encyclopedia

Scuba diving
Scuba diving is a form of underwater diving in which a diver uses a scuba set to breathe underwater....
to measure the time and depth of a dive so that a safe ascent profile can be calculated and displayed so that the diver can avoid decompression sickness
Decompression sickness
Decompression sickness describes a condition arising from dissolved gases coming out of solution into bubbles inside the body on depressurization...
.
Purpose
Dive computers address the same problem as decompression tables, but are able to perform a continuous calculation of the partial pressurePartial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
of inert gases in the body based on the actual depth and time profile
Dive profile
A dive profile is a two dimensional graphical representation of a dive showing depth and time.It is useful as an indication of the risks of decompression sickness and oxygen toxicity and also the volume of open-circuit breathing gas needed for a planned dive as these depend in part upon the depth...
of the diver. As the dive computer automatically measures depth and time, it is able to warn of excessive ascent rates and missed decompression stops and the diver has less reason to carry a separate dive watch and depth gauge
Depth gauge
A depth gauge is a pressure gauge that displays the equivalent depth in water. It is a piece of diving equipment often used by SCUBA divers.Most modern diving depth gauges have an electronic mechanism and digital display. Older types used a mechanical mechanism and analogue display.A diver uses a...
. Many dive computers also provide additional information to the diver including air and water temperature, data used to help prevent oxygen toxicity
Oxygen toxicity
Oxygen toxicity is a condition resulting from the harmful effects of breathing molecular oxygen at elevated partial pressures. It is also known as oxygen toxicity syndrome, oxygen intoxication, and oxygen poisoning...
, a computer-readable dive log, and the pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
of the remaining breathing gas
Breathing gas
Breathing gas is a mixture of gaseous chemical elements and compounds used for respiration.Air is the most common and only natural breathing gas...
in the diving cylinder
Diving cylinder
A diving cylinder, scuba tank or diving tank is a gas cylinder used to store and transport high pressure breathing gas as a component of a scuba set. It provides gas to the scuba diver through the demand valve of a diving regulator....
. This recorded information can be used for the diver's personal log of their activities or as important information in medical review
Forensic pathology
Forensic pathology is a branch of pathology concerned with determining the cause of death by examination of a corpse. The autopsy is performed by the pathologist at the request of a coroner or medical examiner usually during the investigation of criminal law cases and civil law cases in some...
or legal case
Legal case
A legal case is a dispute between opposing parties resolved by a court, or by some equivalent legal process. A legal case may be either civil or criminal...
s following diving accident
Accident
An accident or mishap is an unforeseen and unplanned event or circumstance, often with lack of intention or necessity. It implies a generally negative outcome which may have been avoided or prevented had circumstances leading up to the accident been recognized, and acted upon, prior to its...
s.
Because of the computer's ability to continually re-calculate based on changing data, the diver benefits by being able to safely remain underwater for longer periods of time. For example, a recreational diver who plans to stay within "no-decompression" limits can in many cases simply ascend a few feet each minute, while continuing the dive, and still remain within safe limits, rather than adhering to a pre-planned bottom time and ascending directly. So-called multi-level dives can be planned with traditional dive tables, but the additional calculations become complex and the plan may be cumbersome to follow. Computers allow for a certain amount of spontaneity during the dive.
History

Office of Naval Research
The Office of Naval Research , headquartered in Arlington, Virginia , is the office within the United States Department of the Navy that coordinates, executes, and promotes the science and technology programs of the U.S...
funded a project with the Scripps Institute of Oceanography for the theoretical design of a prototype decompression analog computer
Analog computer
An analog computer is a form of computer that uses the continuously-changeable aspects of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved...
. The Foxboro Decomputer, Mark I was manufactured by the Foxboro Company and evaluated by the US Navy Experimental Diving Unit
United States Navy Experimental Diving Unit
The United States Navy Experimental Diving Unit is the primary source of diving and hyperbaric operational guidance for the US Navy...
in 1957. Confusion between the diffusivity coefficient and the then new concept of tissue half time resulted in a device that did not properly mirror decompression status. Had this error not occurred, the U.S. Navy Tables might never have been developed, and divers might have been using instrumentation to control their dives from 1957 on.
The first recreational
Recreational diving
Recreational diving or sport diving is a type of diving that uses SCUBA equipment for the purpose of leisure and enjoyment. In some diving circles, the term "recreational diving" is used in contradistinction to "technical diving", a more demanding aspect of the sport which requires greater levels...
mechanical analogue dive computer
Analog computer
An analog computer is a form of computer that uses the continuously-changeable aspects of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved...
