
Cleanroom
Encyclopedia





Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
or scientific research, that has a low level of environmental pollutant
Pollutant
A pollutant is a waste material that pollutes air, water or soil, and is the cause of pollution.Three factors determine the severity of a pollutant: its chemical nature, its concentration and its persistence. Some pollutants are biodegradable and therefore will not persist in the environment in the...
s such as dust, airborne microbes, aerosol particles and chemical vapors. More accurately, a cleanroom has a controlled level of contamination that is specified by the number of particles per cubic meter at a specified particle size. To give perspective, the ambient air outside in a typical urban environment contains 35,000,000 particles per cubic meter in the size range 0.5 μm
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
and larger in diameter, corresponding to an ISO 9 cleanroom, while an ISO 1 cleanroom allows no particles in that size range and only 12 particles per cubic meter of 0.3 μm and smaller (see table below).
Overview
Cleanrooms can be very large. Entire manufacturing facilities can be contained within a cleanroom with factory floors covering thousands of square meters. They are used extensively in semiconductor manufacturing, biotechnologyBiotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
, the life sciences
Life sciences
The life sciences comprise the fields of science that involve the scientific study of living organisms, like plants, animals, and human beings. While biology remains the centerpiece of the life sciences, technological advances in molecular biology and biotechnology have led to a burgeoning of...
and other fields that are very sensitive to environmental contamination.
The air entering a cleanroom from outside is filtered to exclude dust, and the air inside is constantly recirculated through high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA
HEPA
High-Efficiency Particulate Air or HEPA is a type of air filter. Filters that are awarded the HEPA accolade are used in various locations, whether in medical facilities, automotive vehicles, airplanes, home filters, or wherever very pure air is sought. The filter must satisfy certain standards of...
) and/or ultra-low penetration air (ULPA
ULPA
ULPA is an acronym for "ultra-low penetration air". An ULPA filter can remove from the air at least 99.999% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria and any airborne particles with a size of 120 nanometres or larger...
) filters to remove internally generated contaminants.
Staff enter and leave through airlock
Airlock
An airlock is a device which permits the passage of people and objects between a pressure vessel and its surroundings while minimizing the change of pressure in the vessel and loss of air from it...
s (sometimes including an air shower
Air shower (room)
The term air shower can refer to the specialized antechamber which is passed through before entering a cleanroom in order to blow off excess dust particles from cleanroom personnel before they enter, to minimize contamination...
stage), and wear protective clothing such as hoods, face masks, gloves, boots and coveralls.
Equipment inside the cleanroom is designed to generate minimal air contamination. Even specialised mop
Mop
A mop is a mass or bundle of coarse strings or yarn, etc., or a piece of cloth, sponge, or other absorbent material, attached to a pole or stick. It is used to soak up liquid, for cleaning floors and other surfaces, or to mop up dust, or for other cleaning purposes...
s and bucket
Bucket
A bucket, also called a pail, is typically a watertight, vertical cylinder or truncated cone, with an open top and a flat bottom, usually attached to a semicircular carrying handle called the bail. A pail can have an open top or can have a lid....
s exist. Cleanroom furniture is also designed to produce a minimum of particles and to be easy to clean.
Common materials such as paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
, pencil
Pencil
A pencil is a writing implement or art medium usually constructed of a narrow, solid pigment core inside a protective casing. The case prevents the core from breaking, and also from marking the user’s hand during use....
s, and fabric
Textile
A textile or cloth is a flexible woven material consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibres often referred to as thread or yarn. Yarn is produced by spinning raw fibres of wool, flax, cotton, or other material to produce long strands...
s made from natural fibers are often excluded; however, alternatives are available. Cleanrooms are not sterile
Sterilization (microbiology)
Sterilization is a term referring to any process that eliminates or kills all forms of microbial life, including transmissible agents present on a surface, contained in a fluid, in medication, or in a compound such as biological culture media...
(i.e., free of uncontrolled microbes) and more attention is given to airborne particles. Particle levels are usually tested using a particle counter
Particle counter
A particle counter is an instrument that detects and counts particles. By its very nature a particle counter is a single particle counter, meaning it detects and counts particles one at a time. The nature of particle counting is based upon either light scattering or light obscuration...
.
