Competition aerobatics
Encyclopedia
Competition aerobatics is an air sport in which judges
rate the skill of pilots performing aerobatic
flying. It is practiced in both piston-powered
single-engine airplanes and gliders
.
An aerobatic competition is sanctioned by a national aero club, its designee, or in the case of international competitions, by the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale
(FAI). The sanctioning body establishes the rules that apply to the competition, including entry qualifications for all participants, operating procedures and judging criteria.
A pilot enters a competition in a category of his or her choice, which defines the level of difficulty of the aerobatic sequences flown. Within each category, a pilot flies one or more flight programs. Each flight receives a total score from the judges; ranking each pilot's combined total scores for all flight programs within each category determines that category's winner.
(and other states that adopt the U.S. model). They vary by difficulty of the individual aerobatic maneuver
s they contain, as well as the combination of those maneuvers within the sequence. In order of increasing difficulty, the power categories are:
Some aero clubs include a Classic category for airplanes without inverted fuel and oil systems. The sequences flown are similar to those flown in the Sportsman category.
Three glider categories are:
Categories flown in a competition are announced in advance.

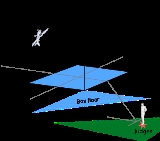
The aerobatic box is a volume of airspace in which the aircraft must remain while performing a sequence. Its length and width are each 1000 metres (3,280.8 ft). Its height varies based on whether FAI, national aero club or local rules apply to the competition. White ground markers at each corner of the box make it visible to the pilot from the air. For most categories, penalties are assessed for flight outside the aerobatic box.
The box has two axes, the identification of which is based on the location of the judges. The X-Axis (called the A-Axis by some aero clubs), runs across the line of sight of the judges. It is along this axis that most figures are usually flown. In some contests a center line is marked along the middle of the X-Axis.
The Y-Axis (called the B-Axis by some aero clubs) runs perpendicular to the X-Axis, toward and away from the judges. This axis is used for cross-box position correction. The official wind direction is always declared by contest officials to be along the X-Axis. This, however, does not always reflect reality, and generally during the course of a sequence the competitor will drift either toward or away from the judging line. The competitor can extend or shorten maneuvers flown along the Y-Axis to obtain the desired positioning.
The box floor is as high as 460 metres (1,509.2 ft) above ground level (AGL) for Primary level competitors and as low as 100 metres (328.1 ft) AGL for Unlimited level competitors. The box ceiling is as high as 1000 metres (3,280.8 ft) above its floor. Before a category starts, a competitor will mark the box by flying along its boundaries at its floor. This allows the judges to visualize the box in the sky and prepares them to adjudge an aircraft flying below the box floor.
At a groundspeed of 300 kilometres per hour (186.4 mph) the pilot has 12 seconds from entering the box on the one side before exiting the box on the other.
 Each category within a competition may have between 3 and 9 grading judges, each of whom is accredited by the contest's sanctioning body. They are positioned between 150 and 250 m (492.1 and 820.2 ft) back from the edge of the box, at the center of the X-Axis and facing that axis. Each grading judge is assisted by an assistant judge, who reads Aresti notation and verbalizes to the grading judge each figure to be flown, and a recorder (also called a writer or scribe), who records scores, commentary and ancillary information on a competitor's score sheet. For some flight programs, a single individual may serve concurrently as assistant judge and recorder.
Each category within a competition may have between 3 and 9 grading judges, each of whom is accredited by the contest's sanctioning body. They are positioned between 150 and 250 m (492.1 and 820.2 ft) back from the edge of the box, at the center of the X-Axis and facing that axis. Each grading judge is assisted by an assistant judge, who reads Aresti notation and verbalizes to the grading judge each figure to be flown, and a recorder (also called a writer or scribe), who records scores, commentary and ancillary information on a competitor's score sheet. For some flight programs, a single individual may serve concurrently as assistant judge and recorder.
A grading judge assesses the quality of each figure flown according to well-defined criteria and assigns it a numerical score between 0 and 10. Under FAI and some national aero clubs' rules, the judge may also assign a score of "hard zero", indicating that the wrong figure was flown. At the conclusion of each flight, the grading judge assigns a presentation score based on the competitor's placement of figures throughout the aerobatic box. A grading judge also determines if the competitor has flown below the floor of the box or above its ceiling. Each grading judge is further charged with assessing whether a competitor is flying safely and advocating for the competitor's disqualification if not.
