
Common Unix Printing System
Encyclopedia
CUPS is a modular printing
system for Unix-like
computer operating systems which allows a computer to act as a print server
. A computer running CUPS is a host
that can accept print jobs from client
computers, process them, and send them to the appropriate printer.
CUPS consists of a print spooler and scheduler, a filter system that converts the print data to a format that the printer will understand, and a backend system that sends this data to the print device. CUPS uses the Internet Printing Protocol
(IPP) as the basis for managing print job
s and queues. It also provides the traditional command line interfaces for the System V
and Berkeley
print systems, and provides support for the Berkeley print system's Line Printer Daemon protocol
and limited support for the server message block
(SMB) protocol. System administrators can configure the device driver
s which CUPS supplies by editing text files in Adobe's PostScript Printer Description
(PPD) format. There are a number of user interfaces for different platforms that can configure CUPS, and it has a built-in web-based interface. CUPS is free software
, provided under the GNU General Public License
and GNU Lesser General Public License
, Version 2.
, who owns Easy Software Products
, started developing CUPS in 1997. The first public betas appeared in 1999.
The original design of CUPS used the LPD
protocol, but due to limitations in LPD and vendor incompatibilities, the Internet Printing Protocol
(IPP) was chosen instead. CUPS was quickly adopted as the default printing system for several Linux distribution
s, including Red Hat Linux
. In March 2002, Apple Inc. adopted CUPS as the printing system for Mac OS X
10.2. In February 2007, Apple Inc. hired chief developer Michael Sweet and purchased the CUPS source code.
 CUPS provides a mechanism that allows print jobs to be sent to printers in a standard fashion. The print-data goes to a scheduler which sends jobs to a filter system that converts the print job into a format the printer will understand. The filter system then passes the data on to a backend—a special filter that sends print data to a device or network connection. The system makes extensive use of PostScript
CUPS provides a mechanism that allows print jobs to be sent to printers in a standard fashion. The print-data goes to a scheduler which sends jobs to a filter system that converts the print job into a format the printer will understand. The filter system then passes the data on to a backend—a special filter that sends print data to a device or network connection. The system makes extensive use of PostScript
and rasterization
of data to convert the data into a format suitable for the destination printer.
CUPS offers a standard and modularised printing system that can process numerous data formats on the print server. Before CUPS, it was difficult to find a standard printer management system that would accommodate the very wide variety of printers on the market using their own printer languages and formats. For instance, the System V and Berkeley printing systems were largely incompatible with each other, and they required complicated scripts and workarounds to convert the program's data format to a printable format. They often could not detect the file format that was being sent to the printer and thus could not automatically and correctly convert the data stream. Additionally, data conversion was performed on individual workstations rather than a central server.
CUPS allows printer manufacturers and printer-driver developers to more easily create drivers that work natively on the print server. Processing occurs on the server, allowing for easier network-based printing than with other Unix printing systems. With Samba installed, users can address printers on remote Windows computers and generic PostScript drivers can be used for printing across the network.
(IPP) over HTTP/1.1. A helper application (cups-lpd) converts Line Printer Daemon protocol
(LPD) requests to IPP. The scheduler also provides a web-based interface for managing print jobs, the configuration of the server, and for documentation about CUPS itself.
An authorization module controls which IPP and HTTP messages can pass through the system.
Once the IPP/HTTP packets are authorized they are sent to the client module, which listens for and processes incoming connections. The client module is also responsible for executing external CGI programs as needed to support web-based printers, classes, and job status monitoring and administration. Once this module has processed its requests, it sends them to the IPP module which performs Uniform Resource Identifier
(URI) validation to prevent a client from sidestepping any access control
s or authentication
on the HTTP server. The URI is a text string
that indicates a name or address that can be used to refer to an abstract or physical resource on a network.
The scheduler allows for classes of printers. Applications can send requests to groups of printers in a class, allowing the scheduler to direct the job to the first available printer in that class.
A jobs module manages print jobs, sending them to the filter and backend processes for final conversion and printing, and monitoring the status messages from those processes.
The CUPS scheduler utilizes a configuration module, which parses configuration files, initializes CUPS data structure
s, and starts and stops the CUPS program. The configuration module will stop CUPS services during configuration file processing and then restart the service when processing is complete.
A logging module handles the logging of scheduler events for access, error, and page log file
s. The main module handles timeouts and dispatch of I/O requests for client connections, watching for signals
, handling child process errors and exits, and reloading the server configuration files as needed.
Other modules used by the scheduler include:
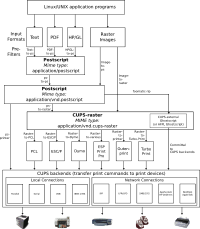 CUPS can process a variety of data formats on the print server. It converts the print-job data into the final language/format of the printer via a series of filters.
