
Data Execution Prevention
Encyclopedia
Data Execution Prevention (DEP) is a security feature included in modern operating system
s.
It is known to be available in Linux
, Mac OS X
, and Microsoft Windows
operating systems and is intended to prevent an application
or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region. This helps prevent certain exploits that store code via a buffer overflow
, for example. DEP runs in two modes: hardware-enforced DEP for CPU
s that can mark memory pages as nonexecutable, and software-enforced DEP with a limited prevention for CPUs that do not have hardware support. Software-enforced DEP does not protect from execution of code in data pages, but instead from another type of attack (SEH overwrite).
DEP was introduced on Linux in 2000, on Windows in 2004 with Windows XP
Service Pack 2, while Apple introduced DEP in 2006.
on compatible CPUs, through the automatic use of PAE
kernel in 32-bit Windows and the native support on 64-bit kernels. Windows Vista DEP works by marking certain parts of memory as being intended to hold only data, which the NX or XD bit enabled processor then understands as non-executable. This helps prevent buffer overflow attacks from succeeding. In Windows, from version Vista, whether DEP is enabled or disabled for a particular process can be viewed on the Processes tab in the Windows Task Manager
.
In some instances, enabling Data Execution Prevention can have the unintended consequence of preventing legitimate software from executing, typically exposing a hitherto unknown bug in the process. In these cases, the affected software needs to be remediated by its developer; in the short term it can be flagged as being allowed to execute code in those parts of memory, but this itself leads to a possible attack if the application isn't rigorous in validating data that is passed into a region of memory that is marked as being executable.
provides support for this feature and it has been enabled, either by the manufacturer or the user, then the NX features are turned on in Windows, on a limited "OptIn" basis. This setting provides protection only for a limited set of Windows system and binary files. To achieve full protection, the user must choose either "OptOut", covering all programs and processes not specifically exempted, or "AlwaysOn", covering all such without exemption. These are configurable through the System Properties interface. If the feature is not supported by the x86 processor, then no protection is given. Outside of the x86 architecture, a version of NX also exists for Intel's IA-64 architecture that is supported by Windows.
, structured exception handler
overwrite protection (SEHOP) and Mandatory Integrity Control
, can be used in conjunction with DEP.
Where code is executed at runtime—a JIT compiler is a prominent example—the compiler can potentially be used to produce exploit code (e.g. using JIT Spray) that has been flagged for execution and therefore would not be trapped by DEP.
These problems may be masked by disabling DEP, but at the risk of increasing exposure of the system to malware. DEP can be turned off on a per-application basis, or turned off entirely for all non-essential Windows programs and services. Microsoft recommends that DEP not be globally disabled where an application crashes due to a DEP error. Instead, the author or vendor of the offending software should firstly be contacted for an updated version that does not violate DEP, or failing that, that DEP be disabled on an exception basis for the offending application only.
DEP is applied to an entire process, so even if an application runs perfectly with DEP, it may need to be disabled if a non-DEP compliant extension is added that runs in the same process space. For example, DEP-related problems can occasionally occur with DEP-compliant core operating system components such as Windows Explorer
, Internet Explorer
and Windows Installer
as they support in-process third party extensions or plugins that may not be DEP-compliant.
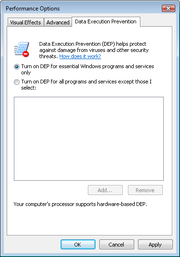 Four DEP modes are available in Windows. The OptIn and OptOut modes can be controlled through the Performance Options dialog box of System applet in Control Panel
Four DEP modes are available in Windows. The OptIn and OptOut modes can be controlled through the Performance Options dialog box of System applet in Control Panel
; the AlwaysOn and AlwaysOff modes can only be controlled through the boot.ini file on Windows XP, with the bcdedit command in the command prompt on Windows Vista or later, or by using the Microsoft TechNet Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit.
OptIn: This setting is the default configuration for Windows XP, Vista and 7. In this mode, DEP is only enabled for limited Windows system applications and services. In general, applications are not forced by the Operating System to opt-in—applications that wish to opt in must explicitly submit a protection request. 64-bit Windows Vista and newer operating system are an exception: 64-bit applications and services are automatically protected in OptIn mode unless they submit an explicit opt-out request.
