
Cluster expansion
Encyclopedia
In statistical mechanics, the cluster expansion (also called the high temperature expansion or hopping expansion) is a power series expansion of the partition function
of a statistical field theory around a model that is a union of non-interacting 0-dimensional field theories. Cluster expansions originated in the work of . Unlike the usual perturbation expansion, it converges in some non-trivial regions, in particular when the interaction is small.
partition function. For N noninteracting particles, the system is described by the Hamiltonian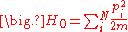 ,
,
and the partition function can be calculated (for the classical case) as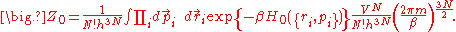
From the partition function, one can calculate the Helmholtz free energy
 and, from that, all the thermodynamic properties of the system, like the entropy
and, from that, all the thermodynamic properties of the system, like the entropy
, the internal energy, the chemical potential
etc.
When the particles of the system interact, an exact calculation of the partition function is usually not possible. For low density, the interactions can be approximated with
a sum of two - particle potentials: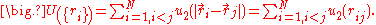
For this interaction potential, the partition function can be written as
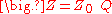 ,
,
and the free energy is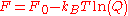 ,
,
where Q is the configuration integral: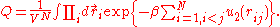
 cannot be calculated analytically for a general pair potential
cannot be calculated analytically for a general pair potential
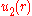 . One way to calculate the potential approximately is to use the Mayer cluster expansion. This expansion is based on the observation that the exponential in the equation for
. One way to calculate the potential approximately is to use the Mayer cluster expansion. This expansion is based on the observation that the exponential in the equation for  can be written as a product of the form
can be written as a product of the form .
.
Next, define the Mayer function by
by 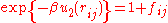 . After substitution, the equation for the configuration integral becomes:
. After substitution, the equation for the configuration integral becomes:
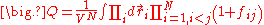
The calculation of the product in the above equation leads into a series of terms; the first is equal to one, the second term is equal to the sum over i and j of the terms , and the process continues until all the higher order terms are calculated.
, and the process continues until all the higher order terms are calculated.
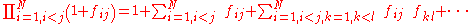
With this expansion it is possible to find terms of different order, in terms of the number of particles that are involved. The first term is the single particle term, the second term corresponds to the two particle interactions, the third to the three particle interactions, and so on. This physical interpretation is the reason this expansion is called the cluster expansion; each term represents the interactions within clusters of a certain number of particles.
Substituting the expansion of the product back into the expression for the configuration integral results in a series expansion for :
:
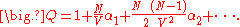
Substituting in the equation for the free energy, it is possible to derive
the equation of state
for the system of interacting particles. The equation will have the form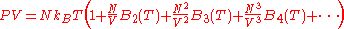 ,
,
which is known as the Virial equation, and the components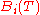 are the Virial coefficients.
are the Virial coefficients.
Each of the virial coefficients corresponds to one term from the cluster expansion (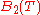 is the two particle interaction term,
is the two particle interaction term, 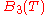 is the three particle interaction term and so on).
is the three particle interaction term and so on).
Keeping only the two particle interaction term, it can be shown that the cluster expansion, some approximations, gives the Van der Waals equation
.
Partition function (statistical mechanics)
Partition functions describe the statistical properties of a system in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is a function of temperature and other parameters, such as the volume enclosing a gas...
of a statistical field theory around a model that is a union of non-interacting 0-dimensional field theories. Cluster expansions originated in the work of . Unlike the usual perturbation expansion, it converges in some non-trivial regions, in particular when the interaction is small.
General Theory
In statistical mechanics, the properties of a system of interacting particles are described using thepartition function. For N noninteracting particles, the system is described by the Hamiltonian
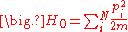 ,
,and the partition function can be calculated (for the classical case) as
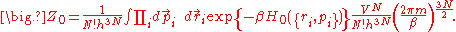
From the partition function, one can calculate the Helmholtz free energy
Helmholtz free energy
In thermodynamics, the Helmholtz free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the “useful” work obtainable from a closed thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and volume...
 and, from that, all the thermodynamic properties of the system, like the entropy
and, from that, all the thermodynamic properties of the system, like the entropyEntropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
, the internal energy, the chemical potential
Chemical potential
Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system...
etc.
When the particles of the system interact, an exact calculation of the partition function is usually not possible. For low density, the interactions can be approximated with
a sum of two - particle potentials:
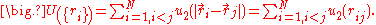
For this interaction potential, the partition function can be written as
 ,
,and the free energy is
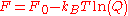 ,
,where Q is the configuration integral:
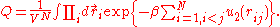
Calculation of the configuration integral
The configuration integral cannot be calculated analytically for a general pair potential
cannot be calculated analytically for a general pair potential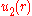 . One way to calculate the potential approximately is to use the Mayer cluster expansion. This expansion is based on the observation that the exponential in the equation for
. One way to calculate the potential approximately is to use the Mayer cluster expansion. This expansion is based on the observation that the exponential in the equation for  can be written as a product of the form
can be written as a product of the form .
.Next, define the Mayer function
 by
by 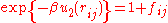 . After substitution, the equation for the configuration integral becomes:
. After substitution, the equation for the configuration integral becomes: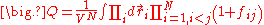
The calculation of the product in the above equation leads into a series of terms; the first is equal to one, the second term is equal to the sum over i and j of the terms
 , and the process continues until all the higher order terms are calculated.
, and the process continues until all the higher order terms are calculated.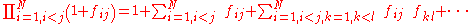
With this expansion it is possible to find terms of different order, in terms of the number of particles that are involved. The first term is the single particle term, the second term corresponds to the two particle interactions, the third to the three particle interactions, and so on. This physical interpretation is the reason this expansion is called the cluster expansion; each term represents the interactions within clusters of a certain number of particles.
Substituting the expansion of the product back into the expression for the configuration integral results in a series expansion for
 :
: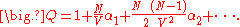
Substituting in the equation for the free energy, it is possible to derive
the equation of state
Equation of state
In physics and thermodynamics, an equation of state is a relation between state variables. More specifically, an equation of state is a thermodynamic equation describing the state of matter under a given set of physical conditions...
for the system of interacting particles. The equation will have the form
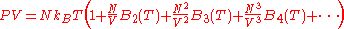 ,
,which is known as the Virial equation, and the components
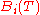 are the Virial coefficients.
are the Virial coefficients.Each of the virial coefficients corresponds to one term from the cluster expansion (
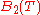 is the two particle interaction term,
is the two particle interaction term, 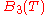 is the three particle interaction term and so on).
is the three particle interaction term and so on).Keeping only the two particle interaction term, it can be shown that the cluster expansion, some approximations, gives the Van der Waals equation
Van der Waals equation
The van der Waals equation is an equation of state for a fluid composed of particles that have a non-zero volume and a pairwise attractive inter-particle force It was derived by Johannes Diderik van der Waals in 1873, who received the Nobel prize in 1910 for "his work on the equation of state for...
.

