
Contact process (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
Markov process
In probability theory and statistics, a Markov process, named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov, is a time-varying random phenomenon for which a specific property holds...
with state space
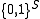 , where
, where 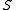 is a finite or countable graph
is a finite or countable graphGraph (mathematics)
In mathematics, a graph is an abstract representation of a set of objects where some pairs of the objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by mathematical abstractions called vertices, and the links that connect some pairs of vertices are called edges...
, usually Z
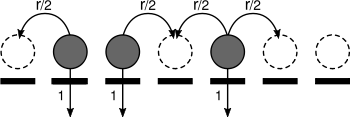
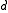 . The process is usually interpreted as a model for the spread of an infection: if the state of the process at a given time is
. The process is usually interpreted as a model for the spread of an infection: if the state of the process at a given time is 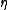 , then a site
, then a site  in
in 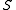 is "infected" if
is "infected" if 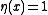 and healthy if
and healthy if 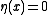 . Infected sites become healthy at a constant rate, while healthy sites become infected at a rate proportional to the number infected neighbors. One can generalize the state space to
. Infected sites become healthy at a constant rate, while healthy sites become infected at a rate proportional to the number infected neighbors. One can generalize the state space to 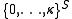 , such is called the multitype contact process. It represents a model when more than one type of infection is competing for space.
, such is called the multitype contact process. It represents a model when more than one type of infection is competing for space.More specifically, the dynamics of the basic contact process is defined by the following transition rates: at site
 ,
,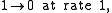
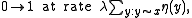
where the sum is over all the neighbors in
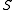 of
of  . This means that each site waits an exponential time with the corresponding rate, and then flips (so 0 becomes 1 and viceversa).
. This means that each site waits an exponential time with the corresponding rate, and then flips (so 0 becomes 1 and viceversa).For each graph
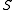 there exists a critical value
there exists a critical value 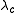 for the parameter
for the parameter 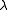 so that if
so that if 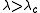 then the 1's survive (that is, if there is at least one 1 at time zero, then at any time there are ones) with positive probability, while if
then the 1's survive (that is, if there is at least one 1 at time zero, then at any time there are ones) with positive probability, while if 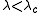 then the process dies out. For contact process on the integer lattice, a major breakthrough came in 1990 when Bezuidenhout and Grimmett showed that the contact process also dies out at the critical value. Their proof makes use of percolation theory
then the process dies out. For contact process on the integer lattice, a major breakthrough came in 1990 when Bezuidenhout and Grimmett showed that the contact process also dies out at the critical value. Their proof makes use of percolation theoryPercolation theory
In mathematics, percolation theory describes the behavior of connected clusters in a random graph. The applications of percolation theory to materials science and other domains are discussed in the article percolation.-Introduction:...
.
Voter model
The voter model (usually in continuous time, but there are discrete versions as well) is a process similar to the contact process. In this process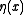 is taken to represent a voter's attitude on a particular topic. Voters reconsider their opinions at times distributed according to independent exponential random variables (this gives a Poisson process locally-- note that there are in general infinitely many voters so no global Poisson process can be used). At times of reconsideration, a voter chooses one neighbor uniformly from amongst all neighbors and takes that neighbor's opinion. One can generalize the process by allowing the picking of neighbors to be something other than uniform.
is taken to represent a voter's attitude on a particular topic. Voters reconsider their opinions at times distributed according to independent exponential random variables (this gives a Poisson process locally-- note that there are in general infinitely many voters so no global Poisson process can be used). At times of reconsideration, a voter chooses one neighbor uniformly from amongst all neighbors and takes that neighbor's opinion. One can generalize the process by allowing the picking of neighbors to be something other than uniform.Discrete time process
In the discrete time voter model in one dimension,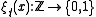 represents the state of particle
represents the state of particle  at time
at time  . Informally each individual is arranged on a line and can "see" other individuals that are within a radius,
. Informally each individual is arranged on a line and can "see" other individuals that are within a radius,  . If more than a certain proportion,
. If more than a certain proportion, 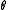 of these people disagree then the individual changes her attitude, otherwise she keeps it the same. Durrett
of these people disagree then the individual changes her attitude, otherwise she keeps it the same. DurrettRick Durrett
Richard Timothy Durrett is a mathematician known for his research andbooks on mathematical probability theory, stochastic processes and theirapplication to mathematical ecology and population genetics....
and Steif (1993) and Steif (1994) show that for large radii there is a critical value
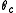 such that if
such that if 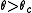 most individuals never change, and for
most individuals never change, and for 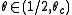 in the limit most sites agree. (Both of these results assume the probability of
in the limit most sites agree. (Both of these results assume the probability of 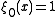 is one half.)
is one half.)This process has a natural generalization to more dimensions, some results for this are discussed in Durrett
Rick Durrett
Richard Timothy Durrett is a mathematician known for his research andbooks on mathematical probability theory, stochastic processes and theirapplication to mathematical ecology and population genetics....
and Steif (1993).
Continuous time process
The continuous time process is similar in that it imagines each individual has a belief at a time and changes it based on the attitudes of its neighbors. The process is described informally by LiggettThomas M. Liggett
Thomas Milton Liggett is a mathematician at the University of California, Los Angeles. He works in probability theory, specializing in interacting particle processes....
(1985, 226), "Periodically (i.e., at independent exponential times), an individual reassesses his view in a rather simple way: he chooses a 'friend' at random with certain probabilities and adopts his position." A model was constructed with this interpretation first by Holley and Liggett
Thomas M. Liggett
Thomas Milton Liggett is a mathematician at the University of California, Los Angeles. He works in probability theory, specializing in interacting particle processes....
(1975).
This process is analogous to a process first suggested by Clifford and Sudbury (1973) where animals are conflicting over territory and the animals are equally matched. A site is selected to be invaded by a neighbor at a given time.

