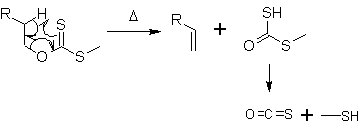Chugaev elimination
Encyclopedia
The Chugaev elimination is a chemical reaction that involves the elimination of water from alcohol
s to produce alkene
s. The intermediate is a xanthate
. It is named for its discoverer, the Russian chemist Lev Aleksandrovich Chugaev
.
In the first step, a potassium xanthate is formed out of the alkoxide
and carbon disulfide
(CS2). With iodomethane
, it is transformed into a xanthate
.
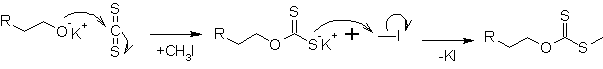
At about 200 °C, the alkene is formed by a syn-elimination
. In a 6-membered cyclic transition state the hydrogen atom is moved from the β-C-atom to the sulfur. The side product decomposes to carbonyl sulfide
(OCS) and methanethiol
.
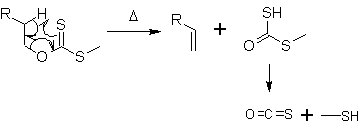
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
s to produce alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
s. The intermediate is a xanthate
Xanthate
Xanthate usually refers to a salt with the formula ROCS2-M+ . The name xanthates is derived from Greek ξανθός , meaning “yellowish, golden”, and indeed most xanthate salts are yellow...
. It is named for its discoverer, the Russian chemist Lev Aleksandrovich Chugaev
Lev Aleksandrovich Chugaev
Lev Aleksandrovich Chugaev was a Russian chemist. The Chugaev reaction, which he discovered during his work on thujene an terpene, is named after him. He was also active in the field of inorganic chemistry especially Platinum group complexes.In literature he is also known as Leo Aleksandrovich...
.
In the first step, a potassium xanthate is formed out of the alkoxide
Alkoxide
An alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They can be written as RO−, where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands...
and carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide is a colorless volatile liquid with the formula CS2. The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non-polar solvent...
(CS2). With iodomethane
Iodomethane
Methyl iodide, also called iodomethane, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally...
, it is transformed into a xanthate
Xanthate
Xanthate usually refers to a salt with the formula ROCS2-M+ . The name xanthates is derived from Greek ξανθός , meaning “yellowish, golden”, and indeed most xanthate salts are yellow...
.
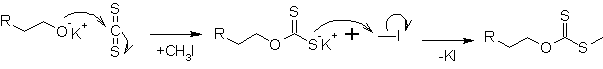
At about 200 °C, the alkene is formed by a syn-elimination
Elimination reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two-step mechanism...
. In a 6-membered cyclic transition state the hydrogen atom is moved from the β-C-atom to the sulfur. The side product decomposes to carbonyl sulfide
Carbonyl sulfide
Carbonyl sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula OCS. Commonly written as COS, it is a colourless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. It is a linear molecule consisting of a carbonyl group double bonded to a sulfur atom...
(OCS) and methanethiol
Methanethiol
Methanethiol is a colorless gas with a smell like rotten cabbage. It is a natural substance found in the blood and brain of humans and other animal as well as plant tissues. It is disposed of through animal feces. It occurs naturally in certain foods, such as some nuts and cheese...
.