OptOut: This setting is the default configuration for Windows Server 2003 SP1. In this mode, DEP is enabled by default for all programs and services. A list of specific programs that should not have DEP applied can be entered using the System dialog box in Control Panel. Network administrators can use the Application Compatibility Toolkit to "opt out" one or more programs from DEP protection. Programs and services that wish not to have DEP protection must explicitly submit an opt out request.
AlwaysOn: This setting provides full DEP coverage for the whole system. All processes always run with DEP applied. The exception list, application compatibility shims and opt-out requests are disregarded.
AlwaysOff: This setting disables DEP entirely. All opt-in requests are disregarded.
The Boot.ini file parameter /noexecute=policy_level adjusts the DEP setting on older versions of Windows, where policy_level can be either OptIn, OptOut, AlwaysOn or AlwaysOff.
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
s.
It is known to be available in Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
, Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
, and Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
operating systems and is intended to prevent an application
Application software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region. This helps prevent certain exploits that store code via a buffer overflow
Buffer overflow
In computer security and programming, a buffer overflow, or buffer overrun, is an anomaly where a program, while writing data to a buffer, overruns the buffer's boundary and overwrites adjacent memory. This is a special case of violation of memory safety....
, for example. DEP runs in two modes: hardware-enforced DEP for CPU
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
s that can mark memory pages as nonexecutable, and software-enforced DEP with a limited prevention for CPUs that do not have hardware support. Software-enforced DEP does not protect from execution of code in data pages, but instead from another type of attack (SEH overwrite).
DEP was introduced on Linux in 2000, on Windows in 2004 with Windows XP
Windows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
Service Pack 2, while Apple introduced DEP in 2006.
Hardware enforcement
Hardware-enforced DEP enables the NX bitNX bit
The NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
on compatible CPUs, through the automatic use of PAE
Physical Address Extension
In computing, Physical Address Extension is a feature to allow x86 processors to access a physical address space larger than 4 gigabytes....
kernel in 32-bit Windows and the native support on 64-bit kernels. Windows Vista DEP works by marking certain parts of memory as being intended to hold only data, which the NX or XD bit enabled processor then understands as non-executable. This helps prevent buffer overflow attacks from succeeding. In Windows, from version Vista, whether DEP is enabled or disabled for a particular process can be viewed on the Processes tab in the Windows Task Manager
Windows Task Manager
Windows Task Manager is a task manager application included with the Microsoft Windows NT family of operating systems that provides detailed information about computer performance and running applications, processes and CPU usage, commit charge and memory information, network activity and...
.
In some instances, enabling Data Execution Prevention can have the unintended consequence of preventing legitimate software from executing, typically exposing a hitherto unknown bug in the process. In these cases, the affected software needs to be remediated by its developer; in the short term it can be flagged as being allowed to execute code in those parts of memory, but this itself leads to a possible attack if the application isn't rigorous in validating data that is passed into a region of memory that is marked as being executable.
Microsoft Windows
If the x86 processor supports this feature in hardware, and if the system's BIOSBIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
provides support for this feature and it has been enabled, either by the manufacturer or the user, then the NX features are turned on in Windows, on a limited "OptIn" basis. This setting provides protection only for a limited set of Windows system and binary files. To achieve full protection, the user must choose either "OptOut", covering all programs and processes not specifically exempted, or "AlwaysOn", covering all such without exemption. These are configurable through the System Properties interface. If the feature is not supported by the x86 processor, then no protection is given. Outside of the x86 architecture, a version of NX also exists for Intel's IA-64 architecture that is supported by Windows.
Software enforcement
Software DEP, while unrelated to the NX bit, is what Microsoft calls their enforcement of "Safe Structured Exception Handling". Software DEP/SafeSEH simply checks when an exception is raised to make sure that the exception is registered in a function table for the application, and requires the program to be built with it. However, even though it creates an impression that software DEP is related to the prevention of executing code in data pages, it is a different form of protection.Limitations
DEP provides some protection against attacks, but of course is not sufficient to protect against all forms of attack. Other security features such as address space layout randomizationAddress space layout randomization
Address space layout randomization is a computer security method which involves randomly arranging the positions of key data areas, usually including the base of the executable and position of libraries, heap, and stack, in a process's address space.- Benefits :Address space randomization hinders...
, structured exception handler
Exception handling
Exception handling is a programming language construct or computer hardware mechanism designed to handle the occurrence of exceptions, special conditions that change the normal flow of program execution....
overwrite protection (SEHOP) and Mandatory Integrity Control
Mandatory Integrity Control
In the context of the Microsoft Windows range of operating systems, Mandatory Integrity Control or Integrity Levels is a core security feature, introduced in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, that adds Integrity Levels to processes running in a...
