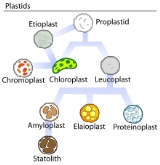
Chromoplast
Encyclopedia
Chromoplasts are plastid
s responsible for pigment
synthesis and storage. They, like all other plastids (including chloroplast
s and leucoplast
s), are organelle
s found in specific photosynthetic eukaryotic species.
Chromoplasts in the traditional sense are the interior found in coloured organs of plants such as fruit and floral petals, to which they give their distinctive colors. This is always associated with a massive increase in the accumulation of carotenoid
pigments. The conversion of chloroplasts to chromoplasts in ripening is a classic example.
Chromoplasts synthesize and store pigments such as orange carotene
, yellow xanthophyll
s, and various other red pigments; as such, their color varies depending on what pigment they contain. The probable main evolutionary role of chromoplasts is to act as an attractant for pollinating animals (e.g., insects) or for seed dispersal via the eating of colored fruits. They allow the accumulation of large quantities of water-insoluble compounds in otherwise watery parts of plants. In chloroplasts, some carotenoids are also used as accessory pigments in photosynthesis
, where they act to increase the efficiency of chlorophyll in harvesting light energy. When leaves
change color in autumn, it is due to the loss of green chlorophyll
unmasking these carotenoids that are already present in the leaf. In this case, relatively little new carotenoids are produced. Therefore, the change in plastid
pigments associated with leaf senescence is somewhat different from the active conversion to chromoplasts observed in fruit and flowers.
The term "chromoplast" is occasionally utilized to include any plastid that has pigment, mostly to emphasize the contrast with the various types of leucoplast
s, which are those plastids that have no pigments. In this sense, chloroplast
s are a specific type of chromoplast. Still, "chromoplast" is more often used to denote those plastids with pigments other than chlorophyll.

Plastid
Plastids are major organelles found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cell...
s responsible for pigment
Pigment
A pigment is a material that changes the color of reflected or transmitted light as the result of wavelength-selective absorption. This physical process differs from fluorescence, phosphorescence, and other forms of luminescence, in which a material emits light.Many materials selectively absorb...
synthesis and storage. They, like all other plastids (including chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
s and leucoplast
Leucoplast
Leucoplasts are a category of plastid and as such are organelles found in plant cells. They are non-pigmented, in contrast to other plastids such as the chloroplast....
s), are organelle
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer....
s found in specific photosynthetic eukaryotic species.
Chromoplasts in the traditional sense are the interior found in coloured organs of plants such as fruit and floral petals, to which they give their distinctive colors. This is always associated with a massive increase in the accumulation of carotenoid
Carotenoid
Carotenoids are tetraterpenoid organic pigments that are naturally occurring in the chloroplasts and chromoplasts of plants and some other photosynthetic organisms like algae, some bacteria, and some types of fungus. Carotenoids can be synthesized fats and other basic organic metabolic building...
pigments. The conversion of chloroplasts to chromoplasts in ripening is a classic example.
Chromoplasts synthesize and store pigments such as orange carotene
Carotene
The term carotene is used for several related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but cannot be made by animals. Carotene is an orange photosynthetic pigment important for photosynthesis. Carotenes are all coloured to the human eye...
, yellow xanthophyll
Xanthophyll
Xanthophylls are yellow pigments that form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group. The name is from Greek xanthos + phyllon , due to their formation of the yellow band seen in early chromatography of leaf pigments...
s, and various other red pigments; as such, their color varies depending on what pigment they contain. The probable main evolutionary role of chromoplasts is to act as an attractant for pollinating animals (e.g., insects) or for seed dispersal via the eating of colored fruits. They allow the accumulation of large quantities of water-insoluble compounds in otherwise watery parts of plants. In chloroplasts, some carotenoids are also used as accessory pigments in photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
, where they act to increase the efficiency of chlorophyll in harvesting light energy. When leaves
Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
change color in autumn, it is due to the loss of green chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in almost all plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Its name is derived from the Greek words χλωρος, chloros and φύλλον, phyllon . Chlorophyll is an extremely important biomolecule, critical in photosynthesis, which allows plants to obtain energy from light...
unmasking these carotenoids that are already present in the leaf. In this case, relatively little new carotenoids are produced. Therefore, the change in plastid
Plastid
Plastids are major organelles found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cell...
pigments associated with leaf senescence is somewhat different from the active conversion to chromoplasts observed in fruit and flowers.
The term "chromoplast" is occasionally utilized to include any plastid that has pigment, mostly to emphasize the contrast with the various types of leucoplast
Leucoplast
Leucoplasts are a category of plastid and as such are organelles found in plant cells. They are non-pigmented, in contrast to other plastids such as the chloroplast....
s, which are those plastids that have no pigments. In this sense, chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
s are a specific type of chromoplast. Still, "chromoplast" is more often used to denote those plastids with pigments other than chlorophyll.
Compare

- PlastidPlastidPlastids are major organelles found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cell...
- ChloroplastChloroplastChloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
and etioplastEtioplastEtioplasts are chloroplasts that have not been exposed to light. They are usually found in flowering plants grown in the dark. If a plant is kept out of light for several days, its normal chloroplasts will actually convert into etioplasts. Etioplasts lack active pigment and can technically be... - Chromoplast
- LeucoplastLeucoplastLeucoplasts are a category of plastid and as such are organelles found in plant cells. They are non-pigmented, in contrast to other plastids such as the chloroplast....
- AmyloplastAmyloplastAmyloplasts are non-pigmented organelles found in some plant cells. They are responsible for the synthesis and storage of starch granules, through the polymerization of glucose. Amyloplasts also convert this starch back into sugar when the plant needs energy...
- ElaioplastElaioplastElaioplasts are a type of leucoplast that is specialized for the storage of lipids in plants. Elaioplasts house oil body deposits as rounded plastoglobuli, which are essentially fat droplets....
- ProteinoplastProteinoplastProteinoplasts are specialized organelles found only in plant cells. They contain crystalline bodies of protein and can be the sites of enzyme activity involving those proteins. Proteinoplasts are found in many seeds, such as brazil nuts and peanuts...
- Amyloplast
- Chloroplast
External links
- http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/C/chromoplast.html
- http://www.thefreedictionary.com/chromoplasts

