
DVB-C
Encyclopedia
DVB-C stands for Digital Video Broadcasting - Cable and it is the DVB European consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital television
over cable
. This system transmits an MPEG-2
or MPEG-4
family digital audio
/digital video
stream, using a QAM modulation with channel coding.
"The results of the DVB-C2 Study Mission already provided clear indications that
technologies are available allowing the performance of the second generation DVB cable
transmission system to get so close to the theoretical Shannon Limit that any further
improvements in the future would most likely not be able to justify the introduction of a
disruptive third generation of cable transmission system." (DVB-C2 CfT)
By using state of the art coding and modulation techniques, DVB-C2 should offer greater than 30% higher spectrum efficiency under the same conditions, and the gains in downstream channel capacity
will be greater than 60% for optimized HFC networks.
The final DVB-C2 specification was approved by the DVB Steering Board in April 2009.
DVB-C2 allows bitrates up to 83.1 Mbit/s on a 8 MHz channel bandwidth when using 4096-QAM modulation; future extensions will allow up to 97 Mbit/s and 110.8 Mbit/s per channel using 16384-QAM and 65536-AQAM modulation.
Modes and features of DVB-C2 in comparison to DVB-C:
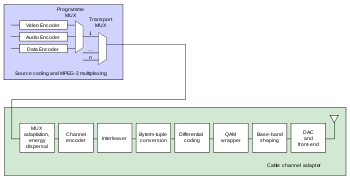 With reference to the figure, a short description of the single processing blocks follows.
With reference to the figure, a short description of the single processing blocks follows.
)
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
over cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
. This system transmits an MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
or MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
family digital audio
Digital audio
Digital audio is sound reproduction using pulse-code modulation and digital signals. Digital audio systems include analog-to-digital conversion , digital-to-analog conversion , digital storage, processing and transmission components...
/digital video
Digital video
Digital video is a type of digital recording system that works by using a digital rather than an analog video signal.The terms camera, video camera, and camcorder are used interchangeably in this article.- History :...
stream, using a QAM modulation with channel coding.
DVB-C2
On February 18, 2008 it was announced that a new standard – DVB-C2 – would be developed during 2008, and a "Call for Technologies" was issued. Proposals including simulation programs and information on patent rights could be submitted until June 16, 2008."The results of the DVB-C2 Study Mission already provided clear indications that
technologies are available allowing the performance of the second generation DVB cable
transmission system to get so close to the theoretical Shannon Limit that any further
improvements in the future would most likely not be able to justify the introduction of a
disruptive third generation of cable transmission system." (DVB-C2 CfT)
By using state of the art coding and modulation techniques, DVB-C2 should offer greater than 30% higher spectrum efficiency under the same conditions, and the gains in downstream channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
will be greater than 60% for optimized HFC networks.
The final DVB-C2 specification was approved by the DVB Steering Board in April 2009.
DVB-C2 allows bitrates up to 83.1 Mbit/s on a 8 MHz channel bandwidth when using 4096-QAM modulation; future extensions will allow up to 97 Mbit/s and 110.8 Mbit/s per channel using 16384-QAM and 65536-AQAM modulation.
Modes and features of DVB-C2 in comparison to DVB-C:
| DVB-C | DVB-C2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Input Interface | Single Transport Stream (TS) | Multiple Transport Stream and Generic Stream Encapsulation (GSE) |
| Modes | Constant Coding & Modulation | Variable Coding & Modulation and Adaptive Coding & Modulation |
| FEC | Reed Solomon (RS) | LDPC + BCH |
| Interleaving | Bit-Interleaving | Bit- Time- and Frequency-Interleaving |
| Modulation | Single Carrier QAM | COFDM |
| Pilots | Not Applicable | Scattered and Continual Pilots |
| Guard Interval | Not Applicable | 1/64 or 1/128 |
| Modulation Schemes | 16- to 256-QAM | 16- to 4096-QAM |
Technical description of the DVB-C transmitter

- Source codingSource codingIn information theory, Shannon's source coding theorem establishes the limits to possible data compression, and the operational meaning of the Shannon entropy....
and MPEG-2 multiplexingMultiplexingThe multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
(MUX): video, audio, and data streams are multiplexed into an MPEG program stream (MPEG-PS). One or more MPEG-PSs are joined together into an MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS). This is the basic digital stream which is being transmitted and received by home set top boxes (STB). Allowed bitrateBitrateIn telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
s for the transported MPEG-2 depend on a number of modulation parameters: it can range from about 6 to about 64 Mbit/s (see the bottom figure for a complete listing). - MUX adaptation and energy dispersal: the MPEG-TS is identified as a sequence of data packets, of fixed length (188 bytes). With a technique called energy dispersal, the byte sequence is decorrelatedCorrelationIn statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
. - External encoder: a first level of protection is applied to the transmitted data, using a nonbinary block codeBlock codeIn coding theory, block codes refers to the large and important family of error-correcting codes that encode data in blocks.There is a vast number of examples for block codes, many of which have a wide range of practical applications...
, a Reed-Solomon RS (204, 188) code, allowing the correction of up to a maximum of 8 wrong bytes for each 188-byte packet. - External interleaverInterleavingIn computer science and telecommunication, interleaving is a way to arrange data in a non-contiguous way to increase performance.It is typically used:* In error-correction coding, particularly within data transmission, disk storage, and computer memory....