A chief judge oversees the operation of the judging line. He or she is often responsible for sequencing competitors into the aerobatic box, identifying and resolving judging and safety issues, reviewing competitors' score sheets, assessing penalties, monitoring the aerobatic box for traffic conflicts, conducting briefings for pilots and judging line personnel, and certifying scores. A chief judge is typically assisted by 2 or more individuals. In some competitions, a chief judge may concurrently serve as a grading judge.
Corner judges (also called boundary judges or line judges) are positioned at the edge of the buffer zones, 50 metres (164 ft) along each axis beyond marked corners of the aerobatic box. They monitor and record each excursion beyond the buffer zone; the competitor earns a penalty for each such excursion. Each corner judge guards 2 of the 4 lines that define the box. In most competitions, 2 corner judges are used, located at opposing corners. In FAI competitions, 4 corner judges are used, one at each corner. Two judges guard each line; they must agree that a competitor has crossed a boundary in order for the competitor earn a penalty.
Deadline judges are positioned along a deadline, if one has been established by the contest's sanctioning body. They monitor and record each infringement of the deadline. The competitor earns a penalty for each such infringement, that penalty being more severe than an excursion out of the aerobatic box.
In the U.S., the International Aerobatic Club
(IAC) is the National Aeronautic Association
's delegate for aerobatics; in the UK
, the Royal Aero Club
designates the British Aerobatic Association
(BAeA) to fill this roll. In South Africa
the FAI appoints the Aeroclub of South Africa which in turn appoints the Sport Aerobatic Club of South Africa to manage all aerobatic events.
Referee
A referee is the person of authority, in a variety of sports, who is responsible for presiding over the game from a neutral point of view and making on the fly decisions that enforce the rules of the sport...
rate the skill of pilots performing aerobatic
Aerobatics
Aerobatics is the practice of flying maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in normal flight. Aerobatics are performed in airplanes and gliders for training, recreation, entertainment and sport...
flying. It is practiced in both piston-powered
Reciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types...
single-engine airplanes and gliders
Glider (sailplane)
A glider or sailplane is a type of glider aircraft used in the sport of gliding. Some gliders, known as motor gliders are used for gliding and soaring as well, but have engines which can, in some cases, be used for take-off or for extending a flight...
.
An aerobatic competition is sanctioned by a national aero club, its designee, or in the case of international competitions, by the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale
Fédération Aéronautique Internationale
The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale is the world governing body for air sports and aeronautics and astronautics world records. Its head office is in Lausanne, Switzerland. This includes man-carrying aerospace vehicles from balloons to spacecraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles...
(FAI). The sanctioning body establishes the rules that apply to the competition, including entry qualifications for all participants, operating procedures and judging criteria.
A pilot enters a competition in a category of his or her choice, which defines the level of difficulty of the aerobatic sequences flown. Within each category, a pilot flies one or more flight programs. Each flight receives a total score from the judges; ranking each pilot's combined total scores for all flight programs within each category determines that category's winner.
Categories
Five power categories are flown in the U.S.United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
(and other states that adopt the U.S. model). They vary by difficulty of the individual aerobatic maneuver
Aerobatic maneuver
Aerobatic maneuvers are flight paths putting aircraft in unusual attitudes, in air shows, dog fights or competition aerobatics. Aerobatics can be performed by a single aircraft or in formation with several others...
s they contain, as well as the combination of those maneuvers within the sequence. In order of increasing difficulty, the power categories are:
- Primary
- Sportsman
- Intermediate
- Advanced
- Unlimited
Some aero clubs include a Classic category for airplanes without inverted fuel and oil systems. The sequences flown are similar to those flown in the Sportsman category.
Three glider categories are:
- Sportsman
- Intermediate
- Unlimited
Categories flown in a competition are announced in advance.
Flight programs
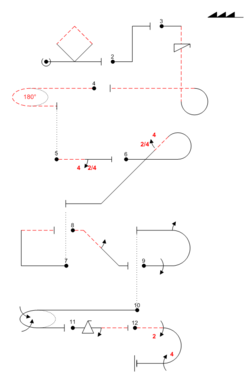
Within each category, each pilot flies one or more flight programs. They are:- Known: Determined each year by the FAI or the national aero club. It is flown by all competitors at all contests all year long. This is sometimes known as the Q (for qualifying) program.
