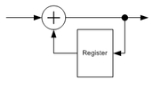
Differential coding
Encyclopedia
In digital communications, differential coding is a technique used to provide unambiguous signal reception when using some types of modulation
. It makes data to be transmitted to depend not only on the current bit (or symbol), but also on the previous one.
The common types of modulation that require differential coding include phase shift keying and quadrature amplitude modulation
.
circuit. However, a carrier can be recovered in different ways, depending upon a valid phases count (2 for BPSK).
For this coding, if a carrier is recovered incorrectly, the received data are inverted.
Assuming that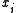 is a bit intended for transmission, and
is a bit intended for transmission, and 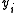 is a bit actually transmitted (differentially encoded), if
is a bit actually transmitted (differentially encoded), if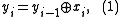
is transmitted, then on the decoding side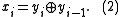
can be reconstructed, where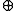 indicates binary or modulo-2
indicates binary or modulo-2
addition.
Now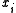 depends only on a difference between
depends only on a difference between 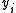 and
and 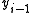 and not on their values. So, whether the data stream is inverted or not, the decoded data will always be correct.
and not on their values. So, whether the data stream is inverted or not, the decoded data will always be correct.
When data is transmitted over twisted-pair wires, it is easy to accidentally insert an extra half-twist in the cable between the transmitter and the receiver.
When this happens, the received data are inverted.
There are several different line code
s designed to be polarity insensitive -- whether the data stream is inverted or not, the decoded data will always be correct.
The line code
s with this property include differential Manchester encoding
, bipolar encoding
, NRZI, biphase mark code, coded mark inversion
, and MLT-3 encoding
.
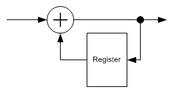
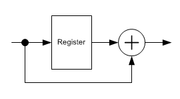 A method illustrated above can deal with a data stream inversion (it is called 180° ambiguity). Sometimes it is enough (e.g. if BPSK is used or if other ambiguities are detected by other circuits, such as a Viterbi decoder
A method illustrated above can deal with a data stream inversion (it is called 180° ambiguity). Sometimes it is enough (e.g. if BPSK is used or if other ambiguities are detected by other circuits, such as a Viterbi decoder
or a frame synchronizer
) and sometimes it isn't.
Generally speaking, a differential coding applies to symbols (these are not necessary the same symbols as used in the modulator). To resolve 180° ambiguity only, bits are used as these symbols. When dealing with 90° ambiguity, pairs of bits are used, and triplets of bits are used to resolve 45° ambiguity (e.g. in 8PSK).
A differential encoder provides the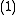 operation, a differential decoder - the
operation, a differential decoder - the 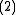 operation.
operation.
Both differential encoder and differential decoder are discrete linear time-invariant systems. The former is recursive and IIR
, the latter is non-recursive and thus FIR
. They can be analyzed as digital filter
s.
A differential encoder is similar to an analog integrator
. It has an impulse response
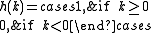
and a transfer function
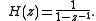
A differential decoder is thus similar to an analog differentiator
, its impulse response being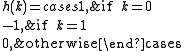
and its transfer function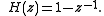
Note that in binary (modulo-2) arithmetic, addition and subtraction (and positive and negative numbers) are equivalent.
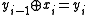 is not the only way of carrying out differential encoding. More generally, it can be any function
is not the only way of carrying out differential encoding. More generally, it can be any function 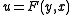 provided that an equation
provided that an equation 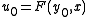 has one and only one solution for any
has one and only one solution for any 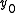 and
and 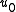 .
.
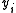 was received incorrectly, two incorrect symbols
was received incorrectly, two incorrect symbols 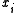 and
and 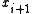 would be at the differential decoder's output, see:
would be at the differential decoder's output, see:
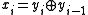 and
and 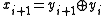 . This approximately doubles the BER at signal-to-noise ratios for which errors rarely occur in consecutive symbols.
. This approximately doubles the BER at signal-to-noise ratios for which errors rarely occur in consecutive symbols.
.
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
. It makes data to be transmitted to depend not only on the current bit (or symbol), but also on the previous one.
The common types of modulation that require differential coding include phase shift keying and quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
.
Purposes of differential coding
To demodulate BPSK one needs to make a local oscillator synchronous with the remote one. This is accomplished by a carrier recoveryCarrier recovery
A carrier recovery system is a circuit used to estimate and compensate for frequency and phase differences between a received signal's carrier wave and the receiver's local oscillator for the purpose of coherent demodulation....
circuit. However, a carrier can be recovered in different ways, depending upon a valid phases count (2 for BPSK).
For this coding, if a carrier is recovered incorrectly, the received data are inverted.
Assuming that
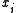 is a bit intended for transmission, and
is a bit intended for transmission, and 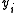 is a bit actually transmitted (differentially encoded), if
is a bit actually transmitted (differentially encoded), if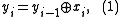
is transmitted, then on the decoding side
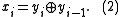
can be reconstructed, where
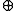 indicates binary or modulo-2
indicates binary or modulo-2Modular arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" after they reach a certain value—the modulus....
addition.
Now
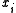 depends only on a difference between
depends only on a difference between 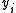 and
and 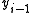 and not on their values. So, whether the data stream is inverted or not, the decoded data will always be correct.
and not on their values. So, whether the data stream is inverted or not, the decoded data will always be correct.When data is transmitted over twisted-pair wires, it is easy to accidentally insert an extra half-twist in the cable between the transmitter and the receiver.
