
Characteristic admittance
Encyclopedia
Characteristic admittance is the mathematical inverse of the characteristic impedance
.
The general expression for the characteristic admittance of a transmission line is:
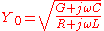
where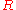 is the resistance
is the resistance
per unit length,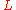 is the inductance
is the inductance
per unit length,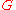 is the conductance of the dielectric per unit length,
is the conductance of the dielectric per unit length, is the capacitance
is the capacitance
per unit length,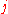 is the imaginary unit
is the imaginary unit
, and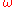 is the angular frequency
is the angular frequency
.
The current and voltage phasor
s on the line are related by the characteristic admittance as: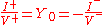
where the superscripts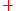 and
and  represent forward- and backward-traveling waves, respectively.
represent forward- and backward-traveling waves, respectively.
Characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
.
The general expression for the characteristic admittance of a transmission line is:
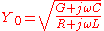
where
 is the resistance
is the resistanceElectrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
per unit length,
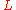 is the inductance
is the inductanceInductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
per unit length,
 is the conductance of the dielectric per unit length,
is the conductance of the dielectric per unit length, is the capacitance
is the capacitanceCapacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
per unit length,
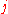 is the imaginary unit
is the imaginary unitImaginary unit
In mathematics, the imaginary unit allows the real number system ℝ to be extended to the complex number system ℂ, which in turn provides at least one root for every polynomial . The imaginary unit is denoted by , , or the Greek...
, and
 is the angular frequency
is the angular frequencyAngular frequency
In physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
.
The current and voltage phasor
Phasor (electronics)
In physics and engineering, a phase vector, or phasor, is a representation of a sine wave whose amplitude and angular frequency are time-invariant. It is a subset of a more general concept called analytic representation. Phasors decompose the behavior of a sinusoid into three independent...
s on the line are related by the characteristic admittance as:
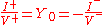
where the superscripts
 and
and  represent forward- and backward-traveling waves, respectively.
represent forward- and backward-traveling waves, respectively.

