.gif)
Colorimetry (chemical method)
Encyclopedia
Physical chemistry
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic, atomic, subatomic, and particulate phenomena in chemical systems in terms of physical laws and concepts...
and analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry is the study of the separation, identification, and quantification of the chemical components of natural and artificial materials. Qualitative analysis gives an indication of the identity of the chemical species in the sample and quantitative analysis determines the amount of...
, colorimetry or colourimetry is a technique "used to determine the concentration of colored compounds in solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
."
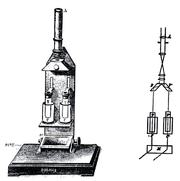
A colorimeter
Colorimeter (chemistry)
Not to be confused with a calorimeter.A colorimeter is a device used in colorimetry. In scientific fields the word generally refers to the device that measures the absorbance of particular wavelengths of light by a specific solution...
is a device used to test the concentration of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light (not to be confused with the tristimulus colorimeter
Tristimulus colorimeter
A Tristimulus colorimeter, colloquially shortened to colorimeter, is used in digital imaging, to profile and calibrate output devices.It takes a limited number of wideband spectral energy readings along the visible spectrum by using filtered photodetectors; e.g...
used to measure colors in general).
To use the colorimeter, different solutions must be made, including a control or reference of known concentration. With a visual colorimeter, for example the Duboscq colorimeter illustrated, the length of the light path through the solutions can be varied while filtered
Filter (optics)
Optical filters are devices which selectively transmit light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as plane glass or plastic devices in the optical path which are either dyed in the mass or have interference coatings....
light transmitted through them is compared for a visual match. The concentration times path length is taken to be equal when the colors match, so the concentration of the unknown can be determined by simple proportions. Nessler tubes work on the same principle.
There are also electronic automated colorimeters; before these machines are used, they must be calibrated with a cuvette
Cuvette
A cuvette is a small tube of circular or square cross section, sealed at one end, made of plastic, glass, or fused quartz and designed to hold samples for spectroscopic experiments. The best cuvettes are as clear as possible, without impurities that might affect a spectroscopic reading...
containing the control solution. The concentration of a sample can be calculated from the intensity of light before and after it passes through the sample by using the Beer–Lambert law. Photoelectric analyzers came to dominate in the 1960s.
The color or wavelength of the filter chosen for the colorimeter is extremely important, as the wavelength of light that is transmitted by the colorimeter has to be same as that absorbed by the substance being measured. For example, the filter on a colorimeter might be set to red if the liquid is blue.
Absorption colorimeter
A colorimeterColorimeter
For articles on Colorimeter see:* Colorimeter * Tristimulus colorimeter...
is a device used to test the concentration of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light. To use this device, different solutions must be made, and a control (usually a mixture of distilled water
Distilled water
Distilled water is water that has many of its impurities removed through distillation. Distillation involves boiling the water and then condensing the steam into a clean container.-History:...
and another solution) is first filled into a cuvette
Cuvette
A cuvette is a small tube of circular or square cross section, sealed at one end, made of plastic, glass, or fused quartz and designed to hold samples for spectroscopic experiments. The best cuvettes are as clear as possible, without impurities that might affect a spectroscopic reading...
and placed inside a colorimeter to calibrate the machine. Only after the device has been calibrated can you use it to find the densities and/or concentrations of the other solutions. You do this by repeating the calibration, except with cuvettes filled with the other solutions.
The filter on a colorimeter must be set to red if the liquid is blue. The size of the filter initially chosen for the colorimeter is extremely important, as the wavelength of light that is transmitted by the colorimeter has to be same as that absorbed by the substance.
Colorimetric Assays
Colorimetric assays use reagents that undergo a measurable color change in the presence of the analyteAnalyte
An analyte, or component , is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. Grammatically, it is important to note that experiments always seek to measure properties of analytes—and that analytes themselves can never be measured. For instance, one cannot...
. They are widely used in biochemistry to test for the presence of enzymes. For example, para-Nitrophenylphosphate
Para-Nitrophenylphosphate
para-Nitrophenylphosphate is a chromogenic substrate for acid and alkaline phosphatase in ELISA assays. Under their influence the decay to yellow para-nitrophenol is catalysed. This product can be measured with a 405 nm spectrophotometer....
is converted into a yellow product by alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase is a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. The process of removing the phosphate group is called dephosphorylation...
. Enzyme linked immunoassays
ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay , is a popular format of a "wet-lab" type analytic biochemistry assay that uses one sub-type of heterogeneous, solid-phase enzyme immunoassay to detect the presence of a substance in a liquid sample."Wet lab" analytic biochemistry assays involves detection of an...
use enzyme-complexed-antibodies to detect antigens, and binding of the antibody is often inferred from the color change of reagents such as TMB
3,3’,5,5’-Tetramethylbenzidine
3,3’,5,5’-Tetramethylbenzidine or TMB is a chromogenic substrate used in staining procedures in immunohistochemistry as well as being a visualising reagent used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays...
.

