
Contact resistance
Encyclopedia
The term contact resistance refers to the contribution to the total resistance
of a material which comes from the electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance, which is an inherent property, independent of the measurement method. The idea of potential drop on the injection electrode was introduced by William Shockley
to explain the difference between the experimental results and the model of gradual channel approximation. The
name "contact resistance" was decided for the consideration of the metal–semiconductor interface as a main contribution to this phenomenon. Beside that also "interface resistance", "transitional resistance", or just simply "correction term" were used. Therefore was later used term "parasitic resistance" as a more general term, where it is usually still assumed that the
contact resistance has a major contribution.
For two electrode systems the specific contact resistivity is experimentally defined as the slope of the I-V curve at V=0:
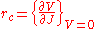
where J is the current density = current/area. The units of specific contact resistivity are typically therefore in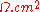 where
where  stands for ohms. When the current is a linear function of the voltage, the device is said to have ohmic contact
stands for ohms. When the current is a linear function of the voltage, the device is said to have ohmic contact
s.
The resistance of contacts can be crudely estimated by comparing the results of a four terminal measurement
to a simple two-lead measurement made with an ohmmeter. In a two-lead experiment, the measurement current causes a potential drop across both the test leads and the contacts so that the resistance of these elements is inseparable from the resistance of the actual device, with which they are in series. In a four-point probe measurement, one pair of leads is used to inject the measurement current while a second pair of leads, in parallel with the first, is used to measure the potential drop across the device. In the four-probe case, there is no potential drop across the voltage measurement leads so the contact resistance drop is not included. The difference between resistance derived from two-lead and four-lead methods is a reasonably accurate measurement of contact resistance assuming that the leads resistance is much smaller. Specific contact resistance can be obtained by multiplying by contact area. It should also be noted that the contact resistance may vary with temperature.
Inductive
and capacitive
methods could be used in principle to measure an intrinsic impedance
without the complication of contact resistance. In practice, direct current
methods are more typically used to determine resistance.
The three electrode systems such as transistors require more complicated methos, e.g. transmission line model, for the contact resistance approximation. The most common approach is the transmission line model (TLM). Here, the total device resistance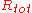 is plotted as a function of the channel length:
is plotted as a function of the channel length:
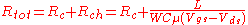
where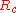 and
and 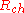 are contact and channel resistancies, respectively,
are contact and channel resistancies, respectively, 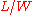 is the channel length/width,
is the channel length/width,  is gate insulator capacitance (per unit of area),
is gate insulator capacitance (per unit of area), 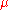 is carrier mobility, and
is carrier mobility, and 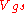 and
and 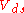 are gate-source and drain-source voltages. Therefore, the linear extrapolation of total resistance to the zero channel length provides the contact resistance. The slope of the linear function is related to the channel transconductance and can be used for estimation of the ”contact resistance-free” carrier mobility. The approximations used here (linear potential drop across the channel region, constant contact resistance,...) lead sometimes to the channel dependent contact resistance .
are gate-source and drain-source voltages. Therefore, the linear extrapolation of total resistance to the zero channel length provides the contact resistance. The slope of the linear function is related to the channel transconductance and can be used for estimation of the ”contact resistance-free” carrier mobility. The approximations used here (linear potential drop across the channel region, constant contact resistance,...) lead sometimes to the channel dependent contact resistance .
Beside the TLM it was proposed the gated four-probe measurement and the modified time-of-flight
method (TOF) . The direct methods able to measure potential drop on the injection electrode directly are the Kelvin probe force microscopy (KFM) and the electric-field induced second harmonic generation .
