
Disilyne
Encyclopedia
A disilyne is a chemical compound
that contains a formal silicon
- silicon triple bond
and as such is formulated R2Si2 (where R is a substituent group) and is the silicon analogue of an alkyne
. The hypothetical parent hydride, Si2H2 does not actually exist, all attempts to synthesize it results in a diradical disilene, with the systematic name of disilene-1,2-diyl. This compound readily tautomerises to disilenylidene. Some chemists use the term silyne to refer to compounds containing a silicon-silicon triple bond whilst others use the term to refer to compounds containing a silicon-carbon triple bond by analogy to silene which often refers to compounds containing silicon- carbon double bonds. The term polysilyne can refer to the layer polymer (SiH)n or substituted derivatives.
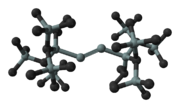 The first example isolated and characterised by X-ray crystallography is an emerald green crystalline compound reported in 2004.
The first example isolated and characterised by X-ray crystallography is an emerald green crystalline compound reported in 2004.
This molecule has the structure:
It was prepared by the reduction of the related tetrabrominated precursor by potassium graphite (KC8), it is air and moisture sensitive and does not melt or decompose until 128 °C.
Considered as a tetrasila-2-yne derivative the four Si atoms in the chain are not collinear and in this respect the compound differs from the related alkyne. The four silicon atoms in the chain are however perfectly coplanar, the first and fourth silicon atoms are trans to one another, and the angle between the triple bond and the adjacent silicon is 137°. The central triple bond is 206 pm (around 4% shorter than Si-Si double bonds (214pm)) and the other Si-Si single bonds are 237 pm. The colour is believed to be due to a weak π - π* transition.
29Si NMR shows upfield shift 89.9 ppm relative to silyl substituted disilenes.
Calculations show a bond order of 2.6. An alternative calculation of the bond order by a different group describes the bonding as essentially due to 2 electron pairs with the other pair in non-bonding orbitals.2. Reaction of this compound with phenylacetylene produced a 1,2 disilabenzene.
Other workers
have also reported another related compound which contains a hexasila-3-yne chain:
In this the Si-Si triple bond length was calculated as 207 pm.
in 2000
tin
and germanium
in 2002. In all of these the substituents attached to the bonded metal atoms are not collinear as in the alkynes but trans bent.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
that contains a formal silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
- silicon triple bond
Triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. The most common triple bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are...
and as such is formulated R2Si2 (where R is a substituent group) and is the silicon analogue of an alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
. The hypothetical parent hydride, Si2H2 does not actually exist, all attempts to synthesize it results in a diradical disilene, with the systematic name of disilene-1,2-diyl. This compound readily tautomerises to disilenylidene. Some chemists use the term silyne to refer to compounds containing a silicon-silicon triple bond whilst others use the term to refer to compounds containing a silicon-carbon triple bond by analogy to silene which often refers to compounds containing silicon- carbon double bonds. The term polysilyne can refer to the layer polymer (SiH)n or substituted derivatives.
The first reported disilynes

This molecule has the structure:
- R′2R′′Si-Si2-SiR′′R′2
- where R′ = HC(SiMe3)2 and R′′ = i-propyl
It was prepared by the reduction of the related tetrabrominated precursor by potassium graphite (KC8), it is air and moisture sensitive and does not melt or decompose until 128 °C.
Considered as a tetrasila-2-yne derivative the four Si atoms in the chain are not collinear and in this respect the compound differs from the related alkyne. The four silicon atoms in the chain are however perfectly coplanar, the first and fourth silicon atoms are trans to one another, and the angle between the triple bond and the adjacent silicon is 137°. The central triple bond is 206 pm (around 4% shorter than Si-Si double bonds (214pm)) and the other Si-Si single bonds are 237 pm. The colour is believed to be due to a weak π - π* transition.
29Si NMR shows upfield shift 89.9 ppm relative to silyl substituted disilenes.
Calculations show a bond order of 2.6. An alternative calculation of the bond order by a different group describes the bonding as essentially due to 2 electron pairs with the other pair in non-bonding orbitals.2. Reaction of this compound with phenylacetylene produced a 1,2 disilabenzene.
Other workers
have also reported another related compound which contains a hexasila-3-yne chain:
- R3Si(SiR3)SiMeSi2SiMe(SiR3)SiR3
- where Me = methyl and R = t-butyl
In this the Si-Si triple bond length was calculated as 207 pm.
Comparison to C-C, Ge-Ge, Sn-Sn, Pb-Pb triple bonds
Triple bonded compounds of the heavier members of group 14 have all been prepared, leadLead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
in 2000
tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
and germanium
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors tin and silicon. The isolated element is a semiconductor, with an appearance most similar to elemental silicon....
in 2002. In all of these the substituents attached to the bonded metal atoms are not collinear as in the alkynes but trans bent.