- Free: In this program, each pilot is given the opportunity to demonstrate his personal flying skills, creative talent and his aircraft performance by designing his own sequence.
- Unknown: This program is made known to the contestants only about 12 hours before the competition. The figures are chosen by either teams or pilots, each submitting a single figure. In Local contests often the governing body or the contest chief judge choose the unknown sequence. The pilots must not practice before flying the unknown sequence. (For classes Intermediate and above.)
- 4-minute Free: Only the top unlimited pilots might be invited to fly this final program. It is for this program that new figures are sometimes flown as pilots strive to display their creativity and superior skills as performers.
Aerobatic box

The aerobatic box is a volume of airspace in which the aircraft must remain while performing a sequence. Its length and width are each 1000 metres (3,280.8 ft). Its height varies based on whether FAI, national aero club or local rules apply to the competition. White ground markers at each corner of the box make it visible to the pilot from the air. For most categories, penalties are assessed for flight outside the aerobatic box.
The box has two axes, the identification of which is based on the location of the judges. The X-Axis (called the A-Axis by some aero clubs), runs across the line of sight of the judges. It is along this axis that most figures are usually flown. In some contests a center line is marked along the middle of the X-Axis.
The Y-Axis (called the B-Axis by some aero clubs) runs perpendicular to the X-Axis, toward and away from the judges. This axis is used for cross-box position correction. The official wind direction is always declared by contest officials to be along the X-Axis. This, however, does not always reflect reality, and generally during the course of a sequence the competitor will drift either toward or away from the judging line. The competitor can extend or shorten maneuvers flown along the Y-Axis to obtain the desired positioning.
The box floor is as high as 460 metres (1,509.2 ft) above ground level (AGL) for Primary level competitors and as low as 100 metres (328.1 ft) AGL for Unlimited level competitors. The box ceiling is as high as 1000 metres (3,280.8 ft) above its floor. Before a category starts, a competitor will mark the box by flying along its boundaries at its floor. This allows the judges to visualize the box in the sky and prepares them to adjudge an aircraft flying below the box floor.
At a groundspeed of 300 kilometres per hour (186.4 mph) the pilot has 12 seconds from entering the box on the one side before exiting the box on the other.
Judging

A grading judge assesses the quality of each figure flown according to well-defined criteria and assigns it a numerical score between 0 and 10. Under FAI and some national aero clubs' rules, the judge may also assign a score of "hard zero", indicating that the wrong figure was flown. At the conclusion of each flight, the grading judge assigns a presentation score based on the competitor's placement of figures throughout the aerobatic box. A grading judge also determines if the competitor has flown below the floor of the box or above its ceiling. Each grading judge is further charged with assessing whether a competitor is flying safely and advocating for the competitor's disqualification if not.
A chief judge oversees the operation of the judging line. He or she is often responsible for sequencing competitors into the aerobatic box, identifying and resolving judging and safety issues, reviewing competitors' score sheets, assessing penalties, monitoring the aerobatic box for traffic conflicts, conducting briefings for pilots and judging line personnel, and certifying scores. A chief judge is typically assisted by 2 or more individuals. In some competitions, a chief judge may concurrently serve as a grading judge.
Corner judges (also called boundary judges or line judges) are positioned at the edge of the buffer zones, 50 metres (164 ft) along each axis beyond marked corners of the aerobatic box. They monitor and record each excursion beyond the buffer zone; the competitor earns a penalty for each such excursion. Each corner judge guards 2 of the 4 lines that define the box. In most competitions, 2 corner judges are used, located at opposing corners. In FAI competitions, 4 corner judges are used, one at each corner. Two judges guard each line; they must agree that a competitor has crossed a boundary in order for the competitor earn a penalty.
Deadline judges are positioned along a deadline, if one has been established by the contest's sanctioning body. They monitor and record each infringement of the deadline. The competitor earns a penalty for each such infringement, that penalty being more severe than an excursion out of the aerobatic box.