CUPS can process a variety of data formats on the print server. It converts the print-job data into the final language/format of the printer via a series of filters.
It uses MIME types
for identifying file formats.
The
For example, to detect an HTML
file, the following entry would be applicable:
The second line matches the file contents to the specified MIME type by determining that the first kilobyte of text in the file holds printable characters and that those characters include html markup. If the pattern above matches, then the filter system would mark the file as the MIME type text/html.
The
The source field designates the MIME type that is determined by looking up the
Some examples:
text/plain application/postscript 50 texttops
application/vnd.cups-postscript application/vnd.cups-raster 50 pstoraster
image/* application/vnd.cups-postscript 50 imagetops
image/* application/vnd.cups-raster 50 imagetoraster
It then determines the type of data that is being input and the filter to be used through the use of the MIME databases, for instance image data will be detected and processed through a particular filter and HTML data detected and processed through another filter.
CUPS can convert supplied data either into PostScript
data or directly into raster data. If it is converted into PostScript data an additional filter is applied called a prefilter, which runs the PostScript data through another PostScript converter so that it can add printer specific options like selecting page ranges to print, setting n-up mode and other device-specific things. After the pre-filtering is done, the data can either be sent directly to a CUPS backend if using a PostScript printer, or it can be passed to another filter like Foomatic
by linuxprinting.org. Alternatively, it can be passed to Ghostscript
, which converts the PostScript into an intermediary CUPS-raster format. The intermediary raster format is then passed onto a final filter which converts the raster data to a printer-specific format. The default filters included with CUPS include:
other proprietary languages like GDI or SPL (Samsung Printer Language) are supported by Splix, a raster to SPL translator.
However, several other alternatives can integrate with CUPS. Easy Software Products
(ESP), the original creators of CUPS, have released their own CUPS filters; Gutenprint
(previously known as Gimp-Print) is a range of high-quality printer drivers for (mostly) inkjet printers, and TurboPrint
for Linux has another range of quality printer drivers for a wide range of printers.
, serial
, and USB ports, as well as network backends that operate via the IPP
, JetDirect
(AppSocket), Line Printer Daemon ("LPD") and SMB
protocols.
, launchd
, the Solaris Service Management Facility
, or xinetd
which use the cups-lpd helper program to support LPD printing. When CUPS is installed the
command and the
commands are installed as compatible programs. This allows a standard interface to CUPS and allows maximum compatibility with existing applications that rely on these printing systems.
631. It particularly helps organisations that need to monitor print jobs and add print queues and printers remotely.
CUPS 1.0 provided a simple class, job, and printer-monitoring interface for web browsers.
CUPS 1.1 replaced this interface with an enhanced administration interface that allows users to add, modify, delete, configure, and control classes, jobs, and printers.
CUPS 1.2 and later provide a revamped web interface which features improved readability and design, support for automatically discovered printers, and a better access to system logs and advanced settings.
CUPS Manager can add new CUPS printers and manage CUPS printers and queues. There are other third-party applications to manage printing, for example GtkLP and its associate tool GtkLPQ, or GtkPSproc.
GNOME's widget toolkit
GTK+
included integrated printing support based on CUPS in its version 2.10, released in 2006.
 The KDEPrint framework for KDE
The KDEPrint framework for KDE
contains various GUI
-tools that act as CUPS front-ends and allows the administration of classes, print queues and print jobs; it includes a printer wizard to assist with adding new printers amongst other features. KDEPrint first appeared in KDE 2.2.
KDEPrint supports several different printing platforms, with CUPS one of the best-supported. It replaced a previous version of printing support in KDE, qtcups and is backwards compatible with this module of KDE. kprinter, a dialogue-box program, serves as the main tool for sending jobs to the print device; it can also be started from the command line. KDEPrint includes a system to pre-filter any jobs before they are handed over to CUPS, or to handle jobs all on itself, such as converting files to PDF
. These filters are described by a pair of Desktop/XML
files.
KDEPrint's main components include:
, and in printer proxy applications which display the print queues and allow additional configuration after printers are set up. Earlier versions of Mac OS X also included a Printer Setup Utility
, which supplied configuration options missing from earlier versions of the Print & Fax preference pane.
 Mandriva Linux
Mandriva Linux
10.1 up to version 2008.1 features a GUI for printing (Printerdrake). It is basically an interface for CUPS and allows users to add, remove and update printers, as well as the control of print jobs. This is done from a centralised configuration program that allows for CUPS server configuration in a centralised set of screens.
it uses the Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Fedora printer frontend, called system-config-printer.