, can be used in conjunction with DEP.
Where code is executed at runtime—a JIT compiler is a prominent example—the compiler can potentially be used to produce exploit code (e.g. using JIT Spray) that has been flagged for execution and therefore would not be trapped by DEP.
Compatibility
DEP occasionally highlights software problems, usually with older software that was not compiled and tested to take advantage of the feature. Users have experienced problems using various command line commands that are a part of Microsoft's Services for Unix, which is included as part of Vista as well as Windows Server 2003 R2.These problems may be masked by disabling DEP, but at the risk of increasing exposure of the system to malware. DEP can be turned off on a per-application basis, or turned off entirely for all non-essential Windows programs and services. Microsoft recommends that DEP not be globally disabled where an application crashes due to a DEP error. Instead, the author or vendor of the offending software should firstly be contacted for an updated version that does not violate DEP, or failing that, that DEP be disabled on an exception basis for the offending application only.
DEP is applied to an entire process, so even if an application runs perfectly with DEP, it may need to be disabled if a non-DEP compliant extension is added that runs in the same process space. For example, DEP-related problems can occasionally occur with DEP-compliant core operating system components such as Windows Explorer
Windows Explorer
This article is about the Windows file system browser. For the similarly named web browser, see Internet ExplorerWindows Explorer is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface...
, Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer
Windows Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year...
and Windows Installer
Windows Installer
The Windows Installer is a software component used for the installation, maintenance, and removal of software on modern Microsoft Windows systems...
as they support in-process third party extensions or plugins that may not be DEP-compliant.
Windows

Control Panel (Windows)
The Control Panel is a part of the Microsoft Windows graphical user interface which allows users to view and manipulate basic system settings and controls via applets, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options...
; the AlwaysOn and AlwaysOff modes can only be controlled through the boot.ini file on Windows XP, with the bcdedit command in the command prompt on Windows Vista or later, or by using the Microsoft TechNet Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit.
OptIn: This setting is the default configuration for Windows XP, Vista and 7. In this mode, DEP is only enabled for limited Windows system applications and services. In general, applications are not forced by the Operating System to opt-in—applications that wish to opt in must explicitly submit a protection request. 64-bit Windows Vista and newer operating system are an exception: 64-bit applications and services are automatically protected in OptIn mode unless they submit an explicit opt-out request.
OptOut: This setting is the default configuration for Windows Server 2003 SP1. In this mode, DEP is enabled by default for all programs and services. A list of specific programs that should not have DEP applied can be entered using the System dialog box in Control Panel. Network administrators can use the Application Compatibility Toolkit to "opt out" one or more programs from DEP protection. Programs and services that wish not to have DEP protection must explicitly submit an opt out request.
AlwaysOn: This setting provides full DEP coverage for the whole system. All processes always run with DEP applied. The exception list, application compatibility shims and opt-out requests are disregarded.
AlwaysOff: This setting disables DEP entirely. All opt-in requests are disregarded.
The Boot.ini file parameter /noexecute=policy_level adjusts the DEP setting on older versions of Windows, where policy_level can be either OptIn, OptOut, AlwaysOn or AlwaysOff.
See also
- NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
– list of names of similar techniques used in other operating systems - Executable space protectionExecutable space protectionIn computer security, executable space protection is the marking of memory regions as non-executable, such that an attempt to execute machine code in these regions will cause an exception...
- Buffer overflowBuffer overflowIn computer security and programming, a buffer overflow, or buffer overrun, is an anomaly where a program, while writing data to a buffer, overruns the buffer's boundary and overwrites adjacent memory. This is a special case of violation of memory safety....
- Heap overflowHeap overflowA heap overflow is a type of buffer overflow that occurs in the heap data area. Heap overflows are exploitable in a different manner to that of stack-based overflows. Memory on the heap is dynamically allocated by the application at run-time and typically contains program data...
- Stack buffer overflowStack buffer overflowIn software, a stack buffer overflow occurs when a program writes to a memory address on the program's call stack outside of the intended data structure; usually a fixed length buffer....
- Stack-smashing protectionStack-smashing protectionBuffer overflow protection refers to various techniques used during software development to enhance the security of executable programs by detecting buffer overflows on stack-allocated variables as they occur and preventing them from becoming serious security vulnerabilities...