Judging Downgrades Summary
Here is a précis of the principal "faults" that you should look for and the number of marks to deduct whilst you are applying standard CIVA rules of critique to sequence programmes at all levels.At the entry to and exit from EVERY figure element
| Horizontal start & finish Lines | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Off axis left or right n-deg | 1 point/5 deg |
| Climbing or diving n-deg | 1 point/5 deg |
| One wing low n-deg | 1 point/5 deg |
| No distinct line drawn | 1 point each |
| Flying in wrong direction on the "A" axis | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
Family 1 - lines and angles
| Horizontal 45's & Verticals | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Climbing or diving n-deg (before or after roll) | 1 point/5 deg |
| Steep or shallow n-deg (before or after roll) | 1 point/5 deg |
| Positive or negative n-deg (before or after roll) | 1 point/5 deg |
| No line drawn before or after roll | 1 point each |
| Longer or shorter line before or after roll | 1 to 3 points |
Family 2 - turns and rolling turns
| Turns | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Rolling entry or exit (i.e. a "co-ordinated" turn) | 1 to 2 points |
| Bank angle too shallow (less than 60 deg) | 1 point/5 deg |
| Bank angle varied | 1 point/variation |
| Rolling Turns | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Roll rate varied | 1 point/variation |
| Roll stopped or turn and then restarted | 2 points |
| Not an even integration of rolls at end | 1 point/5 deg |
| Not enough / too many rolls or a flick-roll seen | Mark = hard zero |
| Both Types | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Turn rate or radius varied | 1 point/variation |
| Climbing or diving in turn | 1 point/5 deg |
| Exit | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Was n-deg early or late | 1 point/5 deg |
Family 3 - combinations of lines
| All Figures | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Smaller or larger 2'nd etc. corner | 1 to 3 points |
| Longer or shorter 2'nd etc. line | 1 to 3 points |
Family 5 - stall turns
| Up/down Lines | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Up/down-line pos/neg/left/right n-deg (before or after roll) | 1 point/5 deg |
| Short, long or no line drawn up/down (before or after roll) | 1 to 3 points |
| The Turn | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Turn-around too wide (pivot beyond wingtip) | 1 point/wing length |
| Rolled or pitched n-deg in turn-around | 1 point/5 deg |
| Exit pull or push radius smaller or larger | 1 to 3 points |
Family 6 - Tail Slides
| Up/Down Lines | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Up/down-line pos/neg/left/right n-deg (before or after roll) | 1 point/5 deg (was 2 per 5 - beware!) |
| Short, long or no line drawn up/down (before or after roll) | 1-3 points |
| The Slide | Deducción |
|---|---|
| No slide seen | Mark = Perception Zero (PZ) |
| Yawed or rolled n-deg in slide | 1 point/5 deg |
| Exit pull/push radius smaller or larger | 1 to 3 points |
| Pitched the wrong way (wheels up or down) | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
Family 7 - Loops and Eights
| Half & Full Loops | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Large or small radius at top or in 1'st/2'nd etc. quarter | 1 to 3 points |
| Line drawn between roll and looping segment | 2 points |
| Roll not central in looping segment | 1 to 3 points |
| Off axis during looping segment | 1 point/5 deg |
| Higher or lower exit | 1 to 3 points |
| Eights | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Smaller or larger 2'nd half | 1 to 3 points |
| Lower or higher 2'nd half (horizontal) | 1 to 3 points |
| With Corners | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Longer or shorter 2'nd etc. line length | 1 to 3 points |
| Larger or smaller 2'nd etc. corner | 1 to 3 points |
| Up/down-line pos/neg/left/right n-deg {before or after roll} | 1 point/5 deg |
| 1'st/2'nd etc. 45 steep or shallow {before or after roll} | 1 point/5 deg |
| Horizontal segment off axis left/right/up/down | 1 point/5 deg |
Family 8 - Combinations of Lines, Angles and Loops
| Humpty Bumps | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Up/down-line pos/neg/left/right n-deg (before or after roll) | 1 point/5 deg |
| Rolled or yawed in half-loop | 1 point/5 deg |
| Larger or smaller 2'nd quarter loop in half-loop | 1 to 3 points |
| Push instead of pull, or pull instead of push | Mark = hard zero |
Family 9 - Rolls and Spins
| Slow Rolls | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Rolled n-deg short or too far | 1 point/5 deg |
| Roll barrelled (pitched and/or yawed whilst rolling) | 1 point/5 deg |
| Roll rate varied | 1 point/variation |
| Axis changed left/right/up/down n-deg during/after roll | 1 point/5deg |
| Hesitation at random point | 2 points |
| Wrong type of roll substituted | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
