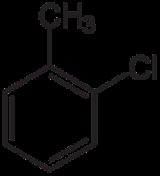
Chlorotoluene
Encyclopedia
Chlorotoluene can refer to any of four isomer
ic chemical compounds. Three isomers (ortho-chlorotoluene, meta-chlorotoluene, and para-chlorotoluene) consisist of a disubsituted benzene
ring with one chlorine atom and one methyl group
. The fourth isomer, alpha-chlorotoluene
(benzyl chloride), consists of toluene
with chlorine substitution on the methyl group.
, which has a chlorine substituted for one of the hydrogens of toluene
's the methyl group. These isomers differ in the location of the chlorine, but have the same chemical formula. All have very similar boiling points, although p-chlorotoluene has a much higher melting point due a more tightly-packed crystal structure.
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
ic chemical compounds. Three isomers (ortho-chlorotoluene, meta-chlorotoluene, and para-chlorotoluene) consisist of a disubsituted benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
ring with one chlorine atom and one methyl group
Methyl group
Methyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion...
. The fourth isomer, alpha-chlorotoluene
Benzyl chloride
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colourless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.-Preparation:...
(benzyl chloride), consists of toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
with chlorine substitution on the methyl group.
Chemical properties
There are three ring-substituted chlorotoluenes, as well as benzyl chlorideBenzyl chloride
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colourless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.-Preparation:...
, which has a chlorine substituted for one of the hydrogens of toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
's the methyl group. These isomers differ in the location of the chlorine, but have the same chemical formula. All have very similar boiling points, although p-chlorotoluene has a much higher melting point due a more tightly-packed crystal structure.
| Chlorotoluene Isomers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||
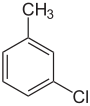
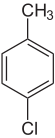
| Common name | o-chlorotoluene | m-chlorotoluene | p-chlorotoluene | Benzyl chloride | |
| Structure | 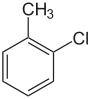 |
 |
 |
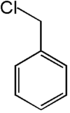 |
|
| Systematic name IUPAC nomenclature A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry .... |
1-chloro-2-methylbenzene | 1-chloro-3-methylbenzene | 1-chloro-4-methylbenzene | chloromethylbenzene | |
| Molecular formula Chemical formula A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound.... |
C7H7Cl (C6H4ClCH3) | ||||
| Molar mass Molar mass Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol... |
126.586 g/mol | ||||
| Appearance | clear, colorless liquid | ||||
| CAS number CAS registry number CAS Registry Numbersare unique numerical identifiers assigned by the "Chemical Abstracts Service" toevery chemical described in the... |
[95-49-8] | [108-41-8] | [106-43-4] | [100-44-7] | |
| Properties | |||||
| Density Density The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight... and phase Phase (matter) In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of space , throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, and chemical composition... |
1.073 g/mL, liquid | 1.072 g/mL, liquid | 1.069 g/mL, liquid | 1.100 g/mL, liquid | |
| Solubility in water | practically insoluble | ||||
| Other solubilities | Soluble in non-polar solvent Solvent A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature... s such as aromatic hydrocarbon Hydrocarbon In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls.... s |
||||
| Melting point Melting point The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure... |
−35 °C (-31 °F; 238 K) | -47 °C (-52.6 °F; 226 K) | 7 °C (44.6 °F; 280 K) | -39 °C (-38.2 °F; 234 K) | |
| Boiling point Boiling point The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid.... |
159 °C (318.2 °F; 432 K) | 162 °C (323.6 °F; 435 K) | 162 °C (323.6 °F; 435 K) | 179 °C (354.2 °F; 452 K) | |