, the "decompression meter" was designed by the Italians De Sanctis & Alinari in 1959 and built in their factory named SOS, which also made depth gauges. The decompression meter was distributed directly by SOS and also by scuba diving equipment firms such as Scubapro and Cressi. It was very simple in principle: a waterproof bladder filled with gas inside a big casing bled into a smaller chamber through a semi-porous ceramic cartridge (to simulate tissue in/out gassing). The chamber pressure was measured by a bourdon tube, calibrated to indicate decompression status. The device functioned so poorly that it was eventually nicknamed "bend-O-meter".
In 1965, Stubbs and Kidd applied their decompression model to a pneumatic analogue decompression computer.
Several analogue decompression meters were subsequently made, some with several bladders for illustrating the effect on various body tissues, but they were sidelined with the arrival on the scene of electronic computers.
In 1980/81, the Hans Hass
Hans Hass
Hans Hass is a diving pioneer known mainly for his documentaries about sharks, the energon theory, and his commitment, later in life, to the protection of the environment. He was born in Vienna, Austria.-Early years:...
DecoBrain, designed and invented by D.I. Juergen Hermann a Swiss electronic engineer, became the first popular decompression diving computer, capable of displaying the information that today's diving computers do. The Deco Brain was based on Prof. Dr. A. Bühlmann's 16 compartment (ZHL-12) tissue model which Hermann implemented on one of Intel's first single-chip microcontrollers as part of his thesis at the Swiss Institute of Technology. Hermann marketed the Deco Brain from 1982 on; in the following years he miniaturized diving computers to the size of a match box (called Micro Brain, DC11, DC12, TRAC and others), and finally sold his company, Divetronic AG, to Scubapro for several million US dollars in 1991. Today, Scubapro/Uwatec is still one of the leading diving computer manufacturers.
The 1984 Orca EDGE was an early example of a no-decompression computer. The EDGE was unable to display a decompression plan, but instead the EDGE showed the ceiling or the so-called "safe-ascent-depth". If the diver was faced by a ceiling, he did not know how long he would have to decompress. At that time, only the Deco Brain was able to compute and display a decompression plan, displaying the total ascent time, the related decompression stops and decompression times.
In 1984 D.I. Juergen Hermann also developed the US Navy diving computer (UDC) which was based on a 9 tissue model of Dr. Edward D. Thalmann
Edward D. Thalmann
Capt. Edward Deforest Thalmann, USN was an American hyperbaric medicine specialist who was principally responsible for developing the current United States Navy dive tables for mixed-gas diving, which are based on his eponymous Thalmann Algorithm...
of the Naval Experimental Diving Unit (NEDU), Panama City, who developed the US Navy tables. Hermann completed the UDC development – as it had been started by the chief engineer Kirk Jennings of the Naval Ocean System Center, Hawaii, and Dr. Thalmann of the NEDU – by adapting the Deco Brain for US Navy warfare use and for their 9-tissue MK-15 mixgas model under an R&D contract of the US Navy. Divetronic also received further R&D work from the US Navy in the following years and received US Navy approval for their UDC's.
In 2001, the US Navy approved the use of Cochran NAVY decompression computer with the VVAL 18 Thalmann algorithm
Thalmann Algorithm
The Thalmann Algorithm is a deterministic decompression model originally designed in 1980 to produce a decompression schedule for divers using the US Navy Mk15 rebreather.It was developed by Capt. Edward D...
for Special Warfare operations.
In 2008, the Underwater Digital Interface (UDI) was released to the market. This dive computer, based on the RGBM model, includes an underwater communication system that enables divers to transmit text messages, also featuring SOS and homing capabilities, and digital 3D compass.
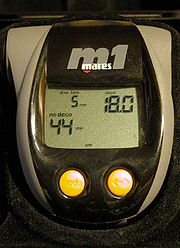
Display information
Dive computers provide a variety of visual dive information to the diver.Modern dive computers display the following information on a LCD
Liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
:
- Current depth.
- Maximum depth reached on this dive.
- No stop time, the time remaining at the current depth without the need for decompression stops on ascent.
- Dive time, often measured from the end of the last longer surface interval.
Many dive computers also display additional information:
- Total ascent time
- Required decompression stop depth and time.
- Water temperature.
- Ascent rate.
- Dive profile (often not displayed during the dive, but transmitted to a personal computer).