| Hesitation Rolls | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Climbed or sank in knife | 1 to 2 points |
| Slower or faster 2'nd etc. half/quarter/eighth | 1 to 3 points |
| Under/over rotated 1'st/2'nd etc. half/quarter/eighth | 1 point/5 deg |
| Hesitation missed (wrong type of roll substituted) | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
| Flick Rolls | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Part flicked and part aileron'd roll | 2 to 5 points |
| Not flicked (no stall seen) | Mark = Perception Zero (PZ) |
| Positive instead of negative, or neg instead of pos | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
| Combinations Of Rolls | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Any line between two rolls | At least 2 points |
| Significant(?) line between rolls | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
| Same direction when opposite required (or vice versa) | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
| Wrong number of rolls where linked | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
| Rolls immediately prior to or just after looping | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Any line between stopping loop/roll and starting roll/loop | At least 2 points |
| Roll starts before loop finishes | 1 point/5 deg (from required line) |
| Significant line between rolls | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
| Spin Entry | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Entry not stalled, and/or "rolled" in – not spinning | Mark = Perception Zero (PZ) |
| Flicked entry (too fast) | Mark = Perception Zero (PZ) |
| Spin Exit | Deducción |
|---|---|
| Spin rotation short or too far n-deg | 1 point/5 deg |
| Line after was positive or negative n-deg | 1 point/5 deg |
| No line drawn after | Mark = Hard Zero (HZ) |
Governing bodies
The FAI is the international governing body for all airborne sports. Its Commission Internationale de Voltige Aerienne (CIVA) governs competition aerobatics. While FAI itself oversees international competitions, it recognizes national aero clubs to regulate competition aerobatics locally. A national aero club often delegates this responsibility to an affiliate organization focused on aerobatics.In the U.S., the International Aerobatic Club
International Aerobatic Club
The International Aerobatic Club is a division of the Experimental Aircraft Association and the National Aeronautics Association...
(IAC) is the National Aeronautic Association
National Aeronautic Association
The National Aeronautic Association of the United States is a non-profit 501 organization and a member of the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale , the international standard setting and record-keeping body for aeronautics and astronautics. NAA is the official record-keeper for United States...
's delegate for aerobatics; in the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, the Royal Aero Club
Royal Aero Club
The Royal Aero Club is the national co-ordinating body for Air Sport in the United Kingdom.The Aero Club was founded in 1901 by Frank Hedges Butler, his daughter Vera and the Hon Charles Rolls , partly inspired by the Aero Club of France...
designates the British Aerobatic Association
British Aerobatic Association
The British Aerobatic Association handles all domestic aerobatic competitions in the United Kingdom.-History:It was formed on May 1 1974. It is based in at West London Aero Club at White Waltham Airfield, Maidenhead.-Activities:...
(BAeA) to fill this roll. In South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
the FAI appoints the Aeroclub of South Africa which in turn appoints the Sport Aerobatic Club of South Africa to manage all aerobatic events.
See also
- FAI World Grand PrixFAI World Grand PrixFAI World Grand Prix is a Grand Prix aerobatics series led by Fédération Aéronautique Internationale.Since 1990th run as Breitling Series up to 1995....
- European and World Glider Aerobatic Championships
- List of articles about Aerobatic pilots
- International Aerobatic ClubInternational Aerobatic ClubThe International Aerobatic Club is a division of the Experimental Aircraft Association and the National Aeronautics Association...
(USA), British Aerobatic AssociationBritish Aerobatic AssociationThe British Aerobatic Association handles all domestic aerobatic competitions in the United Kingdom.-History:It was formed on May 1 1974. It is based in at West London Aero Club at White Waltham Airfield, Maidenhead.-Activities:...
(UK)
External links
- FAI Sporting Code Section 6, "Regulations for the Conduct of International Aerobatic Events, Part 1 - Powered Aircraft"
- Judging tutorial for 2011, The British Aerobatic Association
- International Aerobatic Club
- Commission Internationale de Voltige Aerienne (FAI Aerobatics Commission)
- Sport Aerobatic Club of South Africa
- Olan free software for design of aerobatic sequences
- Aerobatic maneuver website

