
Cirth
Encyclopedia
The Cirth are the letters of an semi-artificial script which was invented by J. R. R. Tolkien
for the constructed language
s he devised and used in his works. The initial C in Cirth is pronounced as a K, never as an S.
The runic alphabet used by the Dwarves
of Middle-earth was adapted by J.R.R. Tolkien from real-life runes. In The Hobbit
, the Anglo-Saxon futhorc
was used in the publication with few changes; in The Lord of the Rings
a new system of runes, the Cirth, was devised.
Since the Cirth is an alphabet, one rune generally stands for one sound (phoneme
) and sounds that would be written with a digraph
in English (such as "sh" and "th") are written with one rune. Words are separated by a dot rather than a space, and double consonants are grouped together into one rune, the same as if it were a single consonant. Presumably this alphabet was meant to be used in conjunction with a Dwarf language, but mostly it is used for transliterations.
In the fictional history of Middle-earth
, the original Certhas Daeron was created by the elf
Daeron, the minstrel
of king Thingol
of Doriath
and was later expanded into what was known as the Angerthas Daeron. Although the Cirth were later largely replaced by the Tengwar
(which were enhanced and brought by Fëanor
), they were adopted by Dwarves
to write down their Khuzdul language (Angerthas Moria and Angerthas Erebor) because their straight lines were better suited to carving than the curved strokes of the Tengwar. Some examples of Cirth writings are the inscription on Balin's
tomb in Moria
and the inscriptions on the top of the title pages for The Lord of the Rings
. Cirth was also adapted, in its older and simpler form, by various kinds of Men
and even Orcs
. For example, it was used by the Men of Dale and the Rohirrim and the Orcs of Moria.
Cirth is plural and is written with a capital C when referring to the writing system—the runes themselves can be called cirth. A single rune is a certh.
Many letters have shapes also found in the historical futhorc
runes (used in The Hobbit
), but their sound values are dissimilar. Rather, the system of assignment of sound values is much more systematic in the Cirth than in the historical runes (e.g., voiced variants of a voiceless sound are expressed by an additional stroke). A similar system has been proposed for a few historical runes (e.g. p ᛈ and w ᚹ as variants of b ᛒ), but is in any case much more obscure. There are a few coincidental identities between cirth and runic letters, i with runic ᛁ, k with Younger Futhark ᚴ and ch with the Futhorc ᚳ; p is furthermore reminiscent of Latin P (runic ᚹ w).
Cirth is written according to a certain mode specifically adapted for a language, and the values of individual certh may vary greatly according to the mode used. Three modes for Cirth are described in detail in Appendix E of The Lord of the Rings
, and others are known to exist or have been developed by enthusiasts.
The Cirth are not yet part of the Unicode
Standard. However the ConScript Unicode Registry
has defined the to U+E0FF range of the Unicode "Private Use Area" for Cirth.
The Angerthas Daeron consists of 60 letters:
This chart showing the runes shared by the Angerthas Daeron and Angerthas Moria is presented in Appendix E of The Return of the King
. Some of the cirth had different values for the Elvish and Dwarvish
languages and some were used in only one system or the other. Where two values are given connected with a hyphen, the first is that of the older Angerthas, the second that of the dwarvish Angerthas Moria. Letters with asterisk are dwarvish only, values in brackets elvish only.
J. R. R. Tolkien
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien, CBE was an English writer, poet, philologist, and university professor, best known as the author of the classic high fantasy works The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Silmarillion.Tolkien was Rawlinson and Bosworth Professor of Anglo-Saxon at Pembroke College,...
for the constructed language
Constructed language
A planned or constructed language—known colloquially as a conlang—is a language whose phonology, grammar, and/or vocabulary has been consciously devised by an individual or group, instead of having evolved naturally...
s he devised and used in his works. The initial C in Cirth is pronounced as a K, never as an S.
The runic alphabet used by the Dwarves
Dwarf (Middle-earth)
In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Dwarves are a race inhabiting the world of Arda, a fictional prehistoric Earth which includes the continent Middle-earth....
of Middle-earth was adapted by J.R.R. Tolkien from real-life runes. In The Hobbit
The Hobbit
The Hobbit, or There and Back Again, better known by its abbreviated title The Hobbit, is a fantasy novel and children's book by J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published on 21 September 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the New York Herald...