When this happens, the received data are inverted.
There are several different line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
s designed to be polarity insensitive -- whether the data stream is inverted or not, the decoded data will always be correct.
The line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
s with this property include differential Manchester encoding
Differential Manchester encoding
Differential Manchester encoding, also called biphase mark code or FM1, is a line code in which data and clock signals are combined to form a single 2-level self-synchronizing data stream. It is a differential encoding, using the presence or absence of transitions to indicate logical value...
, bipolar encoding
Bipolar encoding
In telecommunication, bipolar encoding is a type of line code . A duobinary signal is such an encoding.- Advantages :...
, NRZI, biphase mark code, coded mark inversion
Coded mark inversion
In telecommunication, coded mark inversion is a non-return-to-zero line code. It encodes zero bits as a half bit time of zero followed by a half bit time of one, and while one bits are encoded as a full bit time of a constant level...
, and MLT-3 encoding
MLT-3 encoding
MLT-3 encoding is a line code that uses three voltage levels...
.
Conventional differential coding


Viterbi decoder
A Viterbi decoder uses the Viterbi algorithm for decoding a bitstream that has beenencoded using forward error correction based on a convolutional code....
or a frame synchronizer
Framing
Framing or enframing may refer to:* Framing , the most common carpentry work* Framing or Framing effect , terminology used in communication theory, sociology, and other disciplines where it relates to the construction and presentation of a fact or issue "framed" from a particular perspective*...
) and sometimes it isn't.
Generally speaking, a differential coding applies to symbols (these are not necessary the same symbols as used in the modulator). To resolve 180° ambiguity only, bits are used as these symbols. When dealing with 90° ambiguity, pairs of bits are used, and triplets of bits are used to resolve 45° ambiguity (e.g. in 8PSK).
A differential encoder provides the
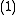 operation, a differential decoder - the
operation, a differential decoder - the 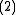 operation.
operation.Both differential encoder and differential decoder are discrete linear time-invariant systems. The former is recursive and IIR
Infinite impulse response
Infinite impulse response is a property of signal processing systems. Systems with this property are known as IIR systems or, when dealing with filter systems, as IIR filters. IIR systems have an impulse response function that is non-zero over an infinite length of time...
, the latter is non-recursive and thus FIR
Finite impulse response
A finite impulse response filter is a type of a signal processing filter whose impulse response is of finite duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. This is in contrast to infinite impulse response filters, which have internal feedback and may continue to respond indefinitely...
. They can be analyzed as digital filter
Digital filter
In electronics, computer science and mathematics, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other major type of electronic filter, the analog filter, which is...
s.
A differential encoder is similar to an analog integrator
Integrator
An integrator is a device to perform the mathematical operation known as integration, a fundamental operation in calculus.The integration function is often part of engineering, physics, mechanical, chemical and scientific calculations....
. It has an impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
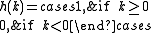
and a transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
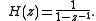
A differential decoder is thus similar to an analog differentiator
Differentiator
A Differentiator is a circuit that is designed such that the output of the circuit is proportional to the time derivative of the input. There are two types of differentiator circuits, active and passive.-Theory:...
, its impulse response being
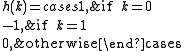
and its transfer function
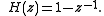
Note that in binary (modulo-2) arithmetic, addition and subtraction (and positive and negative numbers) are equivalent.
Generalized differential coding
Using the relation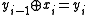 is not the only way of carrying out differential encoding. More generally, it can be any function
is not the only way of carrying out differential encoding. More generally, it can be any function 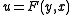 provided that an equation
provided that an equation 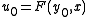 has one and only one solution for any
has one and only one solution for any 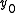 and
and 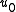 .
.Applications
Differential coding is widely used in satellite and radio relay communications together with PSK and QAM modulations.Drawbacks
Differential coding has one significant drawback: it leads to error multiplication. That is, if one symbol such as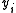 was received incorrectly, two incorrect symbols
was received incorrectly, two incorrect symbols 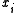 and
and 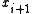 would be at the differential decoder's output, see:
would be at the differential decoder's output, see: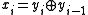 and
and 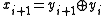 . This approximately doubles the BER at signal-to-noise ratios for which errors rarely occur in consecutive symbols.
. This approximately doubles the BER at signal-to-noise ratios for which errors rarely occur in consecutive symbols.Other techniques to resolve a phase ambiguity
Differential coding is not the only way to deal with a phase ambiguity. The other popular technique is to use sync-words for this purpose. That is, if a frame synchronizer detects repeated inverted sync-words, it inverts the whole stream. This method is used in DVB-SDVB-S
DVB-S is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Satellite; it is the original Digital Video Broadcasting forward error coding and demodulation standard for satellite television and dates from 1994, in its first release, while development lasted from 1993 to 1997...
.
External links and references
- INTELSATIntelsatIntelsat, Ltd. is a communications satellite services provider.Originally formed as International Telecommunications Satellite Organization , it was—from 1964 to 2001—an intergovernmental consortium owning and managing a constellation of communications satellites providing international broadcast...
Earth Station Standard IESS-308 - DVB framing structure, channel coding and modulation for 11/12 GHz satellite services (EN 300 421)

