
Cellulose synthase (UDP-forming)
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a cellulose synthase (UDP-forming) is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are UDP-glucose and a chain of 1,4-beta-D-glucosyl residues, whereas its two products
are UDP
and an elongated chain of glucosyl residues. Glucosyl is the glycosyl
of glucose
, a chain of 1,4-beta-D-glucosyl residues is cellulose
, and enzymes of this class therefore play an important role in the synthesis of cellulose.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hexosyltransferases, specifically to the glycosyltransferase
s. The systematic name of this enzyme class is UDP-glucose:1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-beta-D-glucosyltransferase. Other names in common use include UDP-glucose-beta-glucan glucosyltransferase, UDP-glucose-cellulose glucosyltransferase, GS-I, beta-1,4-glucosyltransferase, uridine diphosphoglucose-1,4-beta-glucan glucosyltransferase, beta-1,4-glucan synthase, beta-1,4-glucan synthetase, beta-glucan synthase, 1,4-beta-D-glucan synthase, 1,4-beta-glucan synthase, glucan synthase, UDP-glucose-1,4-beta-glucan glucosyltransferase, and uridine diphosphoglucose-cellulose glucosyltransferase.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- UDP-glucose + (1,4-beta-D-glucosyl)n
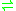 UDP + (1,4-beta-D-glucosyl)n+1
UDP + (1,4-beta-D-glucosyl)n+1
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are UDP-glucose and a chain of 1,4-beta-D-glucosyl residues, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are UDP
Uridine diphosphate
Uridine diphosphate, abbreviated UDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil.-See also:* Nucleoside...
and an elongated chain of glucosyl residues. Glucosyl is the glycosyl
Glycosyl
A glycosyl group is a univalent free radical or substituent structure obtained by removing the hemiacetal hydroxyl group from the cyclic form of a monosaccharide and, by extension, of a lower oligosaccharide....
of glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
, a chain of 1,4-beta-D-glucosyl residues is cellulose
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
, and enzymes of this class therefore play an important role in the synthesis of cellulose.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hexosyltransferases, specifically to the glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferases are enzymes that act as a catalyst for the transfer of a monosaccharide unit from an activated nucleotide sugar to a glycosyl acceptor molecule, usually an alcohol....
s. The systematic name of this enzyme class is UDP-glucose:1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-beta-D-glucosyltransferase. Other names in common use include UDP-glucose-beta-glucan glucosyltransferase, UDP-glucose-cellulose glucosyltransferase, GS-I, beta-1,4-glucosyltransferase, uridine diphosphoglucose-1,4-beta-glucan glucosyltransferase, beta-1,4-glucan synthase, beta-1,4-glucan synthetase, beta-glucan synthase, 1,4-beta-D-glucan synthase, 1,4-beta-glucan synthase, glucan synthase, UDP-glucose-1,4-beta-glucan glucosyltransferase, and uridine diphosphoglucose-cellulose glucosyltransferase.

