Confocal laser scanning microscopy
Overview
Image resolution
Image resolution is an umbrella term that describes the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail....
optical images with depth selectivity. The key feature of confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy
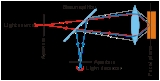
Confocal microscopy is an optical imaging technique used to increase optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole to eliminate out-of-focus light in specimens that are thicker than the focal plane. It enables the reconstruction of...
is its ability to acquire in-focus images from selected depths, a process known as optical sectioning
Optical sectioning
Optical sectioning is the process by which a suitably designed microscope can produce clear images of a focal planes deep within a thick sample. This is used to reduce the need for thin sectioning using instruments such as the microtome...
. Images are acquired point-by-point and reconstructed with a computer, allowing three-dimensional reconstructions of topologically
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
complex objects. For opaque specimens, this is useful for surface profiling
Profilometer
Profilometer is a measuring instrument used to measure a surface's profile, in order to quantify its roughness.While the historical notion of a profilometer was a device similar to a phonograph that measures a surface as the surface is moved relative to the contact profilometer's stylus, this...
, while for non-opaque specimens, interior structures can be imaged.
Unanswered Questions