Some computers are designed to display information from a diving cylinder
Diving cylinder
A diving cylinder, scuba tank or diving tank is a gas cylinder used to store and transport high pressure breathing gas as a component of a scuba set. It provides gas to the scuba diver through the demand valve of a diving regulator....
pressure sensor, such as:
- Gas pressure.
- Estimated remaining air time (RAT) based on available gas, rate of gas consumption and ascent time.
Some information is only shown at the surface to avoid an information overload of the diver during the dive:
- "Time to Fly" display showing when the diver can safely board an airplane.
- Desaturation time
- A log of key information about previous dives.
- Maximum non-decompression bottom times for subsequent dives based on the partial pressure of the gases in the tissue.
- dive planning functions
Audible information
Many dive computers have warning buzzers that warn the diver of events such as:- Excessive ascent rates.
- Missed decompression stops.
- Maximum operation depth exceeded.
- Oxygen toxicityOxygen toxicityOxygen toxicity is a condition resulting from the harmful effects of breathing molecular oxygen at elevated partial pressures. It is also known as oxygen toxicity syndrome, oxygen intoxication, and oxygen poisoning...
limits exceeded.
Operation
Modern dive computers are batteryBattery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
-powered computers within a watertight case. These computers track the dive profile by measuring time and pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
. All dive computers measure the surrounding pressure to estimate the partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
of gases in the human tissue. More advanced dive computers also include additional information into the calculations, for example, the water temperature or the diving cylinder pressure.
The computer then uses the profile and a decompression algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
to estimate the partial pressure of inert gases that has been dissolved in the diver's tissues. Based on these calculations, the computer estimates when a direct ascent is no longer possible, and what decompression stops would be needed.
Examples of decompression algorithms are Bühlmann tables
Bühlmann tables
The Bühlmann decompression algorithm is a mathematical model of the way in which inert gases enter and leave the body as the ambient pressure changes. It is used to create Bühlmann tables. These are decompression tables which allow divers to plan the depth and duration for dives and show...
, the Multi-Tissue Model, the Varying Permeability Model
Varying Permeability Model
The Varying Permeability Model, Variable Permeability Model or VPM is an algorithm that is used to calculate the decompression stops needed for a particular dive profile. It was developed by D.E. Yount and others for use in professional diving and recreational diving...
, and the Reduced Gradient Bubble Model
Reduced Gradient Bubble Model
The reduced gradient bubble model ' is an algorithm developed by Dr Bruce Wienke for calculating decompression stops needed for a particular dive profile. It is based on the Varying Permeability Model....
.
Many dive computers are able to produce a safe decompression schedule for dives that take place at altitude, which requires a slower ascent than at sea level, because the computers measure the atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
before the dive. When divers travel before or after diving and particularly when they fly, they should transport their dive computer with them in the same pressure regime so that the computer can measure the pressure profile that their body has undergone.
Algorithms
The algorithm used helps to minimise a diver's risk of decompression sickness
Decompression sickness
Decompression sickness describes a condition arising from dissolved gases coming out of solution into bubbles inside the body on depressurization...
(DCS). Diving scientists use known data that is recorded and averaged from previous divers to create an algorithm. The computer measures depth and time, then uses the algorithm to determine decompression requirements and no-stop times. An algorithm tries to account for magnitude of pressure reduction, repetitive exposures, rate of ascent, and time at altitude. Some algorithms may not be able to account for age, previous injury, ambient temperature, body type, alcohol consumption, dehydration, and other factors such as patent foramen ovale, when determining the decompression requirements, while others may attempt to compensate for temperature and workload by having sensors that monitor ambient temperature and cylinder pressure.
, the newest dive computers on the market use:
- Liquivision X1: V-Planner Live: VPM-B Varying Permeability ModelVarying Permeability ModelThe Varying Permeability Model, Variable Permeability Model or VPM is an algorithm that is used to calculate the decompression stops needed for a particular dive profile. It was developed by D.E. Yount and others for use in professional diving and recreational diving...
and GAP for X1: Bühlmann GF (Buhlman with Gradient Factors) - MaresMares (scuba gear company)Mares is a manufacturer of scuba equipment. Founded in 1949 by Ludovico Mares in Rapallo, Italy, the company initially made diving masks and spearguns. It has since expanded to become one of the largest scuba manufacturers, having merged with US manufacturer Dacor.- External links :*...
