
Delta Pavonis
Encyclopedia
Delta Pavonis is a star
about 19.9 light years away from Earth. It is in the constellation Pavo
.
of spectral type G8 IV, meaning it is about to stop fusing
hydrogen
in its core and is starting the process of becoming a red giant
. Because of that, Delta Pavonis is slightly brighter than the Sun even though it is cooler. It has 99.1% of the Sun's mass
and is 122% of the Sun's radius. The surface convection zone
extends downward to about 43.1% of the star's radius, but only contains 4.8% of the star's mass.
Spectroscopic examination of this star shows that it has a higher abundance of elements heavier than helium
(or metallicity
, as astronomers call it) than does the Sun. This value is typically given in terms of the relative ratio of iron
(chemical symbol Fe) to hydrogen (H) as compared to the Sun's atmosphere (iron being a relatively easy element to detect in a stellar atmosphere). For Delta Pavonis,
the metallicity is about:
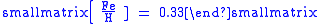
(This notation gives the logarithm
of the iron-to-hydrogen ratio relative to the Sun.) This corresponds to a 214% abundance of iron in this star's atmosphere compared to the solar abundance. Past studies have shown a correlation between the heavy element abundance in stars and the presence of a planetary system, suggesting Delta Pavonis has a greater than average probability of harboring planets. However, no planetary companions have yet been discovered in orbit around this star.
The age of this star is in the range of 6.6–6.9 Gyr
, and the luminosity has increased 60% since it became a zero-age main sequence star. (The later increase is similar to the Sun.)
of the SETI Institute
as the "Best SETI
target" in a survey of nearby stars. Delta Pavonis is the nearest sun-like star
not a member of a binary or multiple star system
.
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
about 19.9 light years away from Earth. It is in the constellation Pavo
Pavo (constellation)
Pavo is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for peacock. It is one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 in...
.
Observations
It is a subgiantSubgiant star
A subgiant star is a star that is slightly brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as true giant stars...
of spectral type G8 IV, meaning it is about to stop fusing
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two or more atomic nuclei join together, or "fuse", to form a single heavier nucleus. This is usually accompanied by the release or absorption of large quantities of energy...
hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
in its core and is starting the process of becoming a red giant
Red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius immense and the surface temperature low, somewhere from 5,000 K and lower...
. Because of that, Delta Pavonis is slightly brighter than the Sun even though it is cooler. It has 99.1% of the Sun's mass
Solar mass
The solar mass , , is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, used to indicate the masses of other stars and galaxies...
and is 122% of the Sun's radius. The surface convection zone
Convection zone
The convection zone of a star is the range of radii in which energy is transported primarily by convection. In the radiation zone, energy is transported by radiation...
extends downward to about 43.1% of the star's radius, but only contains 4.8% of the star's mass.
Spectroscopic examination of this star shows that it has a higher abundance of elements heavier than helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
(or metallicity
Metallicity
In astronomy and physical cosmology, the metallicity of an object is the proportion of its matter made up of chemical elements other than hydrogen and helium...
, as astronomers call it) than does the Sun. This value is typically given in terms of the relative ratio of iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
(chemical symbol Fe) to hydrogen (H) as compared to the Sun's atmosphere (iron being a relatively easy element to detect in a stellar atmosphere). For Delta Pavonis,
the metallicity is about:
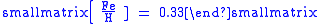
(This notation gives the logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of the iron-to-hydrogen ratio relative to the Sun.) This corresponds to a 214% abundance of iron in this star's atmosphere compared to the solar abundance. Past studies have shown a correlation between the heavy element abundance in stars and the presence of a planetary system, suggesting Delta Pavonis has a greater than average probability of harboring planets. However, no planetary companions have yet been discovered in orbit around this star.
The age of this star is in the range of 6.6–6.9 Gyr
Gyr
Gyr or gyr can mean:* Phoenix Goodyear Airport , an airport in Arizona, United States* Gyrfalcon, a species of bird of prey* Byr or Gyr, abbreviations for gigayear, i.e. a billion years...
, and the luminosity has increased 60% since it became a zero-age main sequence star. (The later increase is similar to the Sun.)
SETI
It has been identified by Maggie Turnbull and Jill TarterJill Tarter
Jill Cornell Tarter is an American astronomer and the current director of the Center for SETI Research, holding the Bernard M. Oliver Chair for SETI at the SETI Institute.-Education:...
of the SETI Institute
SETI Institute
The SETI Institute is a not-for-profit organization whose mission is to “explore, understand and explain the origin, nature and prevalence of life in the universe”. SETI stands for the "search for extraterrestrial intelligence". One program is the use of both radio and optical telescopes to search...
as the "Best SETI
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence is the collective name for a number of activities people undertake to search for intelligent extraterrestrial life. Some of the most well known projects are run by the SETI Institute. SETI projects use scientific methods to search for intelligent life...
target" in a survey of nearby stars. Delta Pavonis is the nearest sun-like star
Solar analog
Solar-type, solar analog, and solar twin stars are those stars that are particularly similar to the Sun. The classification is a hierarchy with solar twin being most like the Sun followed by solar analog and then solar-type...
not a member of a binary or multiple star system
Star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars which orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large number of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a star cluster or galaxy, although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems.-Binary star systems:A stellar...
.