Some cleanrooms are kept at a positive pressure
Positive pressure
Positive pressure is a pressure within a system that is greater than the environment that surrounds that system. Consequently if there is any leak from the positively pressured system it will egress into the surrounding environment....
so that if there are any leaks, air leaks out of the chamber instead of unfiltered air coming in.
Some cleanroom HVAC
HVAC
HVAC refers to technology of indoor or automotive environmental comfort. HVAC system design is a major subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer...
systems control the humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
to low levels, such that extra equipment ("ionizers") are necessary to prevent electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic discharge is a serious issue in solid state electronics, such as integrated circuits. Integrated circuits are made from semiconductor materials such as silicon and insulating materials such as silicon dioxide...
(ESD) problems.
Low-level cleanrooms may only require special shoes, ones with completely smooth soles that do not track in dust or dirt. However, shoe bottoms must not create slipping hazards (safety always takes precedence). Entering a cleanroom usually requires wearing a cleanroom suit
Cleanroom suit
A clean room suit, cleanroom suit, or bunny suit, is an overall garment worn in a clean room. One common type is an all-in-one coverall worn by semiconductor and nanotechnology line production workers, technicians, and process / equipment engineers, as well as people in similar roles creating...
.
In other cleanrooms, in which the standards of air contamination are less rigorous, the entrance to the cleanroom may not have an air shower. There is an anteroom (known as a "gray room"), in which the special suits must be put on, but then a person can walk in directly to the room (as seen in the photograph on the right).
Some manufacturing facilities do not use fully classified cleanrooms, but use some cleanroom practices together to maintain their cleanliness requirements.
Air flow principles
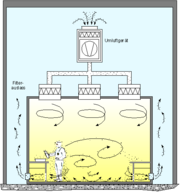 |
 |
Cleanrooms maintain particulate-free air through the use of either HEPA
HEPA
High-Efficiency Particulate Air or HEPA is a type of air filter. Filters that are awarded the HEPA accolade are used in various locations, whether in medical facilities, automotive vehicles, airplanes, home filters, or wherever very pure air is sought. The filter must satisfy certain standards of...
or ULPA
ULPA
ULPA is an acronym for "ultra-low penetration air". An ULPA filter can remove from the air at least 99.999% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria and any airborne particles with a size of 120 nanometres or larger...
filters employing laminar or turbulent air flow principles. Laminar, or unidirectional, air flow systems direct filtered air downward in a constant stream towards filters located on walls near the cleanroom floor or through raised perforated floor panels to be recirculated. Laminar air flow systems are typically employed across 80 percent of a cleanroom ceiling to maintain constant air processing. Stainless steel or other non-shed materials are used to construct laminar air flow filters and hoods to prevent excess particles entering the air. Turbulent, or non-unidirectional, air flow uses both laminar air flow hoods and non-specific velocity filters to keep air in a cleanroom in constant motion, although not all in the same direction. The rough air seeks to trap particles that may be in the air and drive them towards the floor, where they enter filters and leave the cleanroom environment.
Cleanroom classifications
Cleanrooms are classified according to the number and size of particles permitted per volume of air. Large numbers like "class 100" or "class 1000" refer to FED-STD-209EFED-STD-209E
FED-STD-209 E Airborne Particulate Cleanliness Classes in Cleanrooms and Cleanzones was canceled on November 29, 2001 by the U.S. General Services Administration...
, and denote the number of particles of size 0.5 µm or larger permitted per cubic foot of air. The standard also allows interpolation, so it is possible to describe e.g. "class 2000".
A discrete-particle-counting, light-scattering instrument is used to determine the concentration of airborne particles, equal to and larger than the specified sizes, at designated sampling locations.
Small numbers refer to ISO 14644-1 standards, which specify the decimal logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of the number of particles 0.1 µm or larger permitted per cubic metre of air. So, for example, an ISO class 5 cleanroom has at most 105 = 100,000 particles per m³.
Both FS 209E and ISO 14644-1 assume log-log relationships between particle size and particle concentration. For that reason, there is no such thing as zero particle concentration. The table locations without entries are non-applicable combinations of particle sizes and cleanliness classes, and should not be read as zero.
Because 1 m³ is approximately 35 ft³, the two standards are mostly equivalent when measuring 0.5 µm particles, although the testing standards differ. Ordinary room air is approximately class 1,000,000 or ISO 9.
