
Celtiberian script
Encyclopedia
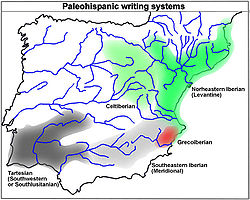
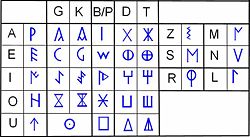
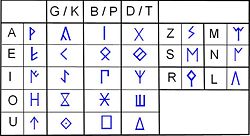
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
that was the main means of written expression of the Celtiberian language
Celtiberian language
Celtiberian is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula lyingbetween the headwaters of the Duero, Tajo, Júcar and Turia rivers and the Ebro river...
, an extinct Continental Celtic language, also expressed in Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
. This script is a direct adaptation of the northeastern Iberian script
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
the most frequently used of the Iberian scripts
Iberian scripts
The Iberian scripts are the Paleohispanic scripts that were used to represent the extinct Iberian language. Most of them are typologically very unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic...
.
All the paleohispanic scripts
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
, with the exception of the Greco-Iberian alphabet
Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the rest of paleohispanic scripts that present signs with syllabic value, for the...
, share a common distinctive typological characteristic: they represent syllabic values for the occlusives, and monophonemic values for the rest of consonants and vowels. From the writing systems point of view they are neither alphabets nor syllabaries, rather, they are mixed scripts that are normally identified as semi-syllabaries. There is no agreement about how the paleohispanic semi-syllabaries
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
originated; some researchers conclude that their origin is linked only to the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, while others believe the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
was also involved.
The basic Celtiberian signary contains 26 signs
Signs
Signs is the plural of sign. See sign .Signs may also refer to:*Signs , a 2002 film by M. Night Shyamalan*Signs , a journal of women's studies...
, instead of the 28 signs of the original model, the northeastern Iberian script
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
, because the Celtiberians
Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were Celtic-speaking people of the Iberian Peninsula in the final centuries BC. The group used the Celtic Celtiberian language.Archaeologically, the Celtiberians participated in the Hallstatt culture in what is now north-central Spain...
exclude one of the two rhotic
Rhotic consonant
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet...
and one of the three nasals
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
: 5 vowels, 15 syllabic signs and 8 consonants (one lateral
Lateral consonant
A lateral is an el-like consonant, in which airstream proceeds along the sides of the tongue, but is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth....
, two sibilants, one rhotic and two nasals
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
). Also, the Iberian sign “s” is transcribed as “z” in Celtiberian, because it is assumed that it sometimes expresses the fricative result of an ancient dental occlusive ("d"), while the Iberian sign “s´” is transcribed as “s”. As for the use of the nasal signs, there are two variants of the Celtiberian script: In the eastern variant, the excluded nasal sign was the Iberian sign “m´”; while in the western variant, the excluded nasal sign was the Iberian sign “m”. This is interpreted as evidence for a double origin of the Celtiberian script. And like the dual variant of the northeastern Iberian script
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
, the western variant shows evidence of the use of the dual system. This system allows differentiation of the occlusive signs (those writing dental and velar sounds) between voiced
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
and unvoiced by the use of an additional stroke, with the result that the simple sign represents the voiced value and the complex sign represents the unvoiced value.
The Celtiberian inscriptions have been found mainly in the Ebre valley and near the sources of the Tejo
Tejo
Tejo can be:*The Tagus, a river on the Iberian Peninsula.*Tejo , a sport and national pastime of Colombia.*The Tutmonda Esperantista Junulara Organizo * Tejo, Ethiopia...
and Douro
Douro
The Douro or Duero is one of the major rivers of the Iberian Peninsula, flowing from its source near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province across northern-central Spain and Portugal to its outlet at Porto...
rivers, where the Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
and Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
sources locate the Celtiberian people. The Celtiberian inscriptions were made on different object types (silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
and bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
coins
COinS
ContextObjects in Spans, commonly abbreviated COinS, is a method to embed bibliographic metadata in the HTML code of web pages. This allows bibliographic software to publish machine-readable bibliographic items and client reference management software to retrieve bibliographic metadata. The...
, ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
recipients, bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
plaques and tessera
Tessera
A tessera is an individual tile in a mosaic, usually formed in the shape of a cube. It is also known as an abaciscus, abaculus, or, in Persian کاشي معرق. In antiquity, mosaics were formed from naturally colored pebbles, but by 200 BC purpose-made tesserae were being used...
s, amphores
Amphora
An amphora is a type of vase-shaped, usually ceramic container with two handles and a long neck narrower than the body...
, stones, spindle
Spindle (textiles)
A spindle is a wooden spike used for spinning wool, flax, hemp, cotton, and other fibres into thread. It is commonly weighted at either the bottom middle or top, most commonly by a circular or spherical object called a whorl, and may also have a hook, groove or notch, though spindles without...
-whorls etc.). They are only almost two hundred surviving inscriptions, but one of them is exceptionally long: the third Botorrita
Botorrita
Botorrita is a municipality located in the province of Zaragoza, Aragon, Spain.Botorrita is known for the archeological artefacts found there, such as the Botorrita plaques....
bronze (Zaragoza
Zaragoza
Zaragoza , also called Saragossa in English, is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain...
) with more than three thousand signs containing a census of near 250 people. Almost always the direction of the writing is left to right. The fact that almost all the Celtiberian inscriptions were found out of archaeological context does not allow a precise chronology to be established, but it seem that the oldest inscriptions in Celtiberian script date to the 2nd century BCE and the recent ones date from the 1st century BCE.

