Colobomycter
Encyclopedia
Colobomycter is a small parareptile known from the Early Permian of Oklahoma
. The genus
was first described from fossil
remains in 1958, at which time it was believed to represent a synapsid
(or "mammal-like reptile"), specifically, a pelycosaur
. However, the discovery of new material and reexamination of the holotype
led to its reclassification as a member of the Eureptilia
. More recent studies indicate that Colobomycter is properly placed within the amniote
clade
Parareptilia
, closely related to the taxon
Acleistorhinus. Together, the two taxa form the Family
Acleistorhinidae
.
No postcranial material is known for Colobomycter, and the skull
material referred to the genus (representing four individuals) has all been recovered from a single locality, the Dolese Brothers Quarry, near Richard's Spur, 11 kilometers north of Fort Sill, Comanche County, Oklahoma. This site comprises a fissure-fill deposit yielding a unique upland fauna
. Other taxa recovered from these strata
preserves a wide array of tetrapods, including lepospondyl and temnospondyl amphibians, the anthracosaur Seymouria
, microsaurs, captorhinomorphs
, protorothyridids
, and synapsids.
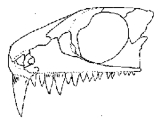
The skull of Colobomycter is considered one of the most enigmatic found in any of the parareptiles primarily due to the presence of greatly enlarged caniniform teeth possessing serrated edges in the premaxilla
and, to a lesser extent, the maxilla
. The length of the premaxillary fang is greater than half the height of the skull. Modesto et Reisz (2008) note that "The large size of the first premaxillary tooth is [otherwise] unheard of among early reptiles." The taxon also possesses unusual "folding" of the dentine at the bases of its larger marginal teeth, a state known as polyplycodont (a condition also seen to have evolved independently in diadectomorphs
, ichthyosaurs, and mosasaurs). Modesto et Reisz (2008, p. 682) speculate that hard-shelled insects and other arthropods may have formed the bulk of its diet, but that Colobomycter could also have fed on vertebrates, including small amphibians and eureptiles. It is notable as the smallest predatory amniote from the Richard's Spur deposits, with a skull measuring a mere 70-80 millimeters in length.
Oklahoma
Oklahoma is a state located in the South Central region of the United States of America. With an estimated 3,751,351 residents as of the 2010 census and a land area of 68,667 square miles , Oklahoma is the 28th most populous and 20th-largest state...
. The genus
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
was first described from fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
remains in 1958, at which time it was believed to represent a synapsid
Synapsid
Synapsids are a group of animals that includes mammals and everything more closely related to mammals than to other living amniotes. They are easily separated from other amniotes by having an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye, leaving a bony arch beneath each, accounting for their name...
(or "mammal-like reptile"), specifically, a pelycosaur
Pelycosaur
The pelycosaurs are an informal grouping composed of basal or primitive Late Paleozoic synapsid amniotes. Some species were quite large and could grow up to 3 meters or more, although most species were much smaller...
. However, the discovery of new material and reexamination of the holotype
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example of an organism, known to have been used when the species was formally described. It is either the single such physical example or one of several such, but explicitly designated as the holotype...
led to its reclassification as a member of the Eureptilia
Eureptilia
Eureptilia is one of the two major clades of the Sauropsida, the other being Anapsida . Eureptilia includes not only all Diapsids, but also a number of primitive Permo-Carboniferous forms previously classified under the Anapsida, in the old order "Cotylosauria".Primitive eureptilians were all...
. More recent studies indicate that Colobomycter is properly placed within the amniote
Amniote
The amniotes are a group of tetrapods that have a terrestrially adapted egg. They include synapsids and sauropsids , as well as their fossil ancestors. Amniote embryos, whether laid as eggs or carried by the female, are protected and aided by several extensive membranes...
clade
Clade
A clade is a group consisting of a species and all its descendants. In the terms of biological systematics, a clade is a single "branch" on the "tree of life". The idea that such a "natural group" of organisms should be grouped together and given a taxonomic name is central to biological...
