
Chrysanthemic acid
Encyclopedia
Chrysanthemic acid is an organic compound
that is related to a variety of natural and synthetic insecticide
s. It is related to the pyrethrin
I and II, as well as the pyrethroid
s. One of the four stereoisomers, (1R,3R)- or (+)-trans-chrysanthemic acid (pictured), is the acid-derived group of pyrethrin I
, which occurs naturally in the seed cases of Chrysanthemum
cinerariaefolium. Many synthetic pyrethroids, for example the allethrin
s, are esters of all four stereoisomers.
ester, which in turn is produced naturally
from dimethylallyl diphosphate.
as a mixture of cis- and trans isomers, followed by hydrolysis of the ester:
 Many pyrethroids are accessible by re-esterification of crysanthemic acid ethylester.
Many pyrethroids are accessible by re-esterification of crysanthemic acid ethylester.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
that is related to a variety of natural and synthetic insecticide
Insecticide
An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and the household. The use of insecticides is believed to be one of the major factors behind...
s. It is related to the pyrethrin
Pyrethrin
The pyrethrins are a pair of natural organic compounds that have potent insecticidal activity. Pyrethrins are neurotoxins that attack the nervous systems of all insects. When present in amounts not fatal to insects, they still appear to have an insect repellent effect. Pyrethrins are gradually...
I and II, as well as the pyrethroid
Pyrethroid
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins produced by the flowers of pyrethrums . Pyrethroids now constitute a major commercial household insecticides...
s. One of the four stereoisomers, (1R,3R)- or (+)-trans-chrysanthemic acid (pictured), is the acid-derived group of pyrethrin I
Pyrethrin I
Pyrethrin I is one of the two pyrethrins, natural organic compounds with potent insecticidal activity. It is an ester of -trans-chrysanthemic acid with --pyrethrolone.- Total synthesis:...
, which occurs naturally in the seed cases of Chrysanthemum
Chrysanthemum
Chrysanthemums, often called mums or chrysanths, are of the genus constituting approximately 30 species of perennial flowering plants in the family Asteraceae which is native to Asia and northeastern Europe.-Etymology:...
cinerariaefolium. Many synthetic pyrethroids, for example the allethrin
Allethrin
The allethrins are a pair of related synthetic compounds used in insecticides. They are synthetic pyrethroids, a synthetic form of a chemical found naturally in the chrysanthemum flower. They were first synthesized in the United States by Milton S. Schechter in 1949...
s, are esters of all four stereoisomers.
Biosynthesis
Chrysanthemic acid is derived from its pyrophosphatePyrophosphate
In chemistry, the anion, the salts, and the esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates. Any salt or ester containing two phosphate groups is called a diphosphate. As a food additive, diphosphates are known as E450.- Chemistry :...
ester, which in turn is produced naturally
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
from dimethylallyl diphosphate.
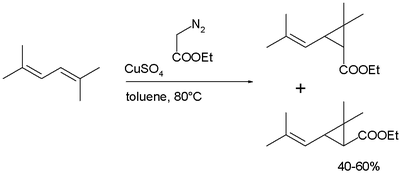
Synthesis
Chrysanthemic acid is produced industrially in a cyclopropanation reaction of a dieneDiene
In organic chemistry a diene or diolefin is a hydrocarbon that contains two carbon double bonds.Conjugated dienes are functional groups, with a general formula of CnH2n-2. Dienes and alkynes are functional isomers...
as a mixture of cis- and trans isomers, followed by hydrolysis of the ester:


