Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II
Encyclopedia
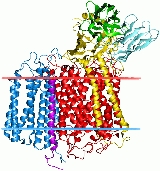
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II, abbreviated CoxII, is the second subunit of cytochrome c oxidase
.
Cytochrome c oxidase
is an oligomeric enzymatic complex which is a component of the respiratory chain and is involved in the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen. In eukaryotes this enzyme complex is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane; in aerobic prokaryotes it is found in the plasma membrane. The enzyme complex consists of 3-4 subunits (prokaryotes) to up to 13 polypeptides (mammals). In Leigh's disease
, there may be an abnormality or deficiency of cytochrome oxidase.
Subunit 2 (CO II) transfers the electrons from cytochrome c
to the catalytic subunit 1
. It contains two adjacent transmembrane regions in its N-terminus and the major part of the protein is exposed to the periplasmic or to the mitochondrial intermembrane space, respectively. CO II provides the substrate-binding site and contains a copper centre called Cu(A) (see ), probably the primary acceptor in cytochrome c oxidase. An exception is the corresponding subunit of the cbb3-type oxidase which lacks the copper A redox-centre. Several bacterial CO II have a C-terminal extension that contains a covalently bound haem c.
The N-terminal domain of cytochrome C oxidase contains two transmembrane alpha-helices.
Cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria and the mitochondrion.It is the last enzyme in the respiratory electron transport chain of mitochondria located in the mitochondrial membrane...
.
Cytochrome c oxidase
Cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria and the mitochondrion.It is the last enzyme in the respiratory electron transport chain of mitochondria located in the mitochondrial membrane...
is an oligomeric enzymatic complex which is a component of the respiratory chain and is involved in the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen. In eukaryotes this enzyme complex is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane; in aerobic prokaryotes it is found in the plasma membrane. The enzyme complex consists of 3-4 subunits (prokaryotes) to up to 13 polypeptides (mammals). In Leigh's disease
Leigh's disease
Leigh's disease, also known as Subacute Necrotizing Encephalomyelopathy , is a rare neurometabolic disorder that affects the central nervous system...
, there may be an abnormality or deficiency of cytochrome oxidase.
Subunit 2 (CO II) transfers the electrons from cytochrome c
Cytochrome c
The Cytochrome complex, or cyt c is a small heme protein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins. Cytochrome c is a highly soluble protein, unlike other cytochromes, with a solubility of about 100 g/L and is an...
to the catalytic subunit 1
Main subunit of cytochrome c oxidase
Cytochrome C and Quinol oxidase polypeptide I is main subunit of cytochrome c oxidase complex.Cytochrome c oxidase is a key enzyme in aerobic metabolism. Proton pumping heme-copper oxidases represent the terminal, energy-transfer enzymes of respiratory chains in prokaryotes and eukaryotes...
. It contains two adjacent transmembrane regions in its N-terminus and the major part of the protein is exposed to the periplasmic or to the mitochondrial intermembrane space, respectively. CO II provides the substrate-binding site and contains a copper centre called Cu(A) (see ), probably the primary acceptor in cytochrome c oxidase. An exception is the corresponding subunit of the cbb3-type oxidase which lacks the copper A redox-centre. Several bacterial CO II have a C-terminal extension that contains a covalently bound haem c.
The N-terminal domain of cytochrome C oxidase contains two transmembrane alpha-helices.
Further Reading
- The whole structure of the 13-subunit oxidized cytochrome c oxidase at 2.8 A. Tsukihara T, Aoyama H, Yamashita E, Tomizaki T, Yamaguchi H, Shinzawa-Itoh K, Nakashima R, Yaono R, Yoshikawa S; Science 1996;272:1136-1144.