Parareptilia
Parareptilia
Parareptilia is a subclass or clade of reptiles which is variously defined as an extinct group of primitive anapsids, or a more cladistically correct alternative to Anapsida...
, closely related to the taxon
Taxon
|thumb|270px|[[African elephants]] form a widely-accepted taxon, the [[genus]] LoxodontaA taxon is a group of organisms, which a taxonomist adjudges to be a unit. Usually a taxon is given a name and a rank, although neither is a requirement...
Acleistorhinus. Together, the two taxa form the Family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Acleistorhinidae
Acleistorhinidae
Acleistorhinidae is a family of Early Permian-aged parareptiles. Presently, the clade consists of only two taxa, Colobomycter and Acleistorhinus, both collected from the Permian of Oklahoma. Sister taxa include Nyctiphruretidae and Sclerosauridae....
.
No postcranial material is known for Colobomycter, and the skull
Skull
The skull is a bony structure in the head of many animals that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. A skull without a mandible is only a cranium. Animals that have skulls are called craniates...
material referred to the genus (representing four individuals) has all been recovered from a single locality, the Dolese Brothers Quarry, near Richard's Spur, 11 kilometers north of Fort Sill, Comanche County, Oklahoma. This site comprises a fissure-fill deposit yielding a unique upland fauna
Fauna
Fauna or faunæ is all of the animal life of any particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is flora.Zoologists and paleontologists use fauna to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess shale fauna"...
. Other taxa recovered from these strata
Stratum
In geology and related fields, a stratum is a layer of sedimentary rock or soil with internally consistent characteristics that distinguish it from other layers...
preserves a wide array of tetrapods, including lepospondyl and temnospondyl amphibians, the anthracosaur Seymouria
Seymouria
Seymouria was a reptile-like labyrinthodont from the early Permian of North America and Europe . It was small, only 2 ft long...
, microsaurs, captorhinomorphs
Captorhinomorpha
Captorhinomorpha is a suborder of prehistoric reptiles which appeared in the Carboniferous period and became extinct after the Early Permian period....
, protorothyridids
Protorothyrididae
Protorothyrididae is a family of small, lizard-like reptiles. Their skulls did not have fenestrae, as is also true of modern turtles and tortoises. Protorothyridids lived from the Late Carboniferous to Early Permian periods, in what is now North America. Many genera of primitive reptiles were...
, and synapsids.
The skull of Colobomycter is considered one of the most enigmatic found in any of the parareptiles primarily due to the presence of greatly enlarged caniniform teeth possessing serrated edges in the premaxilla
Premaxilla
The incisive bone is the portion of the maxilla adjacent to the incisors. It is a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the jaws of many animals, usually bearing teeth, but not always. They are connected to the maxilla and the nasals....
and, to a lesser extent, the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
. The length of the premaxillary fang is greater than half the height of the skull. Modesto et Reisz (2008) note that "The large size of the first premaxillary tooth is [otherwise] unheard of among early reptiles." The taxon also possesses unusual "folding" of the dentine at the bases of its larger marginal teeth, a state known as polyplycodont (a condition also seen to have evolved independently in diadectomorphs
Diadectomorpha
Diadectomorpha are a clade of large reptile-like amphibians that lived in Euramerica during the Carboniferous and Early Permian periods, and are very close to the ancestry of the Amniota. They include both large carnivorous and even larger herbivorous forms, some semi-aquatic and others fully...
, ichthyosaurs, and mosasaurs). Modesto et Reisz (2008, p. 682) speculate that hard-shelled insects and other arthropods may have formed the bulk of its diet, but that Colobomycter could also have fed on vertebrates, including small amphibians and eureptiles. It is notable as the smallest predatory amniote from the Richard's Spur deposits, with a skull measuring a mere 70-80 millimeters in length.
External links
- Images of a maxilla of Colobomycter pholeter from the Richard's Spur locality.