 Starting with Red Hat Linux 9, Red Hat provided an integrated print manager based on CUPS and integrated into GNOME
Starting with Red Hat Linux 9, Red Hat provided an integrated print manager based on CUPS and integrated into GNOME
. This allowed adding printers via a user interface similar to the one Microsoft Windows
uses, where a new printer could be added using an add new printer wizard, along with changing default printer-properties in a window containing a list of installed printers. Jobs could also be started and stopped using a print manager and the printer could be paused using a context menu
that pops up when the printer icon is right-clicked.
Eric Raymond
criticised this system in his piece The Luxury of Ignorance. Raymond had attempted to install CUPS using the Fedora Core 1 print manager but found it non-intuitive; he criticised the interface designers for not designing with the user's point-of-view in mind. He found the idea of printer queues was not obvious because users create queues on their local computer but these queues are actually created on the CUPS server.
He also found the plethora of queue type options confusing as he could choose from between networked CUPS (IPP), networked Unix (LPD
), networked Windows (SMB
), networked Novell (NCP
) or networked JetDirect
. He found the help file singularly unhelpful and largely irrelevant to a user's needs. Raymond used CUPS as a general topic to show that user interface design on Linux desktops needs rethinking and more careful design. He stated:
, the original creators of CUPS, created a GUI, provided support for many printers and implemented a PostScript RIP
. ESP Print Pro ran on Windows, UNIX and Linux, but is no longer available and support for this product ended on 31 December 2007.
Computer printer
In computing, a printer is a peripheral which produces a text or graphics of documents stored in electronic form, usually on physical print media such as paper or transparencies. Many printers are primarily used as local peripherals, and are attached by a printer cable or, in most new printers, a...
system for Unix-like
Unix-like
A Unix-like operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, while not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification....
computer operating systems which allows a computer to act as a print server
Print server
A print server, or printer server, is a device that connects printers to client computers over a network. It can accept print jobs from the computers and send the jobs to the appropriate printers....
. A computer running CUPS is a host
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
that can accept print jobs from client
Client (computing)
A client is an application or system that accesses a service made available by a server. The server is often on another computer system, in which case the client accesses the service by way of a network....
computers, process them, and send them to the appropriate printer.
CUPS consists of a print spooler and scheduler, a filter system that converts the print data to a format that the printer will understand, and a backend system that sends this data to the print device. CUPS uses the Internet Printing Protocol
Internet Printing Protocol
In computing, the Internet Printing Protocol provides a standard network protocol for remote printing as well as for managing print jobs, media size, resolution, and so forth....
(IPP) as the basis for managing print job
Print job
In computing, a print job is a file or set of files that has been submitted to be printed.Jobs are typically identified by a unique number, and are assigned to a particular destination, usually a printer...
s and queues. It also provides the traditional command line interfaces for the System V
System V printing system
The UNIX System V printing system is one of several standard architectures for printing on the UNIX platform, and is typical of commercial System V-based operating systems such as Solaris and SCO OpenServer...
and Berkeley
Berkeley printing system
The Berkeley printing system is one of several standard architectures for printing on the Unix platform. It originated in 4.2BSD, and is used in BSD derivatives such as FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, and DragonFly BSD...
print systems, and provides support for the Berkeley print system's Line Printer Daemon protocol
Line Printer Daemon protocol
The Line Printer Daemon protocol/Line Printer Remote protocol is a network protocol for submitting print jobs to a remote printer. The original implementation of LPD was in the Berkeley printing system in the BSD UNIX operating system; the LPRng project also supports that protocol...
and limited support for the server message block
Server Message Block
In computer networking, Server Message Block , also known as Common Internet File System operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used to provide shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an...
(SMB) protocol. System administrators can configure the device driver
Device driver
In computing, a device driver or software driver is a computer program allowing higher-level computer programs to interact with a hardware device....
s which CUPS supplies by editing text files in Adobe's PostScript Printer Description
PostScript Printer Description
PostScript Printer Description files are created by vendors to describe the entire set of features and capabilities available for their PostScript printers.A PPD also contains the PostScript code used to invoke features for the print job...
(PPD) format. There are a number of user interfaces for different platforms that can configure CUPS, and it has a built-in web-based interface. CUPS is free software
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
, provided under the GNU General Public License
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....
and GNU Lesser General Public License
GNU Lesser General Public License
The GNU Lesser General Public License or LGPL is a free software license published by the Free Software Foundation . It was designed as a compromise between the strong-copyleft GNU General Public License or GPL and permissive licenses such as the BSD licenses and the MIT License...
, Version 2.
History
Michael SweetMichael Sweet (programmer)
Michael Sweet is a computer scientist and is the primary developer and architect of CUPS, flPhoto, HTMLDOC, and Mini-XML. He was the original developer of the Gimp-Print software and contributes to other free software projects such as FLTK, Newsd, and Samba...
