
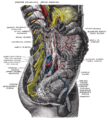
Celiac plexus
Encyclopedia
The celiac plexus or coeliac plexus, also known as the solar plexus, is a complex network of nerves (a plexus
) located in the abdomen, where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery
, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta
. It is behind the stomach
and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra, L1.
The plexus is formed (in part) by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves
of both sides, and also parts of the right vagus nerve
.
The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia
with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus.
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
 The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus, generally in the context of a blow to the stomach. In many of these cases, it is not the celiac plexus itself being referred to, but rather the region where it is located. A blow to the stomach can upset this region. This can cause the diaphragm to spasm, resulting in difficulty in breathing—a sensation commonly known as "getting the wind knocked out of you
The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus, generally in the context of a blow to the stomach. In many of these cases, it is not the celiac plexus itself being referred to, but rather the region where it is located. A blow to the stomach can upset this region. This can cause the diaphragm to spasm, resulting in difficulty in breathing—a sensation commonly known as "getting the wind knocked out of you
". A blow to this region can also affect the celiac plexus itself, possibly interfering with the functioning of the viscera, as well as causing great pain
.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically
guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as pancreatic cancer
. Frequently, celiac plexus block is performed by pain management specialists and radiologists, with CT scans for guidance. Intractable pain related to chronic pancreatitis
is an important indication for celiac plexus ablation.
Nerve plexus
A nerve plexus is a network of intersecting nerves. Except for the ventral rami of Th2-Th11 nerves, they combine sets of ventral rami of spinal nerves that serve the same area of the body into one large grouped nerve...
) located in the abdomen, where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery
Superior mesenteric artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.-Location...
, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta
Abdominal aorta
The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta .-Path:...
. It is behind the stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra, L1.
The plexus is formed (in part) by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves
Splanchnic nerves
The splanchnic nerves are paired nerves that contribute to the innervation of the viscera, carrying fibers of the autonomic nervous system as well as sensory fibers from the organs...
of both sides, and also parts of the right vagus nerve
Vagus nerve
The vagus nerve , also called pneumogastric nerve or cranial nerve X, is the tenth of twelve paired cranial nerves...
.
The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia
Celiac ganglia
The celiac ganglia or coeliac ganglia are two large irregularly shaped masses of nerve tissue in the upper abdomen. Part of the sympathetic subdivision of the autonomic nervous system , the two celiac ganglia are the largest ganglia in the ANS, and they innervate most of the digestive tract.They...
with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus.
Related plexuses
The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:- Hepatic plexusHepatic plexusThe hepatic plexus, the largest offset from the celiac plexus, receives filaments from the left vagus and right phrenic nerves.It accompanies the hepatic artery, ramifying upon its branches, and upon those of the portal vein in the substance of the liver....
- Splenic plexusSplenic plexusThe splenic plexus is formed by branches from the celiac plexus, the left celiac ganglion, and from the right vagus nerve....
- Gastric plexus
- Pancreatic plexusPancreatic plexusThe pancreatic plexus is a division of the celiac plexus ....
- Suprarenal plexusSuprarenal plexusThe suprarenal plexus is formed by branches from the celiac plexus, from the celiac ganglion, and from the phrenic and greater splanchnic nerves, a ganglion being formed at the point of junction with the latter nerve....
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
- Renal plexusRenal plexusThe renal plexus is formed by filaments from the celiac plexus, the aorticorenal ganglion, and the aortic plexus .It is joined also by the least splanchnic nerve....
- Testicular plexus / ovarian plexusOvarian plexusIn the female, the ovarian plexus arises from the renal plexus, and is distributed to the ovary, and fundus of the uterus.It is carried in the suspensory ligament of the ovary....
- Superior mesenteric plexusSuperior mesenteric plexusThe superior mesenteric plexus is a continuation of the lower part of the celiac plexus, receiving a branch from the junction of the right vagus nerve with the plexus....
- Inferior mesenteric plexusInferior mesenteric plexusThe inferior mesenteric plexus is derived chiefly from the aortic plexus.It surrounds the inferior mesenteric artery, and divides into a number of secondary plexuses, which are distributed to all the parts supplied by the artery, viz., the left colic and sigmoid plexuses, which supply the...
Clinical significance

Getting the wind knocked out of you
Getting the wind knocked out of you is a commonly used idiom that refers to a kind of diaphragm spasm that occurs when sudden force is applied to the abdomen which puts pressure on the solar plexus. This often happens in contact sports or by falling on the back. It results in a temporary paralysis...
". A blow to this region can also affect the celiac plexus itself, possibly interfering with the functioning of the viscera, as well as causing great pain
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy is an imaging technique commonly used by physicians to obtain real-time moving images of the internal structures of a patient through the use of a fluoroscope. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and fluorescent screen between which a patient is placed...
guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. The most common type of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 95% of these tumors is adenocarcinoma, which arises within the exocrine component of the pancreas. A minority arises from the islet cells and is classified as a...
. Frequently, celiac plexus block is performed by pain management specialists and radiologists, with CT scans for guidance. Intractable pain related to chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters its normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pain or malabsorption....
is an important indication for celiac plexus ablation.