, the Anglo-Saxon futhorc
Anglo-Saxon Futhorc
Futhorc , a runic alphabet used by the Anglo-Saxons, was descended from the Elder Futhark of 24 runes and contained between 26 and 33 characters. It was used probably from the fifth century onward, for recording Old English and Old Frisian....
was used in the publication with few changes; in The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings is a high fantasy epic written by English philologist and University of Oxford professor J. R. R. Tolkien. The story began as a sequel to Tolkien's earlier, less complex children's fantasy novel The Hobbit , but eventually developed into a much larger work. It was written in...
a new system of runes, the Cirth, was devised.
Since the Cirth is an alphabet, one rune generally stands for one sound (phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
) and sounds that would be written with a digraph
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph or digram is a pair of characters used to write one phoneme or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined...
in English (such as "sh" and "th") are written with one rune. Words are separated by a dot rather than a space, and double consonants are grouped together into one rune, the same as if it were a single consonant. Presumably this alphabet was meant to be used in conjunction with a Dwarf language, but mostly it is used for transliterations.
In the fictional history of Middle-earth
Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of the majority of author J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy writings. The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings take place entirely in Middle-earth, as does much of The Silmarillion and Unfinished Tales....
, the original Certhas Daeron was created by the elf
Elf (Middle-earth)
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, Elves are one of the races that inhabit a fictional Earth, often called Middle-earth, and set in the remote past. They appear in The Hobbit and in The Lord of the Rings, but their complex history is described more fully in The Silmarillion...
Daeron, the minstrel
Minstrel
A minstrel was a medieval European bard who performed songs whose lyrics told stories of distant places or of existing or imaginary historical events. Although minstrels created their own tales, often they would memorize and embellish the works of others. Frequently they were retained by royalty...
of king Thingol
Thingol
Elu Thingol is a fictional character in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He appears in The Silmarillion, The Lays of Beleriand and Children of Húrin as well as in numerous stories in the many volumes of The History of Middle-earth...
of Doriath
Doriath
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional Middle-earth, Doriath is the realm of the Sindar, the Grey Elves of King Thingol in Beleriand. Along with the other great forests of Tolkien's legendarium such as Mirkwood, Fangorn and Lothlórien it serves as the central stage in the theatre of its time, the First Age...
and was later expanded into what was known as the Angerthas Daeron. Although the Cirth were later largely replaced by the Tengwar
Tengwar
The Tengwar are an artificial script created by J. R. R. Tolkien. In his fictional universe of Middle-earth, the tengwar were invented by the Elf Fëanor, and used first to write the Elven tongues: Quenya, Telerin, and also Valarin. Later a great number of languages of Middle-earth were written...
(which were enhanced and brought by Fëanor
Fëanor
Fëanor is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium who plays an important part in The Silmarillion. He was the eldest son of Finwë, the High King of the Noldor, and his first wife Míriel Serindë...
), they were adopted by Dwarves
Dwarf (Middle-earth)
In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Dwarves are a race inhabiting the world of Arda, a fictional prehistoric Earth which includes the continent Middle-earth....
to write down their Khuzdul language (Angerthas Moria and Angerthas Erebor) because their straight lines were better suited to carving than the curved strokes of the Tengwar. Some examples of Cirth writings are the inscription on Balin's
Balin (Middle-earth)
Balin is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. He is an important supporting character in The Hobbit, and is mentioned in The Fellowship of the Ring.-In the books:...
tomb in Moria
Moria (Middle-earth)
In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, Moria was the name given by the Eldar to an enormous underground complex in north-western Middle-earth, comprising a vast network of tunnels, chambers, mines and huge halls or 'mansions', that ran under and ultimately through the Misty Mountains...
and the inscriptions on the top of the title pages for The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings is a high fantasy epic written by English philologist and University of Oxford professor J. R. R. Tolkien. The story began as a sequel to Tolkien's earlier, less complex children's fantasy novel The Hobbit , but eventually developed into a much larger work. It was written in...
. Cirth was also adapted, in its older and simpler form, by various kinds of Men
Man (Middle-earth)
The race of Men in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth books, such as The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings, refers to humanity and does not denote gender...
and even Orcs
Orc (Middle-earth)
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy writings, Orcs or Orks are a race of creatures who are used as soldiers and henchmen by both the greater and lesser villains of The Silmarillion and The Lord of the Rings — Morgoth, Sauron and Saruman...
