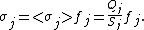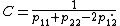Coefficients of potential
Encyclopedia
In electrostatics
, the coefficients of potential determine the relationship between the charge
and electrostatic potential (electrical potential), which is purely geometric: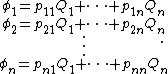
where Qi is the surface charge on conductor i. The coefficients of potential are the coefficients pij. φi should be correctly read as the potential due to charge 1, and hence "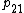 " is the p due to charge 2 on charge 1.
" is the p due to charge 2 on charge 1.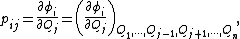
or more formally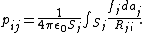
Note that:
The physical content of the symmetry is as follows:
In general, the coefficients is used when describing system of conductors, such as in the capacitor
.
or the point P chosen on surface i) contained in a system of conductors j = 1, 2, ..., n: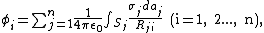
where Rji = |ri - rj|, i.e. the distance from the area-element daj to a particular point ri on conductor i. σj is not, in general, uniformly distributed across the surface. Let us introduce the factor fj that describes how the actual charge density differs from the average and itself on a position on the surface of the j-th conductor: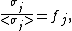
or
Then,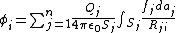
can be written in the form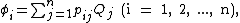
i.e.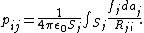
For a two-conductor system, the system of linear equations is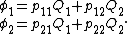
On a capacitor
, the charge on the two conductors is equal and opposite: Q = Q1 = -Q2. Therefore,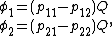
and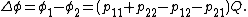
Hence,
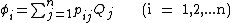
can be inverted to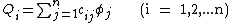
where cii is called the coefficients of capacitance and the cij with i ≠ j is called the coefficients of induction.
The capacitance
of this system can be expressed as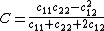
(the system of conductors can be shown to have similar symmetry cij = cji.)
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is the branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges....
, the coefficients of potential determine the relationship between the charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
and electrostatic potential (electrical potential), which is purely geometric:
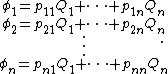
where Qi is the surface charge on conductor i. The coefficients of potential are the coefficients pij. φi should be correctly read as the potential due to charge 1, and hence "
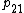 " is the p due to charge 2 on charge 1.
" is the p due to charge 2 on charge 1.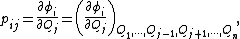
or more formally
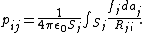
Note that:
- pij = pji, by symmetry, and
- pij is not dependent on the charge,
The physical content of the symmetry is as follows:
- if a charge Q on conductor j brings conductor i to a potential φ, then the same charge placed on i would bring j to the same potential φ.
In general, the coefficients is used when describing system of conductors, such as in the capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
.
Theory
Given the electrical potential on a conductor surface Si (the equipotential surfaceEquipotential surface
Equipotential surfaces are surfaces of constant scalar potential. They are used to visualize an -dimensional scalar potential function in dimensional space...
or the point P chosen on surface i) contained in a system of conductors j = 1, 2, ..., n:
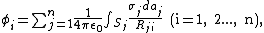
where Rji = |ri - rj|, i.e. the distance from the area-element daj to a particular point ri on conductor i. σj is not, in general, uniformly distributed across the surface. Let us introduce the factor fj that describes how the actual charge density differs from the average and itself on a position on the surface of the j-th conductor:
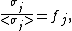
or
Then,
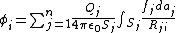
can be written in the form
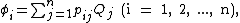
i.e.
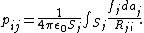
Example
In this example, we employ the method of coefficients of potential to determine the capacitance on a two-conductor system.For a two-conductor system, the system of linear equations is
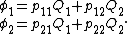
On a capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
, the charge on the two conductors is equal and opposite: Q = Q1 = -Q2. Therefore,
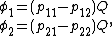
and
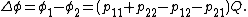
Hence,
Related coefficients
Note that the array of linear equations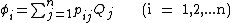
can be inverted to
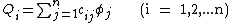
where cii is called the coefficients of capacitance and the cij with i ≠ j is called the coefficients of induction.
The capacitance
Capacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
of this system can be expressed as
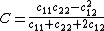
(the system of conductors can be shown to have similar symmetry cij = cji.)