
Cauchy matrix
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a Cauchy matrix is an m×n matrix
with elements aij in the form

where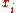 and
and 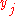 are elements of a field
are elements of a field
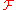 , and
, and 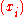 and
and 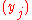 are injective sequences (they do not contain repeated elements; elements are distinct).
are injective sequences (they do not contain repeated elements; elements are distinct).
The Hilbert matrix is a special case of the Cauchy matrix, where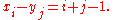
Every submatrix of a Cauchy matrix is itself a Cauchy matrix.
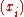 and
and 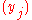 . If the sequences were not injective, the determinant would vanish, and tends to infinity if some
. If the sequences were not injective, the determinant would vanish, and tends to infinity if some 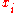 tends to
tends to 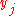 . A subset of its zeros and poles are thus known. The fact is that there are no more zeros and poles:
. A subset of its zeros and poles are thus known. The fact is that there are no more zeros and poles:
The determinant of a square Cauchy matrix A is known as a Cauchy determinant and can be given explicitly as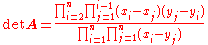 (Schechter 1959, eqn 4).
(Schechter 1959, eqn 4).
It is always nonzero, and thus all square Cauchy matrices are invertible. The inverse A−1 = B = [bij] is given by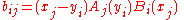 (Schechter 1959, Theorem 1)
(Schechter 1959, Theorem 1)
where Ai(x) and Bi(x) are the Lagrange polynomials for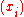 and
and 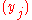 , respectively. That is,
, respectively. That is,
with

Defining X=diag(xi), Y=diag(yi), one sees that both Cauchy and Cauchy-like matrices satisfy the displacement equation

(with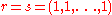 for the Cauchy one). Hence Cauchy-like matrices have a common displacement structure, which can be exploited while working with the matrix. For example, there are known algorithms in literature for
for the Cauchy one). Hence Cauchy-like matrices have a common displacement structure, which can be exploited while working with the matrix. For example, there are known algorithms in literature for
Here denotes the size of the matrix (one usually deals with square matrices, though all algorithms can be easily generalized to rectangular matrices).
denotes the size of the matrix (one usually deals with square matrices, though all algorithms can be easily generalized to rectangular matrices).
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a Cauchy matrix is an m×n matrix
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
with elements aij in the form

where
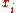 and
and 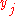 are elements of a field
are elements of a fieldField (mathematics)
In abstract algebra, a field is a commutative ring whose nonzero elements form a group under multiplication. As such it is an algebraic structure with notions of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, satisfying certain axioms...
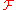 , and
, and 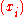 and
and 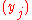 are injective sequences (they do not contain repeated elements; elements are distinct).
are injective sequences (they do not contain repeated elements; elements are distinct).The Hilbert matrix is a special case of the Cauchy matrix, where
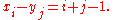
Every submatrix of a Cauchy matrix is itself a Cauchy matrix.
Cauchy determinants
The determinant of a Cauchy matrix is clearly a rational fraction in the parameters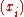 and
and 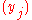 . If the sequences were not injective, the determinant would vanish, and tends to infinity if some
. If the sequences were not injective, the determinant would vanish, and tends to infinity if some 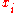 tends to
tends to 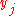 . A subset of its zeros and poles are thus known. The fact is that there are no more zeros and poles:
. A subset of its zeros and poles are thus known. The fact is that there are no more zeros and poles:The determinant of a square Cauchy matrix A is known as a Cauchy determinant and can be given explicitly as
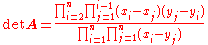 (Schechter 1959, eqn 4).
(Schechter 1959, eqn 4).It is always nonzero, and thus all square Cauchy matrices are invertible. The inverse A−1 = B = [bij] is given by
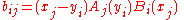 (Schechter 1959, Theorem 1)
(Schechter 1959, Theorem 1)where Ai(x) and Bi(x) are the Lagrange polynomials for
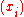 and
and 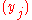 , respectively. That is,
, respectively. That is,
with

Generalization
A matrix C is called Cauchy-like if it is of the form
Defining X=diag(xi), Y=diag(yi), one sees that both Cauchy and Cauchy-like matrices satisfy the displacement equation

(with
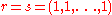 for the Cauchy one). Hence Cauchy-like matrices have a common displacement structure, which can be exploited while working with the matrix. For example, there are known algorithms in literature for
for the Cauchy one). Hence Cauchy-like matrices have a common displacement structure, which can be exploited while working with the matrix. For example, there are known algorithms in literature for
- approximate Cauchy matrix-vector multiplication with
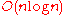 opsFloating pointIn computing, floating point describes a method of representing real numbers in a way that can support a wide range of values. Numbers are, in general, represented approximately to a fixed number of significant digits and scaled using an exponent. The base for the scaling is normally 2, 10 or 16...
opsFloating pointIn computing, floating point describes a method of representing real numbers in a way that can support a wide range of values. Numbers are, in general, represented approximately to a fixed number of significant digits and scaled using an exponent. The base for the scaling is normally 2, 10 or 16...
(e.g. the fast multipole methodFast Multipole MethodThe fast multipole method is a mathematical technique that was developed to speed up the calculation of long-ranged forces in the n-body problem...
), - (pivoted) LU factorization with
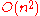 ops (GKO algorithm), and thus linear system solving,
ops (GKO algorithm), and thus linear system solving, - approximated or unstable algorithms for linear system solving in
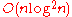 .
.
Here
 denotes the size of the matrix (one usually deals with square matrices, though all algorithms can be easily generalized to rectangular matrices).
denotes the size of the matrix (one usually deals with square matrices, though all algorithms can be easily generalized to rectangular matrices).