, who owns Easy Software Products
Easy Software Products
Easy Software Products is the vendor who originally invented the Common Unix Printing System and HTMLDOC software. It was founded near Washington, D.C. in 1993 and is now located in Morgan Hill, California. ESP sold CUPS to Apple Inc. in 2007 but still develops and sells its HTMLDOC...
, started developing CUPS in 1997. The first public betas appeared in 1999.
The original design of CUPS used the LPD
Line Printer Daemon protocol
The Line Printer Daemon protocol/Line Printer Remote protocol is a network protocol for submitting print jobs to a remote printer. The original implementation of LPD was in the Berkeley printing system in the BSD UNIX operating system; the LPRng project also supports that protocol...
protocol, but due to limitations in LPD and vendor incompatibilities, the Internet Printing Protocol
Internet Printing Protocol
In computing, the Internet Printing Protocol provides a standard network protocol for remote printing as well as for managing print jobs, media size, resolution, and so forth....
(IPP) was chosen instead. CUPS was quickly adopted as the default printing system for several Linux distribution
Linux distribution
A Linux distribution is a member of the family of Unix-like operating systems built on top of the Linux kernel. Such distributions are operating systems including a large collection of software applications such as word processors, spreadsheets, media players, and database applications...
s, including Red Hat Linux
Red Hat Linux
Red Hat Linux, assembled by the company Red Hat, was a popular Linux based operating system until its discontinuation in 2004.Red Hat Linux 1.0 was released on November 3, 1994...
. In March 2002, Apple Inc. adopted CUPS as the printing system for Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
10.2. In February 2007, Apple Inc. hired chief developer Michael Sweet and purchased the CUPS source code.
Overview

PostScript
PostScript is a dynamically typed concatenative programming language created by John Warnock and Charles Geschke in 1982. It is best known for its use as a page description language in the electronic and desktop publishing areas. Adobe PostScript 3 is also the worldwide printing and imaging...
and rasterization
Raster graphics
In computer graphics, a raster graphics image, or bitmap, is a data structure representing a generally rectangular grid of pixels, or points of color, viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium...
of data to convert the data into a format suitable for the destination printer.
CUPS offers a standard and modularised printing system that can process numerous data formats on the print server. Before CUPS, it was difficult to find a standard printer management system that would accommodate the very wide variety of printers on the market using their own printer languages and formats. For instance, the System V and Berkeley printing systems were largely incompatible with each other, and they required complicated scripts and workarounds to convert the program's data format to a printable format. They often could not detect the file format that was being sent to the printer and thus could not automatically and correctly convert the data stream. Additionally, data conversion was performed on individual workstations rather than a central server.
CUPS allows printer manufacturers and printer-driver developers to more easily create drivers that work natively on the print server. Processing occurs on the server, allowing for easier network-based printing than with other Unix printing systems. With Samba installed, users can address printers on remote Windows computers and generic PostScript drivers can be used for printing across the network.
Scheduler
The CUPS scheduler implements Internet Printing ProtocolInternet Printing Protocol
In computing, the Internet Printing Protocol provides a standard network protocol for remote printing as well as for managing print jobs, media size, resolution, and so forth....
(IPP) over HTTP/1.1. A helper application (cups-lpd) converts Line Printer Daemon protocol
Line Printer Daemon protocol
The Line Printer Daemon protocol/Line Printer Remote protocol is a network protocol for submitting print jobs to a remote printer. The original implementation of LPD was in the Berkeley printing system in the BSD UNIX operating system; the LPRng project also supports that protocol...
(LPD) requests to IPP. The scheduler also provides a web-based interface for managing print jobs, the configuration of the server, and for documentation about CUPS itself.
An authorization module controls which IPP and HTTP messages can pass through the system.
Once the IPP/HTTP packets are authorized they are sent to the client module, which listens for and processes incoming connections. The client module is also responsible for executing external CGI programs as needed to support web-based printers, classes, and job status monitoring and administration. Once this module has processed its requests, it sends them to the IPP module which performs Uniform Resource Identifier
Uniform Resource Identifier
In computing, a uniform resource identifier is a string of characters used to identify a name or a resource on the Internet. Such identification enables interaction with representations of the resource over a network using specific protocols...
(URI) validation to prevent a client from sidestepping any access control
Access control
Access control refers to exerting control over who can interact with a resource. Often but not always, this involves an authority, who does the controlling. The resource can be a given building, group of buildings, or computer-based information system...
s or authentication
Authentication
Authentication is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a datum or entity...
on the HTTP server. The URI is a text string
String (computer science)
In formal languages, which are used in mathematical logic and theoretical computer science, a string is a finite sequence of symbols that are chosen from a set or alphabet....
that indicates a name or address that can be used to refer to an abstract or physical resource on a network.
The scheduler allows for classes of printers. Applications can send requests to groups of printers in a class, allowing the scheduler to direct the job to the first available printer in that class.