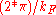 , where
, where 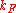 is Fermi wavevector
is Fermi wavevector
of the conducting material, Ohm's law
does not hold anymore. These small devices are called quantum point contact
s. Their conductance must be an integer multiple of the value , where
, where  is the electronic charge
is the electronic charge
and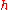 is Planck's constant. Quantum point contacts behave more like waveguide
is Planck's constant. Quantum point contacts behave more like waveguide
s than the classical wires of everyday life and may be described by the Landauer
scattering formalism. Point-contact tunneling is an important technique for characterizing superconductors.
are also subject to contact resistance. Similarly, a drop in hydrostatic pressure (analogous to electrical voltage
) occurs when fluid flow transitions from one channel to another.
clamps can frustrate attempts to start a vehicle
that has a dead battery
. Dirty or corroded
contacts on a fuse
or its holder can give the false impression that the fuse is blown. A sufficiently high contact resistance can cause substantial heating
in a high current device. Unpredictable or noisy contacts are a major cause of the failure of electrical equipment.
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
of a material which comes from the electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance, which is an inherent property, independent of the measurement method. The idea of potential drop on the injection electrode was introduced by William Shockley
William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley Jr. was an American physicist and inventor. Along with John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brattain, Shockley co-invented the transistor, for which all three were awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics.Shockley's attempts to commercialize a new transistor design in the 1950s...
to explain the difference between the experimental results and the model of gradual channel approximation. The
name "contact resistance" was decided for the consideration of the metal–semiconductor interface as a main contribution to this phenomenon. Beside that also "interface resistance", "transitional resistance", or just simply "correction term" were used. Therefore was later used term "parasitic resistance" as a more general term, where it is usually still assumed that the
contact resistance has a major contribution.
Experimental characterization
Here we need to distinguish the contact resistance evaluation in two-electrode systems (e.g. diodes) and three-electrode systems (e.g. transistors).For two electrode systems the specific contact resistivity is experimentally defined as the slope of the I-V curve at V=0:
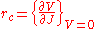
where J is the current density = current/area. The units of specific contact resistivity are typically therefore in
 where
where  stands for ohms. When the current is a linear function of the voltage, the device is said to have ohmic contact
stands for ohms. When the current is a linear function of the voltage, the device is said to have ohmic contactOhmic contact
An ohmic contact is a region on a semiconductor device that has been prepared so that the current-voltage curve of the device is linear and symmetric. If the I-V characteristic is non-linear and asymmetric, the contact is not ohmic, but is a blocking or Schottky contact...
s.
The resistance of contacts can be crudely estimated by comparing the results of a four terminal measurement
Four-terminal sensing
Four-terminal sensing , 4-wire sensing, or 4-point probes method is an electrical impedance measuring technique that uses separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing electrodes to make more accurate measurements than traditional two-terminal sensing...
to a simple two-lead measurement made with an ohmmeter. In a two-lead experiment, the measurement current causes a potential drop across both the test leads and the contacts so that the resistance of these elements is inseparable from the resistance of the actual device, with which they are in series. In a four-point probe measurement, one pair of leads is used to inject the measurement current while a second pair of leads, in parallel with the first, is used to measure the potential drop across the device. In the four-probe case, there is no potential drop across the voltage measurement leads so the contact resistance drop is not included. The difference between resistance derived from two-lead and four-lead methods is a reasonably accurate measurement of contact resistance assuming that the leads resistance is much smaller. Specific contact resistance can be obtained by multiplying by contact area. It should also be noted that the contact resistance may vary with temperature.
Inductive
Inductive coupling
In electrical engineering, two conductors are referred to as mutual-inductively coupled or magnetically coupled when they are configured such that change in current flow through one wire induces a voltage across the ends of the other wire through electromagnetic induction...
and capacitive
Capacitive coupling
In electronics, capacitive coupling is the transfer of energy within an electrical network by means of the capacitance between circuit nodes. This coupling can have an intentional or accidental effect...
methods could be used in principle to measure an intrinsic impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
without the complication of contact resistance. In practice, direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
methods are more typically used to determine resistance.
