
Chlorate
Encyclopedia
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
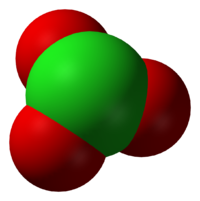
atom is in the +5 oxidation state
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
. "Chlorate" can also refer to chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s containing this anion; chlorates are the salts of chloric acid
Chloric acid
Chloric acid, HClO3, is an oxoacid of chlorine, and the formal precursor of chlorate salts. It is a strong acid and oxidizing agent....
. "Chlorate", when followed by a roman numeral in parentheses, e.g. chlorate(VII), refers to a particular oxyanion of chlorine.
As predicted by VSEPR, chlorate anions have trigonal pyramidal structures
Trigonal pyramid (chemistry)
In chemistry, a trigonal pyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the apex and three atoms at the corners of a trigonal base. When all three atoms at the corners are identical, the molecule belongs to point group C3v. One example of a molecule with a trigonal pyramidal geometry is ammonia...
.
Chlorates are powerful oxidizers and should be kept away from organics or easily oxidized materials.
Mixtures of chlorate salts with virtually any combustible material (sugar, sawdust, charcoal, organic solvents, metals, etc.) will readily deflagrate. Chlorates were once widely used in pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics is the science of using materials capable of undergoing self-contained and self-sustained exothermic chemical reactions for the production of heat, light, gas, smoke and/or sound...
for this reason, though their use has fallen due to their instability. Most pyrotechnic applications which formerly used chlorates in the past now use the more stable perchlorate
Perchlorate
Perchlorates are the salts derived from perchloric acid . They occur both naturally and through manufacturing. They have been used as a medicine for more than 50 years to treat thyroid gland disorders. They are used extensively within the pyrotechnics industry, and ammonium perchlorate is also a...
s instead.
Structure and bonding
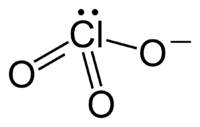
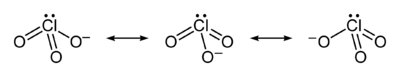
The chlorate ion cannot be satisfactorily represented by just one Lewis structureLewis structure
Lewis structures are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. A Lewis structure can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds...
, since all the Cl-O bonds are the same length (1.49 Å in potassium chlorate
Potassium chlorate
Potassium chlorate is a compound containing potassium, chlorine and oxygen atoms, with the molecular formula KClO3. In its pure form, it is a white crystalline substance. It is the most common chlorate in industrial use...
), and the chlorine atom is hypervalent
Hypervalent molecule
A hypervalent molecule is a molecule that contains one or more main group elements formally bearing more than eight electrons in their valence shells...
. Instead, it is often thought of as a hybrid of multiple resonance structures
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula...
:
Laboratory
Metal chlorates can be prepared by adding chlorineChlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
to hot metal hydroxide
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a...
s like KOH
Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, commonly called caustic potash.Along with sodium hydroxide , this colorless solid is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications. Most applications exploit its reactivity toward acids and its corrosive...
:
- 3 Cl2 + 6 KOH → 5 KCl + KClO3 + 3 H2O
In this reaction chlorine undergoes disproportionation
Disproportionation
Disproportionation, also known as dismutation is used to describe a specific type of redox reaction in which a species is simultaneously reduced and oxidized so as to form two different products....
, both reduction and oxidation. Chlorine, oxidation number 0, forms chloride Cl− (oxidation number −1) and chlorate(V) ClO (oxidation number +5). Reaction of cold aqueous metal hydroxides with chlorine produces the chloride and hypochlorite
Hypochlorite
The hypochlorite ion, also known as chlorate anion is ClO−. A hypochlorite compound is a chemical compound containing this group, with chlorine in oxidation state +1.Hypochlorites are the salts of hypochlorous acid...
(oxidation number +1) instead.
Industrial
The industrial scale synthesis for sodium chlorateSodium chlorate
Sodium chlorate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . When pure, it is a white crystalline powder that is readily soluble in water. It is hygroscopic. It decomposes above 250 °C to release oxygen and leave sodium chloride...
starts from aqueous sodium chloride
Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms...
solution (brine) rather than chlorine gas. If equipment for electrolysis allows mixing of the chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
and the sodium hydroxide, then the disproportionation reaction described above occurs. The heating of the reactants to 50-70°C is performed by the electrical power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
used for electrolysis
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
.
Compounds (salts)
Examples of chlorates include- potassium chloratePotassium chloratePotassium chlorate is a compound containing potassium, chlorine and oxygen atoms, with the molecular formula KClO3. In its pure form, it is a white crystalline substance. It is the most common chlorate in industrial use...
, KClO3 - sodium chlorateSodium chlorateSodium chlorate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . When pure, it is a white crystalline powder that is readily soluble in water. It is hygroscopic. It decomposes above 250 °C to release oxygen and leave sodium chloride...
, NaClO3 - magnesium chlorate, Mg(ClO3)2
Other oxyanions
If a Roman numeral in brackets follows the word "chlorate", this indicates the oxyanionOxyanion
An oxyanion or oxoanion is a chemical compound with the generic formula AxOyz− . Oxoanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxoanions are determined by the octet rule...
contains chlorine in the indicated oxidation state, namely:
| Common name | Stock name | Oxidation state | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypochlorite Hypochlorite The hypochlorite ion, also known as chlorate anion is ClO−. A hypochlorite compound is a chemical compound containing this group, with chlorine in oxidation state +1.Hypochlorites are the salts of hypochlorous acid... |
Chlorate(I) | +1 | ClO |
| Chlorite Chlorite The chlorite ion is ClO2−. A chlorite is a compound that contains this group,with chlorine in oxidation state +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous acid.-Oxidation states:... |
Chlorate(III) | +3 | ClO |
| Chlorate | Chlorate(V) | +5 | ClO |
| Perchlorate Perchlorate Perchlorates are the salts derived from perchloric acid . They occur both naturally and through manufacturing. They have been used as a medicine for more than 50 years to treat thyroid gland disorders. They are used extensively within the pyrotechnics industry, and ammonium perchlorate is also a... |
Chlorate(VII) | +7 | ClO |
Using this convention, "chlorate" means any chlorine oxyanion. Commonly, "chlorate" refers only to chlorine in the +5 oxidation state.