A jobs module manages print jobs, sending them to the filter and backend processes for final conversion and printing, and monitoring the status messages from those processes.
The CUPS scheduler utilizes a configuration module, which parses configuration files, initializes CUPS data structure
Data structure
In computer science, a data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.Different kinds of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks...
s, and starts and stops the CUPS program. The configuration module will stop CUPS services during configuration file processing and then restart the service when processing is complete.
A logging module handles the logging of scheduler events for access, error, and page log file
Log file
The term log file can refer to:*Text saved by a computer operating system to recored its activities, such as by the Unix syslog facility*Output produced by a data loggerAlso see Wikibooks chapter...
s. The main module handles timeouts and dispatch of I/O requests for client connections, watching for signals
Signal (computing)
A signal is a limited form of inter-process communication used in Unix, Unix-like, and other POSIX-compliant operating systems. Essentially it is an asynchronous notification sent to a process in order to notify it of an event that occurred. When a signal is sent to a process, the operating system...
, handling child process errors and exits, and reloading the server configuration files as needed.
Other modules used by the scheduler include:
- the MIME module, which handles a Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) type and conversion database used in the filtering process that converts print data to a format suitable for a print device;
- a PPD module that handles a list of Postscript Printer DescriptionPostScript Printer DescriptionPostScript Printer Description files are created by vendors to describe the entire set of features and capabilities available for their PostScript printers.A PPD also contains the PostScript code used to invoke features for the print job...
(PPD) files; - a devices module that manages a list of devices that are available in the system;
- a printers module that handles printers and PPDs within CUPS.
Filter system

It uses MIME types
Internet media type
An Internet media type, originally called a MIME type after MIME and sometimes a Content-type after the name of a header in several protocols whose value is such a type, is a two-part identifier for file formats on the Internet.The identifiers were originally defined in RFC 2046 for use in email...
for identifying file formats.
MIME databases
After the CUPS system has assigned the print job to the scheduler, it is passed to the CUPS filter system. This converts the data to a format suitable for the printer. During start-up, the CUPS daemon loads two MIME databases:mime.types that defines the known file types that CUPS can accept data for, and mime.convs that defines the programs that process each particular MIME type.The
mime.types file has the syntax:mimetype { [file-extensions] | [pattern-match] }For example, to detect an HTML
HTML
HyperText Markup Language is the predominant markup language for web pages. HTML elements are the basic building-blocks of webpages....
file, the following entry would be applicable:
text/html html htm \printable(0,1024) + (string(0,"") string(0,"
The second line matches the file contents to the specified MIME type by determining that the first kilobyte of text in the file holds printable characters and that those characters include html markup. If the pattern above matches, then the filter system would mark the file as the MIME type text/html.
The
mime.convs file has the syntax:source destination cost programThe source field designates the MIME type that is determined by looking up the
mime.types file, while the destination field lists the type of output requested and determines what program should be used. This is also retrieved from mime.types. The cost field assists in the selection of sets of filters when converting a file. The last field, program, determines which filter program to use to perform the data conversion.Some examples:
text/plain application/postscript 50 texttops
application/vnd.cups-postscript application/vnd.cups-raster 50 pstoraster
image/* application/vnd.cups-postscript 50 imagetops
image/* application/vnd.cups-raster 50 imagetoraster
Filtering process
The filtering process works by taking input data pre-formatted with six arguments:- the job ID of the print job
- the user-name
- the job-name
- the number of copies to print
- any print options
- the filename (though this is unnecessary if it has been redirected from standard input).
It then determines the type of data that is being input and the filter to be used through the use of the MIME databases, for instance image data will be detected and processed through a particular filter and HTML data detected and processed through another filter.
CUPS can convert supplied data either into PostScript
PostScript
PostScript is a dynamically typed concatenative programming language created by John Warnock and Charles Geschke in 1982. It is best known for its use as a page description language in the electronic and desktop publishing areas. Adobe PostScript 3 is also the worldwide printing and imaging...
data or directly into raster data. If it is converted into PostScript data an additional filter is applied called a prefilter, which runs the PostScript data through another PostScript converter so that it can add printer specific options like selecting page ranges to print, setting n-up mode and other device-specific things. After the pre-filtering is done, the data can either be sent directly to a CUPS backend if using a PostScript printer, or it can be passed to another filter like Foomatic
Foomatic
Foomatic is a configurable printing filter. It uses PPD files as configuration to generate appropriate output for a given printer. It is intended to be used with the Common Unix Printing System . It uses ghostscript in the background, using options according to the PPD file of the printer...
by linuxprinting.org. Alternatively, it can be passed to Ghostscript
Ghostscript
Ghostscript is a suite of software based on an interpreter for Adobe Systems' PostScript and Portable Document Format page description languages.- Features :...
