
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit III
Encyclopedia
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit III is one of main transmembrane subunits of cytochrome c oxidase
Cytochrome c oxidase
is the terminal enzyme of the respiratory chain of mitochondria and many aerobic bacteria. It catalyzes the transfer of electrons from reduced cytochrome c to molecular oxygen:
This reaction is coupled to the pumping of four additional protons across the mitochondrial or bacterial membrane.
Cytochrome c oxidase is an oligomeric enzymatic complex that is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane of eukaryotes and in the plasma membrane of aerobic prokaryotes. The core structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase contains three common subunits, I, II
and III. In prokaryotes, subunits I and III can be fused and a fourth subunit is sometimes found, whereas in eukaryotes there are a variable number of additional small subunits.
As the bacterial respiratory systems are branched, they have a number of distinct terminal oxidases, rather than the single cytochrome c oxidase present in the eukaryotic mitochondrial systems. Although the cytochrome o oxidases do not catalyze the cytochrome c but the quinol (ubiquinol) oxidation they belong to the same haem-copper oxidase superfamily as cytochrome c oxidases. Members of this family share sequence similarities in all three core subunits: subunit I is the most conserved subunit, whereas subunit II
is the least conserved.
Cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria and the mitochondrion.It is the last enzyme in the respiratory electron transport chain of mitochondria located in the mitochondrial membrane...
Cytochrome c oxidase
Cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria and the mitochondrion.It is the last enzyme in the respiratory electron transport chain of mitochondria located in the mitochondrial membrane...
is the terminal enzyme of the respiratory chain of mitochondria and many aerobic bacteria. It catalyzes the transfer of electrons from reduced cytochrome c to molecular oxygen:
- 4 cytochrome c+2 + 4 H+ + O2
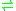 4 cytochrome c+3 + 2 H2O
4 cytochrome c+3 + 2 H2O
This reaction is coupled to the pumping of four additional protons across the mitochondrial or bacterial membrane.
Cytochrome c oxidase is an oligomeric enzymatic complex that is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane of eukaryotes and in the plasma membrane of aerobic prokaryotes. The core structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase contains three common subunits, I, II
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II, abbreviated CoxII, is the second subunit of cytochrome c oxidase.Cytochrome c oxidase is an oligomeric enzymatic complex which is a component of the respiratory chain and is involved in the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen...
and III. In prokaryotes, subunits I and III can be fused and a fourth subunit is sometimes found, whereas in eukaryotes there are a variable number of additional small subunits.
As the bacterial respiratory systems are branched, they have a number of distinct terminal oxidases, rather than the single cytochrome c oxidase present in the eukaryotic mitochondrial systems. Although the cytochrome o oxidases do not catalyze the cytochrome c but the quinol (ubiquinol) oxidation they belong to the same haem-copper oxidase superfamily as cytochrome c oxidases. Members of this family share sequence similarities in all three core subunits: subunit I is the most conserved subunit, whereas subunit II
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II, abbreviated CoxII, is the second subunit of cytochrome c oxidase.Cytochrome c oxidase is an oligomeric enzymatic complex which is a component of the respiratory chain and is involved in the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen...
is the least conserved.
Subfamilies
- Cytochrome o ubiquinol oxidase, subunit III
- Cytochrome aa3 quinol oxidase, subunit III