: Mares-Wienke Reduced Gradient Bubble ModelReduced Gradient Bubble ModelThe reduced gradient bubble model ' is an algorithm developed by Dr Bruce Wienke for calculating decompression stops needed for a particular dive profile. It is based on the Varying Permeability Model.... - Pelagic Pressure Systems: modified Haldanean/DSATDiving Science and TechnologyDiving Science and Technology is a corporate affiliate of the Professional Association of Diving Instructors and the developer of the Recreational Dive Planner. DSAT has held scientific workshops for diver safety and education....
Database or Bühlmann ZHL-16C(called Z+) - SeikoSeiko, more commonly known simply as Seiko , is a Japanese watch company.-History and ongoing developments:The company was founded in 1881, when Kintarō Hattori opened a watch and jewelry shop called in the Ginza area of Tokyo, Japan. Eleven years later, in 1892, he began to produce clocks under the...
: Bühlmann ZHL-12 + Randy Bohrer - SuuntoSuuntoSuunto Oy, based in Finland, is a company that produces and markets sports precision instruments for Diving, Training and Outdoor sports. Headquartered in Vantaa, Suunto employs more than 500 people worldwide, and its products are sold in over 100 countries...
: Suunto-Wienke Reduced Gradient Bubble ModelReduced Gradient Bubble ModelThe reduced gradient bubble model ' is an algorithm developed by Dr Bruce Wienke for calculating decompression stops needed for a particular dive profile. It is based on the Varying Permeability Model.... - Uwatec: Bühlmann ZH-L8 /ADT (Adaptive), MB (Micro Bubble), PMGPMGThe initialism or three letter acronym PMG may refer to:* Piped medical gases - i.e. oxygen and nitrous oxide which are often piped to every bed.* Polymicrogyria* Postmaster General or the Postmaster-General's Department...
(Predictive Multigas) - Heinrichs Weikamp OSTC and DR5: Bühlmann ZHL-16 and Bühlmann ZHL-16 plus Erick Baker's Gradient Factors deep stop algorithm both for open circuit and fixed set point closed circuit rebreather.
Special purpose dive computers
Some dive computers are able to calculate decompression schedules for breathing gasBreathing gas
Breathing gas is a mixture of gaseous chemical elements and compounds used for respiration.Air is the most common and only natural breathing gas...
es other than air, such as nitrox, pure oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, trimix or heliox
Heliox
Heliox is a breathing gas composed of a mixture of helium and oxygen .Heliox has been used medically since the 1930s, and although the medical community adopted it initially to alleviate symptoms of upper airway obstruction, its range of medical uses has since expanded greatly, mostly because of...
. The more basic nitrox dive computers only support one or two gas mixes for each dive. Others support many different mixes.
Most dive computers calculate decompression for 'open circuit' SCUBA
Scuba set
A scuba set is an independent breathing set that provides a scuba diver with the breathing gas necessary to breathe underwater during scuba diving. It is much used for sport diving and some sorts of work diving....
where the proportions of the breathing gases are constant: these are "constant fraction" dive computers. Other dive computers are designed to model the gases in some 'closed circuit' SCUBA (rebreather
Rebreather
A rebreather is a type of breathing set that provides a breathing gas containing oxygen and recycled exhaled gas. This recycling reduces the volume of breathing gas used, making a rebreather lighter and more compact than an open-circuit breathing set for the same duration in environments where...
s), which maintain constant partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
s of gases by varying the proportions of gases in the mixture: these are "constant partial pressure" dive computers.
Precautions
The ease of use of dive computers, however, also exposes the diver to other dangers. Dive computers allow divers to perform complex dives with little planning. This may lead divers to exceed their competence and experience by relying too much on the computer rather than proper planning, discipline and monitoring.Many dive computers have menus, various selectable options and various display modes, which are controlled by a small number of buttons on the front of the computer. The diver should become familiar with the control of the computer on a series of shallow and undemanding dives before relying on it for more challenging dives.
For safety reasons it is recommended that a dive plan should be established before the dive and then followed throughout the dive unless the dive is aborted. This dive plan should be within the limits of the decompression tables. This increases the margin of safety, and also provides a backup decompression schedule based on the dive tables in case the computer fails underwater. The main problem in establishing dive computer algorithms is that the gas absorption and release under pressure in the human body is still not completely understood. Furthermore, the risk of decompression sickness also depends on the physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
, fitness, condition and health of the individual diver.