: convolutional interleaving is used to rearrange the transmitted data sequence, such way it becomes more rugged to long sequences of errors. - Byte/m-tuple conversion: data bytes are encoded into bit m-tuples (m = 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8).
- Differential coding: In order to get a rotation-invariant constellation, this unit shall apply a differential encoding of the two Most Significant Bits (MSBs) of each symbol.
- QAM Mapper: the bit sequence is mapped into a base-band digital sequence of complex symbols. There are 5 allowed modulationModulationIn electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
modes: 16-QAM, 32-QAM, 64-QAM, 128-QAM, 256-QAM. - Base-band shaping: the QAM signal is filtered with a raised-cosine shaped filter, in order to remove mutual signal interference at the receiving side.
- DAC and front-end: the digital signal is transformed into an analog signal, with a digital-to-analog converterDigital-to-analog converterIn electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
(DAC), and then modulated to radio frequencyRadio frequencyRadio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
by the RF front-endFront-end and back-endFront end and back end are generalized terms that refer to the initial and the end stages of a process. The front end is responsible for collecting input in various forms from the user and processing it to conform to a specification the back end can use...
.
| Modulation | | Bandwidth (MHz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 10 | |
| 16QAM | 6,41 | 12,82 | 19,23 | 25,64 | 32,05 |
| 32QAM | 8,01 | 16,03 | 24,04 | 32,05 | 40,07 |
| 64QAM | 9,92 | 19,23 | 28,85 | 38,47 | 48,08 |
| 128QAM | 11,22 | 22,44 | 33,66 | 44,88 | 56,10 |
| 256QAM | 12,82 | 25,64 | 38,47 | 51,29 | 64,11 |
Technical description of the receiver
The receiving STB adopts techniques which are dual to those ones used in the transmission.- Front-end and ADC: the analog RF signal is converted to base-band and transformed into a digital signal, using an analog-to-digital converterAnalog-to-digital converterAn analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
(ADC).
- QAM Demodulation
- Equalization
- Differential decoding
- Outer deinterleaving
- Outer decoding
- MUX adaptation
- MPEG-2 demultiplexing and source decoding
- Programmable Transport Stream
Countries that use DVB-C
(FoxtelFoxtel
Foxtel is an Australian pay television company, operating cable, direct broadcast satellite television and IPTV services. It was formed in 1995 through a joint venture established between Telstra and News Corporation....
)
- Bosnia and HerzegovinaBosnia and HerzegovinaBosnia and Herzegovina , sometimes called Bosnia-Herzegovina or simply Bosnia, is a country in Southern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. Bordered by Croatia to the north, west and south, Serbia to the east, and Montenegro to the southeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for the...
(ViNet) (CosmosTV, MTIS) (B.net) (UPCUPC-Companies:* United Pan-Europe Communications, a European provider of cable television, telephone and broadband content owned by Liberty Global-Technology:* Universal Product Code * Unified Parallel C* Uniform Plumbing Code* Uplink Power Control...
) (Digi TV Hungary) (UPC IrelandUPC IrelandUPC Ireland is Liberty Global Europe's telecommunications operation in Ireland. UPC Ireland is the largest digital cable television provider within the Republic of Ireland. As of September 2010 the company offers broadband internet, digital television and digital telephony to over 531,000 customers...
) (TelstraClearTelstraClearTelstraClear is New Zealand's second-largest telecommunications company and is a wholly owned subsidiary of Telstra Corporation , with around 400,000 customers....
) (GET) (RCSRCS&RDSRCS&RDS is the largest Romanian cable and internet provider, offering nationwide satellite television, cable television, cable internet, VOIP, and 3G services...
, UPC) (SBBSerbia BroadbandSBB is the leading cable TV and broadband Internet provider in Serbia.Ownership structure:* Mid Europa Partners...
, IKOM, Radijus VektorRadijus VektorRadijus Vektor is a Serbian company providing cable television and high-speed Internet. It is one of the largest cable operators in the Republic of Serbia.-Divisions:...
) (TeledünyaTeledünyaTeledünya is a Turkish digital cable TV service that was founded on November 1, 2008 by Turksat. It also provides internet by the same cable.-Channel list:...
) (Virgin MediaVirgin MediaVirgin Media Inc. is a company which provides fixed and mobile telephone, television and broadband internet services to businesses and consumers in the United Kingdom...
)- Isle of WightIsle of WightThe Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent...
(WightCableWightCableWight Cable 2005 Ltd is the only provider of commercial and residential cable television services on the Isle of Wight. They also provide telephone and broadband internet services....
) (Volia, Triolan)
- Isle of Wight
See also
- ATSC Standards
- Digital cableDigital cableDigital cable is a generic term for any type of cable television distribution using digital video compression or distribution. The technology was originally developed by Motorola.-Background:...
- Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB)
- DMBDigital Multimedia BroadcastingDigital Multimedia Broadcasting is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea as part of the national IT project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones...
(Digital Multimedia BroadcastingDigital Multimedia BroadcastingDigital Multimedia Broadcasting is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea as part of the national IT project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones...
) - Digital televisionDigital televisionDigital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
(DTV) - Redesign project, project set up by cable operators, equipment manufacturers, and research organisations
External links
- Website of the DVB Project
- DVB-C2 Webpage
- DVB-C2, 2nd Generation Cable DVB Fact Sheet - September 2010]
- DVB-C2 IP-Core for forward error correction