US FED STD 209E cleanroom standards
| Class | maximum particles/ft³ | ISO equivalent |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥0.1 µm | ≥0.2 µm | ≥0.3 µm | ≥0.5 µm | ≥5 µm | ||
| 1 | 35 | 7 | 3 | 1 | ISO 3 | |
| 10 | 350 | 75 | 30 | 10 | ISO 4 | |
| 100 | 750 | 300 | 100 | ISO 5 | ||
| 1,000 | 1,000 | 7 | ISO 6 | |||
| 10,000 | 10,000 | 70 | ISO 7 | |||
| 100,000 | 100,000 | 700 | ISO 8 | |||
US FED STD 209E was officially cancelled by the General Services Administration of the US Department of Commerce November 29, 2001, but is still widely used.
ISO 14644-1 cleanroom standards
| Class | maximum particles/m³ | FED STD 209E equivalent |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥0.1 µm | ≥0.2 µm | ≥0.3 µm | ≥0.5 µm | ≥1 µm | ≥5 µm | ||
| ISO 1 | 10 | 2 | |||||
| ISO 2 | 100 | 24 | 10 | 4 | |||
| ISO 3 | 1,000 | 237 | 102 | 35 | 8 | Class 1 | |
| ISO 4 | 10,000 | 2,370 | 1,020 | 352 | 83 | Class 10 | |
| ISO 5 | 100,000 | 23,700 | 10,200 | 3,520 | 832 | 29 | Class 100 |
| ISO 6 | 1,000,000 | 237,000 | 102,000 | 35,200 | 8,320 | 293 | Class 1000 |
| ISO 7 | 352,000 | 83,200 | 2,930 | Class 10,000 | |||
| ISO 8 | 3,520,000 | 832,000 | 29,300 | Class 100,000 | |||
| ISO 9 | 35,200,000 | 8,320,000 | 293,000 | Room air | |||
BS 5295 cleanroom standards
| maximum particles/m³ | ||||||
| Class | ≥0.5 µm | ≥1 µm | ≥5 µm | ≥10 µm | ≥25 µm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 3,000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Class 2 | 300,000 | 2,000 | 30 | |||
| Class 3 | 1,000,000 | 20,000 | 4,000 | 300 | ||
| Class 4 | 200,000 | 40,000 | 4,000 | |||
BS 5295 Class 1 also requires that the greatest particle present in any sample does not exceed 5 μm.
GMP EU classification
| Class | maximum particles/m³ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| under equipped conditions | under equipped conditions | under working conditions | under working conditions | |
| 0.5 µm | 5 µm | 0.5 µm | 5 µm | |
| Class A | 3500 | 0 | 3500 | 0 |
| Class B | 3500 | 0 | 350000 | 2000 |
| Class C | 350000 | 2000 | 3500000 | 20000 |
| Class D | 3500000 | 20000 | n/a | n/a |
See also
- Air Quality IndexAir Quality IndexAir quality is defined as a measure of the condition of air relative to the requirements of one or more biotic species or to any human need or purpose. Air quality indices are numbers used by government agencies to characterize the quality of the air at a given location...
- Cleanroom (pharmaceutical)
- Cleanroom safety
- Clean room worker
- Data recovery lab
- Secure environmentSecure environmentIn computing, a secure environment is any system which implements the controlled storage and use of information. In the event of computing data loss, a secure environment is used to protect personal and/or confidential data....
- Sterile Quality Index
- ISO 14644ISO 14644ISO 14644 Standards were first formed from the US Federal Standard 209E Airborne Particulate Cleanliness Classes in Cleanrooms and Clean Zones. The need for a single standard for cleanroom classification and testing was long felt...
- ISO 14698ISO 14698The ISO 14698 Standards features two International Standards on Biocontamination control. IEST, the Secretariat and Administrator of ISO Technical Committee 209, helped develop this series of ISO 14698 Standards....
- Contamination controlContamination controlContamination control is the generic term for all activities aiming to control the existence, growth and proliferation of contamination in certain areas...
- Pneumatic filterPneumatic filterA pneumatic filter is a device which removes contaminants from a compressed air stream. This can be done using a number of different techniques, from using a "media" type that traps particulates, but allows air to pass through to a venturi, to a membrane that only allows air to pass through.-...
- Semiconductor device fabrication
- Sterile room

