
Cosmolabe
Encyclopedia
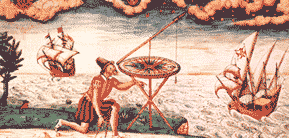
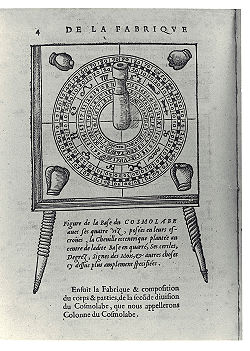
Astrolabe
An astrolabe is an elaborate inclinometer, historically used by astronomers, navigators, and astrologers. Its many uses include locating and predicting the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars, determining local time given local latitude and longitude, surveying, triangulation, and to...
, formerly used for measuring the angles between heavenly bodies. It is also called pantacosm. Jacques Besson
Jacques Besson
Jacques Besson was a French Protestant inventor, mathematician, and philosopher, chiefly remembered for his popular treatise on machines Theatrum Instrumentorum , which saw many reprints in different languages.-Life:...
also uses this name, or universal instrument, for his invention described in Le cosmolabe (1567), which could be used for astrometry
Astrometry
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky...
, cartography
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
, navigation
Navigation
Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
, and surveying
Surveying
See Also: Public Land Survey SystemSurveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, and science of accurately determining the terrestrial or three-dimensional position of points and the distances and angles between them...
.