. For example, it was used by the Men of Dale and the Rohirrim and the Orcs of Moria.
Cirth is plural and is written with a capital C when referring to the writing system—the runes themselves can be called cirth. A single rune is a certh.
Many letters have shapes also found in the historical futhorc
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
runes (used in The Hobbit
The Hobbit
The Hobbit, or There and Back Again, better known by its abbreviated title The Hobbit, is a fantasy novel and children's book by J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published on 21 September 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the New York Herald...
), but their sound values are dissimilar. Rather, the system of assignment of sound values is much more systematic in the Cirth than in the historical runes (e.g., voiced variants of a voiceless sound are expressed by an additional stroke). A similar system has been proposed for a few historical runes (e.g. p ᛈ and w ᚹ as variants of b ᛒ), but is in any case much more obscure. There are a few coincidental identities between cirth and runic letters, i with runic ᛁ, k with Younger Futhark ᚴ and ch with the Futhorc ᚳ; p is furthermore reminiscent of Latin P (runic ᚹ w).
Cirth is written according to a certain mode specifically adapted for a language, and the values of individual certh may vary greatly according to the mode used. Three modes for Cirth are described in detail in Appendix E of The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings is a high fantasy epic written by English philologist and University of Oxford professor J. R. R. Tolkien. The story began as a sequel to Tolkien's earlier, less complex children's fantasy novel The Hobbit , but eventually developed into a much larger work. It was written in...
, and others are known to exist or have been developed by enthusiasts.
The Cirth are not yet part of the Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard. However the ConScript Unicode Registry
ConScript Unicode Registry
The ConScript Unicode Registry is a volunteer project to coordinate the assignment of code points in the Unicode Private Use Area for the encoding of artificial scripts. It was founded by and is maintained by John Cowan and Michael Everson...
has defined the to U+E0FF range of the Unicode "Private Use Area" for Cirth.
The Angerthas Daeron consists of 60 letters:
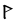 |
p | 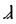 |
zh | 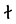 |
l | 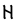 |
e |
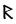 |
b |  |
nj-z | 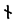 |
lh |  |
ē |
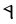 |
f | 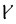 |
k | 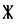 |
ng–nd | 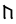 |
a |
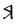 |
v | 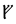 |
g |  |
s–h | 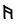 |
ā |
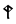 |
hw | 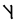 |
kh | 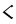 |
s–’ |  |
o |
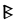 |
m | 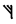 |
gh |  |
z–ŋ | 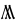  |
ō |
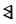 |
(mh), mb |  |
ŋ–n |  |
ng* | 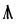 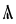 |
ö |
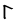 |
t |  |
kw | 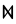 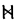 |
nd–nj |  |
n* |
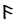 |
d | 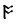 |
gw |  |
i, (y) |  |
h–s |
 |
th | 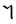 |
khw |  |
y* | 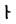 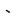 |
* |
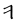 |
dh | 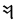 |
ghw, w |  |
hy* |  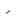 |
* |
 |
n–r | 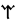 |
ngw | 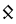 |
u |  |
ps* |
 |
ch | 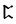 |
nw |  |
ū | 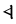 |
ts* |
 |
j |  |
r–j |  |
w |  |
+h |
 |
sh |  |
rh–zh | 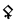  |
ü | 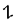 |
& |
This chart showing the runes shared by the Angerthas Daeron and Angerthas Moria is presented in Appendix E of The Return of the King
The Return of the King
The Return of the King is the third and final volume of J. R. R. Tolkien's The Lord of the Rings, following The Fellowship of the Ring and The Two Towers.-Title:...
. Some of the cirth had different values for the Elvish and Dwarvish
Khuzdul
Khuzdul is a constructed language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien. It is one of the many fictional language set in his Secondary world, often called Middle-earth...
languages and some were used in only one system or the other. Where two values are given connected with a hyphen, the first is that of the older Angerthas, the second that of the dwarvish Angerthas Moria. Letters with asterisk are dwarvish only, values in brackets elvish only.
External links
- Article on Tolkien's Cirthic runes
- Cirth.de - Explore the appearances of runes in Tolkien's work (in German)
- Dan Smith's Cirth article Information and font to download
- History of Elven writing systems
- Official proposal to encode Cirth in Unicode
- Cirth proposal for ConScript Unicode Registry
- Generator for Cirth Runes and Tengwar

