
China Syndrome
Encyclopedia
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
operations accident characterized by the severe meltdown
Nuclear meltdown
Nuclear meltdown is an informal term for a severe nuclear reactor accident that results in core damage from overheating. The term is not officially defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency or by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission...
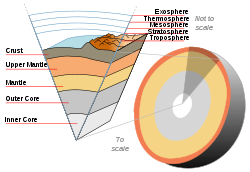
of the core components of the reactor, which then burn through the containment vessel and the housing building, then notionally through the crust and body of the Earth until reaching China.
Catastrophic meltdown
The China syndrome is a catastrophic accident, which is a possible result of the meltdown of a nuclear reactorNuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
, which begins with the loss of coolant fluid in the reactor vessel, and the partial or complete exposure of the fuel element assemblies. Despite the nuclear chain reaction
Nuclear chain reaction
A nuclear chain reaction occurs when one nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more nuclear reactions, thus leading to a self-propagating number of these reactions. The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes or the fusion of light isotopes...
having been stopped with control rod
Control rod
A control rod is a rod made of chemical elements capable of absorbing many neutrons without fissioning themselves. They are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of uranium and plutonium...
s, or other means, the fuel element assemblies continue radiating much residual, decay heat
Decay heat
Decay heat is the heat released as a result of radioactive decay. This is when the radiation interacts with materials: the energy of the alpha, beta or gamma radiation is converted into the thermal movement of atoms.-Natural occurrence:...
for days, because of the further decay of the fission products produced. If not properly cooled, the fuel rod assemblies might overheat, soften, and melt, falling to the bottom of the reactor vessel, where, without neutron-absorbing control rods to moderate the chain reaction, nuclear fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
might resume. Hence, the temperature of the molten fuel rod assemblies would rise to a temperature that would burn through the containment vessels and housing buildings until reaching the atmosphere and the environment.
History and usage
The system designSystems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
of the nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is one or more nuclear reactors. As in a conventional thermal power station the heat is used to generate steam which drives a steam turbine connected to a generator which produces electricity.Nuclear power plants are usually...
s built in the late 1960s raised questions of operational safety, and raised the concern that a severe reactor accident could release large quantities of radioactive materials into the atmosphere and environment. By 1970, there were doubts about the ability of the emergency cooling systems of a nuclear reactor to prevent a loss of coolant accident and the consequent meltdown of the fuel core; the subject proved popular in the technical and the popular presses. In 1971, in the article Thoughts on Nuclear Plumbing, former Manhattan Project
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program, led by the United States with participation from the United Kingdom and Canada, that produced the first atomic bomb during World War II. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the US Army...
(1942–1946) nuclear physicist
Nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies the building blocks and interactions of atomic nuclei. The most commonly known applications of nuclear physics are nuclear power generation and nuclear weapons technology, but the research has provided application in many fields, including those...
Ralph Lapp
Ralph Lapp
Ralph Eugene Lapp was an American physicist who participated in the Manhattan Project.He was born in Buffalo, New York, and attended the University of Chicago. After completing his graduate studies at the University he joined the Manhattan Project; and became the assistant Director of the...
used the term "China syndrome" to describe a possible burn-through, after a loss of coolant accident, of the nuclear fuel rods and core components melting the containment structures, and the subsequent escape of radioactive material(s) into the atmosphere and environment; the hypothesis derived from a 1967 report by a group of nuclear physicists, headed by W. K. Ergen. In the event, Lapp’s hypothetical nuclear accident was cinematically adapted as The China Syndrome
The China Syndrome
The China Syndrome is a 1979 American thriller film that tells the story of a reporter and cameraman who discover safety coverups at a nuclear power plant. It stars Jane Fonda, Jack Lemmon, Michael Douglas, Scott Brady, James Hampton, Peter Donat, Richard Herd, and Wilford Brimley.The film was...
(1979).
The geographic, planet-piercing concept of the China syndrome derives from the misperception that China is the antipode
Antipodes
In geography, the antipodes of any place on Earth is the point on the Earth's surface which is diametrically opposite to it. Two points that are antipodal to one another are connected by a straight line running through the centre of the Earth....
of the United States; to many Americans, it is the “the other side of the world”. The idea that the molten fuel would melt the earth's crust, let alone reach China, is obviously nonsense, intended as a joke.

