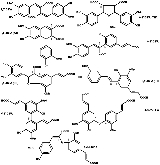
Diferulic acids
Encyclopedia
Diferulic acids are organic compounds that have the general chemical formula C20H18O8, they are formed by dimerisation of ferulic acid
. Just as ferulic acid is not the proper IUPAC name, the diferulic acids also tend to have trivial names that are more commonly used than the correct IUPAC name. Diferulic acids are found in plant cell walls, particularly those of grasses.
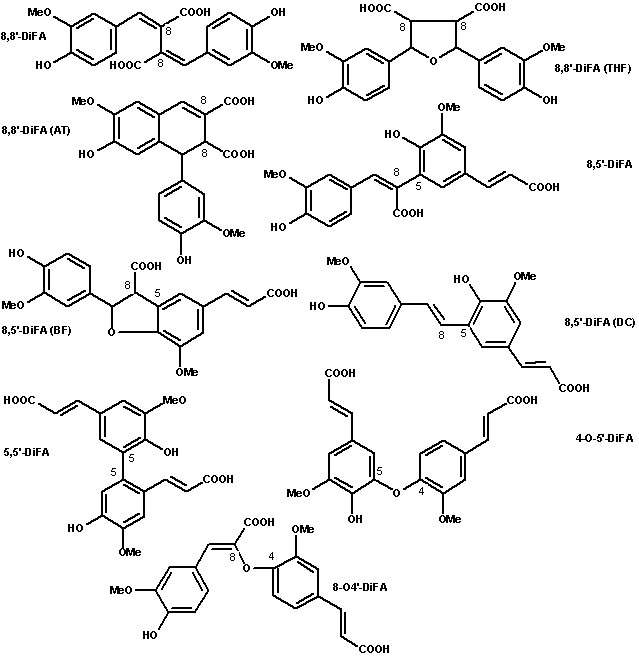 Erratum: the formula of 5,5`-diferulic acid actually is one of a 5,6`-diferulic acid.
Erratum: the formula of 5,5`-diferulic acid actually is one of a 5,6`-diferulic acid.
) and also sugar beet
and Chinese water chestnut. The 8-O-4'-DiFA tends to predominate in grasses, but 5,5'-DiFA predomintes in barley bran. In chufa
(tiger nut) and sugar beet the predominant diferulic acids are 8-O-4'-DiFA and 8,5'-DiFA respectively. Diferulic acids are thought to have a structural function in plant cell walls, where they form cross-links between polysaccharide chains. They have been extracted attached to a few sugar molecules at both ends, but so far no definitive proof of them linking separate polysaccharide chains has been found. In suspension-cultured maize cells, dimerisation of ferulic acid esterified to polysaccharides occurs mostly in the protoplasm, but may occur in the cell walls when peroxide levels increase due to pathogenesis. In suspension-cultured wheat cells, only the 8,5'-diferulic acid is formed intraprotoplasmically with the other dimers being formed in the cell wall.
with a UV detector or by LC-MS
. Alternatively they can be derivatised to make them volatile and therefore suitable for GC-MS
. Curcumin
can be hydrolyzed (alkaline) to yield two molecules of ferulic acid. Peroxidase
s can produce dimers of ferulic acid, in the presence of hydrogen peroxide
through radical polymerization
.
Ferulic acid
Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, a type of organic compound. It is an abundant phenolic phytochemical found in plant cell wall components such as arabinoxylans as covalent side chains. It is related to trans-cinnamic acid. As a component of lignin, ferulic acid is a precursor in the...
. Just as ferulic acid is not the proper IUPAC name, the diferulic acids also tend to have trivial names that are more commonly used than the correct IUPAC name. Diferulic acids are found in plant cell walls, particularly those of grasses.
Structures
There are currently nine known structures for diferulic acids. They are usually named after the positions on each molecule that form the bond between them. Included in the group are 8,5'-DiFA (DC) and 8,8'-DiFA (THF), which are not true diferulic acids, but probably have a similar biological function. The 8,5'-DiFA (DC) lost CO2 during its formation, the 8,8'-DiFA (THF) gained H2O during its formation. Ferulic acid can also form trimers and tetramers, known as triferulic and tetraferulic acids respectively.
Occurrence
They have been found in the cell walls of most plants, but are present at higher levels in the grasses (PoaceaePoaceae
The Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
) and also sugar beet
Sugar beet
Sugar beet, a cultivated plant of Beta vulgaris, is a plant whose tuber contains a high concentration of sucrose. It is grown commercially for sugar production. Sugar beets and other B...
and Chinese water chestnut. The 8-O-4'-DiFA tends to predominate in grasses, but 5,5'-DiFA predomintes in barley bran. In chufa
Cyperus esculentus
Cyperus esculentus is a species of sedge native to warm temperate to subtropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere, often cultivated for its edible tubers . It is an annual or perennial plant, growing to 90 cm tall, with solitary stems growing from a tuber...
(tiger nut) and sugar beet the predominant diferulic acids are 8-O-4'-DiFA and 8,5'-DiFA respectively. Diferulic acids are thought to have a structural function in plant cell walls, where they form cross-links between polysaccharide chains. They have been extracted attached to a few sugar molecules at both ends, but so far no definitive proof of them linking separate polysaccharide chains has been found. In suspension-cultured maize cells, dimerisation of ferulic acid esterified to polysaccharides occurs mostly in the protoplasm, but may occur in the cell walls when peroxide levels increase due to pathogenesis. In suspension-cultured wheat cells, only the 8,5'-diferulic acid is formed intraprotoplasmically with the other dimers being formed in the cell wall.
Preparation
Most diferulic acids are not commercially available and must be synthesised in lab. Synthetic routes have been published, but it is often simpler to extract them from plant material. They can be extracted from plant cell walls (often maize bran) by concentrated solutions of alkali, the resulting solution is then acidified and phase separated into an organic solvent. The resulting solution is evaporated to give a mixture of ferulic acid moieties that can be separated by column chromatography. Identification is often by high performance liquid chromatographyHigh performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography , HPLC, is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture.HPLC typically utilizes different types of stationary...
with a UV detector or by LC-MS
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry. LC-MS is a powerful technique used for many applications which has very high...
. Alternatively they can be derivatised to make them volatile and therefore suitable for GC-MS
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry is a method that combines the features of gas-liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. Applications of GC-MS include drug detection, fire investigation, environmental analysis, explosives investigation,...
. Curcumin
Curcumin
Curcumin is the principal curcuminoid of the popular Indian spice turmeric, which is a member of the ginger family . The other two curcuminoids are desmethoxycurcumin and bis-desmethoxycurcumin. The curcuminoids are natural phenols and are responsible for the yellow color of turmeric...
can be hydrolyzed (alkaline) to yield two molecules of ferulic acid. Peroxidase
Peroxidase
Peroxidases are a large family of enzymes that typically catalyze a reaction of the form:For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides...
s can produce dimers of ferulic acid, in the presence of hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
through radical polymerization
Radical polymerization
Free radical polymerization is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free radical building blocks. Free radicals can be formed via a number of different mechanisms usually involving separate initiator molecules...
.

