Distributive law between monads
Encyclopedia
In category theory
, an abstract branch of mathematics
, distributive laws between monads are a way to express abstractly that two algebraic structures distribute one over the other one.
Suppose that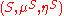 and
and 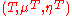 are two monads
are two monads
on a category
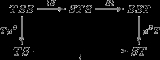
C. In general, there is no natural monad structure on the composite functor ST. On the other hand, there is a natural monad structure on the functor ST if there is a distributive law of the monad S over the monad T.
Formally, a distributive law of the monad S over the monad T is a natural transformation

such that the diagrams
commute.
This law induces a composite monad ST with
Category theory
Category theory is an area of study in mathematics that examines in an abstract way the properties of particular mathematical concepts, by formalising them as collections of objects and arrows , where these collections satisfy certain basic conditions...
, an abstract branch of mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, distributive laws between monads are a way to express abstractly that two algebraic structures distribute one over the other one.
Suppose that
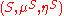 and
and 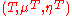 are two monads
are two monadsMonad (category theory)
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, a monad, Kleisli triple, or triple is an functor, together with two natural transformations...
on a category
Category theory
Category theory is an area of study in mathematics that examines in an abstract way the properties of particular mathematical concepts, by formalising them as collections of objects and arrows , where these collections satisfy certain basic conditions...
C. In general, there is no natural monad structure on the composite functor ST. On the other hand, there is a natural monad structure on the functor ST if there is a distributive law of the monad S over the monad T.
Formally, a distributive law of the monad S over the monad T is a natural transformation
Natural transformation
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, a natural transformation provides a way of transforming one functor into another while respecting the internal structure of the categories involved. Hence, a natural transformation can be considered to be a "morphism of functors". Indeed this intuition...

such that the diagrams
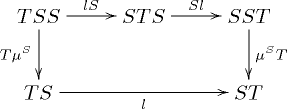
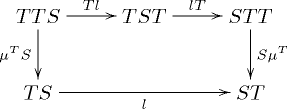
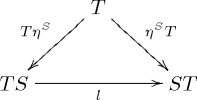 and
and 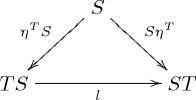
commute.
This law induces a composite monad ST with
- as multiplication:
 ,
, - as unit:
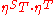 .
.