The three electrode systems such as transistors require more complicated methos, e.g. transmission line model, for the contact resistance approximation. The most common approach is the transmission line model (TLM). Here, the total device resistance
 is plotted as a function of the channel length:
is plotted as a function of the channel length: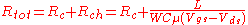
where
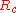 and
and 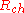 are contact and channel resistancies, respectively,
are contact and channel resistancies, respectively, 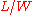 is the channel length/width,
is the channel length/width,  is gate insulator capacitance (per unit of area),
is gate insulator capacitance (per unit of area),  is carrier mobility, and
is carrier mobility, and 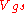 and
and 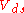 are gate-source and drain-source voltages. Therefore, the linear extrapolation of total resistance to the zero channel length provides the contact resistance. The slope of the linear function is related to the channel transconductance and can be used for estimation of the ”contact resistance-free” carrier mobility. The approximations used here (linear potential drop across the channel region, constant contact resistance,...) lead sometimes to the channel dependent contact resistance .
are gate-source and drain-source voltages. Therefore, the linear extrapolation of total resistance to the zero channel length provides the contact resistance. The slope of the linear function is related to the channel transconductance and can be used for estimation of the ”contact resistance-free” carrier mobility. The approximations used here (linear potential drop across the channel region, constant contact resistance,...) lead sometimes to the channel dependent contact resistance .Beside the TLM it was proposed the gated four-probe measurement and the modified time-of-flight
Time-of-flight
Time of flight describes a variety of methods that measure the time that it takes for an object, particle or acoustic, electromagnetic or other wave to travel a distance through a medium...
method (TOF) . The direct methods able to measure potential drop on the injection electrode directly are the Kelvin probe force microscopy (KFM) and the electric-field induced second harmonic generation .
Quantum limit
When a conductor has spatial dimensions close to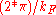 , where
, where 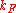 is Fermi wavevector
is Fermi wavevectorFermi surface
In condensed matter physics, the Fermi surface is an abstract boundary useful for predicting the thermal, electrical, magnetic, and optical properties of metals, semimetals, and doped semiconductors. The shape of the Fermi surface is derived from the periodicity and symmetry of the crystalline...
of the conducting material, Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
does not hold anymore. These small devices are called quantum point contact
Quantum point contact
A Quantum Point Contact is a narrow constriction between two wide electrically conducting regions, of a width comparable to the electronic wavelength . Quantum point contacts were first reported in 1988 by a Dutch group and, independently, by a British group...
s. Their conductance must be an integer multiple of the value
 , where
, where  is the electronic charge
is the electronic chargeElementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
and
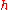 is Planck's constant. Quantum point contacts behave more like waveguide
is Planck's constant. Quantum point contacts behave more like waveguideWaveguide
A waveguide is a structure which guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound waves. There are different types of waveguides for each type of wave...
s than the classical wires of everyday life and may be described by the Landauer
Rolf Landauer
Rolf William Landauer was an IBM physicist who in 1961 argued that when information is lost in an irreversible circuit, the information becomes entropy and an associated amount of energy is dissipated as heat...
scattering formalism. Point-contact tunneling is an important technique for characterizing superconductors.
Other forms of contact resistance
Measurements of thermal conductivityThermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
are also subject to contact resistance. Similarly, a drop in hydrostatic pressure (analogous to electrical voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
) occurs when fluid flow transitions from one channel to another.
Significance
Bad contacts are the cause of failure or poor performance in a wide variety of electrical devices. For example, corroded jumper cableJump start (vehicle)
A jump start, also called a boost, is a method of starting an automobile or other vehicle powered by an internal combustion engine when the vehicle's battery has been discharged. A second battery is temporarily connected to provide starting power to the disabled vehicle...
clamps can frustrate attempts to start a vehicle
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
that has a dead battery
Lead-acid battery
Lead–acid batteries, invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté, are the oldest type of rechargeable battery. Despite having a very low energy-to-weight ratio and a low energy-to-volume ratio, their ability to supply high surge currents means that the cells maintain a relatively large...
. Dirty or corroded
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
contacts on a fuse
Fuse (electrical)
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit...
or its holder can give the false impression that the fuse is blown. A sufficiently high contact resistance can cause substantial heating
Joule heating
Joule heating, also known as ohmic heating and resistive heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor releases heat. It was first studied by James Prescott Joule in 1841. Joule immersed a length of wire in a fixed mass of water and measured the temperature...
in a high current device. Unpredictable or noisy contacts are a major cause of the failure of electrical equipment.