, which converts the PostScript into an intermediary CUPS-raster format. The intermediary raster format is then passed onto a final filter which converts the raster data to a printer-specific format. The default filters included with CUPS include:
- raster to PCLPrinter Command LanguagePrinter Command Language, more commonly referred to as PCL, is a page description language developed by Hewlett-Packard as a printer protocol and has become a de facto industry standard. Originally developed for early inkjet printers in 1984, PCL has been released in varying levels for thermal,...
- raster to ESC/PESC/PESC/P is a command language developed by Epson to control computer printers. It was mainly used in dot matrix printers and some inkjet printers. During the era of dot matrix printers, it was also used by other manufacturers , sometimes in modified form...
or ESC/P2 (an Epson printer language, now largely superseded by their new ESC/P-Raster format) - raster to DymoDYMOThe DYMO routing protocol is successor to the popular Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Routing protocol and shares many of its benefits. It is, however, slightly easier to implement and designed with future enhancements in mind....
(another printer company). - raster to Zebra Programming Language or ZPL (a Zebra TechnologiesZebra TechnologiesZebra Technologies is a manufacturer of thermal bar code label and receipt printers, RFID smart label printer/encoders, card and kiosk printers, based in Vernon Hills, Illinois. Zebra has products in 100 countries around the world...
printer language)
other proprietary languages like GDI or SPL (Samsung Printer Language) are supported by Splix, a raster to SPL translator.
However, several other alternatives can integrate with CUPS. Easy Software Products
Easy Software Products
Easy Software Products is the vendor who originally invented the Common Unix Printing System and HTMLDOC software. It was founded near Washington, D.C. in 1993 and is now located in Morgan Hill, California. ESP sold CUPS to Apple Inc. in 2007 but still develops and sells its HTMLDOC...
(ESP), the original creators of CUPS, have released their own CUPS filters; Gutenprint
Gutenprint
Gutenprint is a collection of free software printer drivers for use with UNIX spooling systems, such as CUPS, lpr and LPRng...
(previously known as Gimp-Print) is a range of high-quality printer drivers for (mostly) inkjet printers, and TurboPrint
TurboPrint
TurboPrint is a closed source printer driver system for Linux, AmigaOS and MorphOS. It supports a number of printers that don't yet have a free driver, and fuller printer functionality on some printer models. It integrates with the CUPS printing system....
for Linux has another range of quality printer drivers for a wide range of printers.
Backends
The backends are the ways in which CUPS sends data to printers. There are several backends available for CUPS: parallelParallel port
A parallel port is a type of interface found on computers for connecting various peripherals. In computing, a parallel port is a parallel communication physical interface. It is also known as a printer port or Centronics port...
, serial
Serial port
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time...
, and USB ports, as well as network backends that operate via the IPP
Internet Printing Protocol
In computing, the Internet Printing Protocol provides a standard network protocol for remote printing as well as for managing print jobs, media size, resolution, and so forth....
, JetDirect
Jetdirect
JetDirect is the name of a technology sold by Hewlett-Packard that allows computer printers to be directly attached to a Local Area Network. The "JetDirect" designation covers a range of models from the external 1 and 3 port parallel print servers known as the 300x and 500x, to the internal EIO...
(AppSocket), Line Printer Daemon ("LPD") and SMB
Server Message Block
In computer networking, Server Message Block , also known as Common Internet File System operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used to provide shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an...
protocols.
Compatibility
CUPS provides both the System V and Berkeley printing commands, so users can continue with traditional commands for printing via CUPS. CUPS uses port 631 (TCP and UDP), which is the standard IPP port, and optionally on port 515 by inetdInetd
inetd is a super-server daemon on many Unix systems that manages Internet services. First appearing in 4.3BSD , it is generally located at /usr/sbin/inetd.-Function:...
, launchd
Launchd
launchd is a unified, open-source service management framework for starting, stopping and managing daemons, applications, processes, and scripts...
, the Solaris Service Management Facility
Service Management Facility
Service Management Facility is a feature of the Solaris operating system that creates a supported, unified model for services and service management on each Solaris system and replaces init.d scripts. SMF introduces:...
, or xinetd
Xinetd
In computer networking, xinetd, the eXtended InterNET Daemon, is an open-source super-server daemon which runs on many Unix-like systems and manages Internet-based connectivity...
which use the cups-lpd helper program to support LPD printing. When CUPS is installed the
lpLp (Unix)The lp command is used on many Unix-like systems to assign jobs to printer queues. The name derives from "lineprinter", though it has become the commonly used command for any sort of printer...