A diver wishing to reduce the risk of decompression sickness can take a number of precautionary measures such as:
- Use dive computers with a conservative decompression model
- Use safety factors with dive computers (e.g. using a high altitude dive mode for a dive at sea level)
- Add additional deep safety stops during a deep dive
- Make a slow ascent
- Add additional shallow safety stops
- Have a long surface interval between dives
Many computers go into a "lockout" mode for 24 hours if the diver violates the computer's safety limits, to discourage continued diving after an unsafe dive. While in lockout mode, these computers will not function until the lockout period has ended. Other computers, for example Delta P's VR3, will continue to function, providing 'best guess' functionality whilst warning the diver that a stop has been missed, or stop depth exceeded.
Manufacturers
- CitizenCitizen Watch Co.is the core company of a Japanese global corporate group based in Tokyo, Japan. The company was originally founded as Shokosha Watch Research Institute in 1918 and is currently known as the manufacturer of CINCOM precision lathe machine tools as well as CITIZEN watches. The trade name originated...
- Cochran Undersea Technology
- HeinrichsWeikamp (Open sourceOpen sourceThe term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
) - Heliox Technologies
- HTM Sports: DacorDacor (scuba diving)Dacor is a former USA manufacturer scuba diving gear. Dacor was one of the five original United States diving gear makers: U.S. Divers, Healthways, Voit, Dacor, and Swimaster. Dacor is now merged with Mares.- External links :...
and MaresMares (scuba gear company)Mares is a manufacturer of scuba equipment. Founded in 1949 by Ludovico Mares in Rapallo, Italy, the company initially made diving masks and spearguns. It has since expanded to become one of the largest scuba manufacturers, having merged with US manufacturer Dacor.- External links :*... - HydroSpace Engineering
- Liquivision
- Orca Industries Inc. (No longer in business)
- Pelagic group: Aeris, Hollis and OceanicOceanic WorldwideOceanic is a company which currently designs and manufactures sport-type scuba gear. They were founded by Bob Hollis in 1972 and are based in San Leandro, California, USA.-Rebreathers:...
- Scubapro-UWATEC by Johnson OutdoorsJohnson OutdoorsJohnson Outdoors Inc. produces outdoor recreational products such as watercraft, diving equipment, compasses and navigational products, and outdoor clothing.-Company history:...
- SeikoSeiko, more commonly known simply as Seiko , is a Japanese watch company.-History and ongoing developments:The company was founded in 1881, when Kintarō Hattori opened a watch and jewelry shop called in the Ginza area of Tokyo, Japan. Eleven years later, in 1892, he began to produce clocks under the...
- Shearwater Research
- SuuntoSuuntoSuunto Oy, based in Finland, is a company that produces and markets sports precision instruments for Diving, Training and Outdoor sports. Headquartered in Vantaa, Suunto employs more than 500 people worldwide, and its products are sold in over 100 countries...
- uemis
- Underwater Technology Center
- VR Technology
Other retailers sell computer clones made by Seiko (Apeks, Cressi, Dive Rite, ScubaPro, Tusa, Zeagle) or Pelagic Pressure Systems (Beuchat
Beuchat
Beuchat International, known as Beuchat, was established in 1934 in Marseille, France and is now a worldwide leader in the design, manufacture and marketing of underwater equipment.-Business:Beuchat currently has 3 core ranges:...
, Genesis, Seemann, Sherwood) or Benemec Oy (A.P.Valves).
See also
- Bühlmann tablesBühlmann tablesThe Bühlmann decompression algorithm is a mathematical model of the way in which inert gases enter and leave the body as the ambient pressure changes. It is used to create Bühlmann tables. These are decompression tables which allow divers to plan the depth and duration for dives and show...
- Reduced Gradient Bubble ModelReduced Gradient Bubble ModelThe reduced gradient bubble model ' is an algorithm developed by Dr Bruce Wienke for calculating decompression stops needed for a particular dive profile. It is based on the Varying Permeability Model....
- Thalmann AlgorithmThalmann AlgorithmThe Thalmann Algorithm is a deterministic decompression model originally designed in 1980 to produce a decompression schedule for divers using the US Navy Mk15 rebreather.It was developed by Capt. Edward D...
- Varying Permeability ModelVarying Permeability ModelThe Varying Permeability Model, Variable Permeability Model or VPM is an algorithm that is used to calculate the decompression stops needed for a particular dive profile. It was developed by D.E. Yount and others for use in professional diving and recreational diving...
External links
- Dive computer reviews by Scuba Diving magazine.
- Dive computer group tests by DIVERNET magazine.
- Dive computer individual tests by DIVERNET magazine.
- Dive computer reviews by DIVE magazine.