System V printing systemSystem V printing system
The UNIX System V printing system is one of several standard architectures for printing on the UNIX platform, and is typical of commercial System V-based operating systems such as Solaris and SCO OpenServer...
command and the
lpr Berkeley printing systemBerkeley printing system
The Berkeley printing system is one of several standard architectures for printing on the Unix platform. It originated in 4.2BSD, and is used in BSD derivatives such as FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, and DragonFly BSD...
commands are installed as compatible programs. This allows a standard interface to CUPS and allows maximum compatibility with existing applications that rely on these printing systems.
CUPS web-based administration interface
On all platforms, CUPS has a web-based administration interface that runs on portTCP and UDP port
In computer networking, a port is an application-specific or process-specific software construct serving as a communications endpoint in a computer's host operating system. A port is associated with an IP address of the host, as well as the type of protocol used for communication...
631. It particularly helps organisations that need to monitor print jobs and add print queues and printers remotely.
CUPS 1.0 provided a simple class, job, and printer-monitoring interface for web browsers.
CUPS 1.1 replaced this interface with an enhanced administration interface that allows users to add, modify, delete, configure, and control classes, jobs, and printers.
CUPS 1.2 and later provide a revamped web interface which features improved readability and design, support for automatically discovered printers, and a better access to system logs and advanced settings.
GNOME
The GNOMEGNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
CUPS Manager can add new CUPS printers and manage CUPS printers and queues. There are other third-party applications to manage printing, for example GtkLP and its associate tool GtkLPQ, or GtkPSproc.
GNOME's widget toolkit
Widget toolkit
In computing, a widget toolkit, widget library, or GUI toolkit is a set of widgets for use in designing applications with graphical user interfaces...
GTK+
GTK+
GTK+ is a cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces. It is licensed under the terms of the GNU LGPL, allowing both free and proprietary software to use it. It is one of the most popular toolkits for the X Window System, along with Qt.The name GTK+ originates from GTK;...
included integrated printing support based on CUPS in its version 2.10, released in 2006.
KDE

KDE
KDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
contains various GUI
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
-tools that act as CUPS front-ends and allows the administration of classes, print queues and print jobs; it includes a printer wizard to assist with adding new printers amongst other features. KDEPrint first appeared in KDE 2.2.
KDEPrint supports several different printing platforms, with CUPS one of the best-supported. It replaced a previous version of printing support in KDE, qtcups and is backwards compatible with this module of KDE. kprinter, a dialogue-box program, serves as the main tool for sending jobs to the print device; it can also be started from the command line. KDEPrint includes a system to pre-filter any jobs before they are handed over to CUPS, or to handle jobs all on itself, such as converting files to PDF
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
. These filters are described by a pair of Desktop/XML
XML
Extensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
files.
KDEPrint's main components include:
- a Print Dialog box, which allows printer properties to be modified
- a Print Manager, which allows management of printers, such as adding and removing printers, through an Add Printer Wizard
- a Job Viewer/Manager, which manages printer jobs, such as hold/release, cancel and move to another printer
- a CUPS configuration module (integrated into KDE)
Mac OS X
In Mac OS X 10.5, printers are configured in the Print & Fax pane in System PreferencesSystem Preferences
System Preferences is an application included with the Mac OS X operating system that allows users to modify various system settings which are divided into separate preference panes...
, and in printer proxy applications which display the print queues and allow additional configuration after printers are set up. Earlier versions of Mac OS X also included a Printer Setup Utility
Printer Setup Utility
The Printer Setup Utility was an application in Mac OS X that served to allow the user to configure printers physically connected to the computer, or connected via a network...
, which supplied configuration options missing from earlier versions of the Print & Fax preference pane.
Mandriva Linux

Mandriva Linux
Mandriva Linux is a Linux distribution distributed by Mandriva. It uses the RPM Package Manager...
10.1 up to version 2008.1 features a GUI for printing (Printerdrake). It is basically an interface for CUPS and allows users to add, remove and update printers, as well as the control of print jobs. This is done from a centralised configuration program that allows for CUPS server configuration in a centralised set of screens.
it uses the Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Fedora printer frontend, called system-config-printer.
PrinterSetup
The PrinterSetup system can manage CUPS queues. It takes the approach of assigning a text file to describe each print queue. These 'PrinterSetupFiles' may then be added to other text files called 'PrinterSetupLists'. This allows logical grouping of printers. the PrinterSetup project remains in its infancy.Red Hat Linux/Fedora

GNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
. This allowed adding printers via a user interface similar to the one Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
uses, where a new printer could be added using an add new printer wizard, along with changing default printer-properties in a window containing a list of installed printers. Jobs could also be started and stopped using a print manager and the printer could be paused using a context menu
Context menu
A context menu is a menu in a graphical user interface that appears upon user interaction, such as a right mouse click or middle click mouse operation...
that pops up when the printer icon is right-clicked.
Eric Raymond
Eric S. Raymond
Eric Steven Raymond , often referred to as ESR, is an American computer programmer, author and open source software advocate. After the 1997 publication of The Cathedral and the Bazaar, Raymond was for a number of years frequently quoted as an unofficial spokesman for the open source movement...
criticised this system in his piece The Luxury of Ignorance. Raymond had attempted to install CUPS using the Fedora Core 1 print manager but found it non-intuitive; he criticised the interface designers for not designing with the user's point-of-view in mind. He found the idea of printer queues was not obvious because users create queues on their local computer but these queues are actually created on the CUPS server.
He also found the plethora of queue type options confusing as he could choose from between networked CUPS (IPP), networked Unix (LPD
Line Printer Daemon protocol
The Line Printer Daemon protocol/Line Printer Remote protocol is a network protocol for submitting print jobs to a remote printer. The original implementation of LPD was in the Berkeley printing system in the BSD UNIX operating system; the LPRng project also supports that protocol...
), networked Windows (SMB
Server Message Block
In computer networking, Server Message Block , also known as Common Internet File System operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used to provide shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an...
), networked Novell (NCP
NetWare Core Protocol
The NetWare Core Protocol is a network protocol used in some products from Novell, Inc. It is usually associated with the NetWare operating system, but parts of it have been implemented on other platforms such as Linux, Windows NT and various flavors of Unix.It is used to access file, print,...
) or networked JetDirect
Jetdirect
JetDirect is the name of a technology sold by Hewlett-Packard that allows computer printers to be directly attached to a Local Area Network. The "JetDirect" designation covers a range of models from the external 1 and 3 port parallel print servers known as the 300x and 500x, to the internal EIO...
. He found the help file singularly unhelpful and largely irrelevant to a user's needs. Raymond used CUPS as a general topic to show that user interface design on Linux desktops needs rethinking and more careful design. He stated:
The meta-problem here is that the configuration wizard does all the approved rituals (GUI with standardized clicky buttons, help popping up in a browser, etc. etc.) but doesn't have the central attribute these are supposed to achieve: discoverability. That is, the quality that every point in the interface has prompts and actions attached to it from which you can learn what to do next. Does your project have this quality?
ESP Print Pro
Easy Software ProductsEasy Software Products
Easy Software Products is the vendor who originally invented the Common Unix Printing System and HTMLDOC software. It was founded near Washington, D.C. in 1993 and is now located in Morgan Hill, California. ESP sold CUPS to Apple Inc. in 2007 but still develops and sells its HTMLDOC...
, the original creators of CUPS, created a GUI, provided support for many printers and implemented a PostScript RIP
Raster image processor
A raster image processor is a component used in a printing system which produces a raster image also known as a bitmap. The bitmap is then sent to a printing device for output. The input may be a page description in a high-level page description language such as PostScript, Portable Document...
. ESP Print Pro ran on Windows, UNIX and Linux, but is no longer available and support for this product ended on 31 December 2007.
Name
CUPS began life as "The Common UNIX Printing System". The name was shortened to just "CUPS" beginning with CUPS 1.4 due to legal concerns with the UNIX trademark.See also
- FoomaticFoomaticFoomatic is a configurable printing filter. It uses PPD files as configuration to generate appropriate output for a given printer. It is intended to be used with the Common Unix Printing System . It uses ghostscript in the background, using options according to the PPD file of the printer...
- GutenprintGutenprintGutenprint is a collection of free software printer drivers for use with UNIX spooling systems, such as CUPS, lpr and LPRng...
- HP Linux Imaging and Printing
- LPRngLPRngLPRng is a printing system compatible with the Berkeley printing system. It provides printer spooling and network print server functionality using the Line Printer Daemon protocol....
- Scanner Access Now EasyScanner Access Now EasyScanner Access Now Easy is an application programming interface that provides standardized access to any raster image scanner hardware ....
- SpoolingSpoolingIn computer science, spool refers to the process of placing data in a temporary working area for another program to process. The most common use is in writing files on a magnetic tape or disk and entering them in the work queue for another process. Spooling is useful because devices access data at...
- XprintXprintXprint is a deprecated printing extension for the X Window System. It allows an application to render output to a printer just as it would to any other display device. The server portion, Xprt, uses an extension to handle paged output devices...
Further reading
- Sweet, Michael (July 10, 2000). CUPS overview. Easy Software Products.
- CUPS software administration manual : Managing printers from the web (version 1.1.21, 2004). Easy Software Products. Retrieved January 5, 2005.
- http://www.cups.org/articles.php How-to articles and FAQs about using CUPS
- Design of CUPS Filtering System — including the context for Mac OS X ("Jaguar"). LinuxPrinting.org. Retrieved January 5, 2005.
- KDEKDEKDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
. KDEPrint information. KDE-printing website. Retrieved January 14, 2005.

