
Category management
Encyclopedia

Retailing
Retail consists of the sale of physical goods or merchandise from a fixed location, such as a department store, boutique or kiosk, or by mail, in small or individual lots for direct consumption by the purchaser. Retailing may include subordinated services, such as delivery. Purchasers may be...
and supply management
Supply management
The term supply management describes the methods and processes of modern corporate or institutional buying. This may be for the purchasing of supplies for internal use referred to as indirect goods and services, purchasing raw materials for the consumption during the manufacturing process, or for...
concept in which the range of products purchased by a business organisation or sold by a retailer is broken down into discrete groups of similar or related products; these groups are known as product categories (examples of grocery categories might be: tinned fish, washing detergent, toothpastes). It is a systematic, disciplined approach to managing a product category as a strategic business unit.
Category Management in a retail context
Each category is run as a "mini business" (business unit) in its own right, with its own set of turnover and/or profitabilityProfit (accounting)
In accounting, profit can be considered to be the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market whatever it is that is accounted as an enterprise in terms of the component costs of delivered goods and/or services and any operating or other expenses.-Definition:There are...
targets and strategies. Introduction of Category Management in a business tends to alter the relationship between retailer and supplier: instead of the traditional adversarial relationship, the relationship moves to one of collaboration
Collaboration
Collaboration is working together to achieve a goal. It is a recursive process where two or more people or organizations work together to realize shared goals, — for example, an intriguing endeavor that is creative in nature—by sharing...
, with exchange of information, sharing of data and joint business building.
The focus of all supplier negotiations is the effect on turnover of the category as whole, not just the sales of individual products. Suppliers are expected, indeed in many cases mandated, to only suggest new product introductions, a new planogram
Planogram
A planogram is "a diagram or model that indicates the placement of retail products on shelves in order to maximize sales".Also known as plano-grams, plan-o-grams, schematics and POGs, planograms are a tool used in visual merchandising.-Overview:A planogram is often received before a product reaches...
or promotional activity if it is expected to have a beneficial effect on the turnover or profit of the total category and be beneficial to the shoppers of that category.
The concept originated in grocery (mass merchandising) retailing, and has since expanded to other retail sectors such as DIY, cash and carry
Cash and carry
Cash and carry may refer to:*Cash and Carry , the first network-televised game show*Cash and carry , a revision of the Neutrality Acts, designed to aid the British...
, pharmacy
Pharmacy
Pharmacy is the health profession that links the health sciences with the chemical sciences and it is charged with ensuring the safe and effective use of pharmaceutical drugs...
, and book retailing.
Definition of category management (retail)
Category management lacks a single definition thus leading to some ambiguity even among industry professionals as to its exact function. Three comparative mainstream definitions are as follows:Category management is a process that involves managing product categories as business units and customizing them [on a store by store basis] to satisfy customer needs. (Nielsen)
The strategic management of product groups through trade partnerships which aims to maximize sales and profit by satisfying consumer and shopper needs (Institute of Grocery Distribution)
.. marketing strategy in which a full line of products (instead of the individual products or brands) is managed as a strategic business unit (SBU). (Business Dictionary)
The Nielsen definition, published in 1992, was a little ahead of its time in that customising product offerings on a store by store basis is logistically difficult and is now not considered a necessary part of category management; it is a concept now referred to as micromarketing
Micromarketing
Micromarketing"Micromarketing" was first referred to in the UK marketing press in November 1988 in respect of the application of geodemographics to consumer marketing....
. Nevertheless, most grocery retailers will segment stores at least by size, and select product assortments accordingly. Wal*Mart's Store of the Community, implemented in North America is one of the few examples of where product offerings are tailored right down to the specific store.
Rationale for category management
One key reason for the introduction of category management was the retailers' desire for suppliers to add value to their (i.e. the retailer's) business rather than just the supplier's own. For example, in a category containing brands A and B, the situation could arise such that every time brand A promoted its products, the sales of brand B would go down by the amount that brand A would increase, resulting in no net gain for the retailer. The introduction of category management imposed the condition that all actions undertaken, such as new promotionsPromotion (marketing)
Promotion is one of the four elements of marketing mix . It is the communication link between sellers and buyers for the purpose of influencing, informing, or persuading a potential buyer's purchasing decision....
, new products, re-vamped planogram
Planogram
A planogram is "a diagram or model that indicates the placement of retail products on shelves in order to maximize sales".Also known as plano-grams, plan-o-grams, schematics and POGs, planograms are a tool used in visual merchandising.-Overview:A planogram is often received before a product reaches...
, introduction of point of sale
Point of sale
Point of sale or checkout is the location where a transaction occurs...
advertising
Advertising
Advertising is a form of communication used to persuade an audience to take some action with respect to products, ideas, or services. Most commonly, the desired result is to drive consumer behavior with respect to a commercial offering, although political and ideological advertising is also common...
etc. were beneficial to the retailer and the shopper in the store.
A second reason was the realization that only a finite amount of profit could be milked from price negotiations and that there was more profit to be made in increasing the total level of sales.
A third reason was that the collaboration with the supplier meant that supplier's expertise about the market could be drawn upon, and also that a considerable amount of workload in developing the category could be delegated to the supplier.
Definition of a category
The Nielsen definition of a category, used as the basic definition across the industry is that the products should meet a similar consumer need, or that the products should be inter-related or substitutable. The Nielsen definition also includes a provision that products placed together in the same category should be logistically manageable in store (for example there may be issues in having room-temperature and chilled products together in the same category even though the initial two conditions are met).However, this definition does not explain how the process often works in practical retailing situations, where demographic or marketing considerations take precedence.
The category management 8-step process
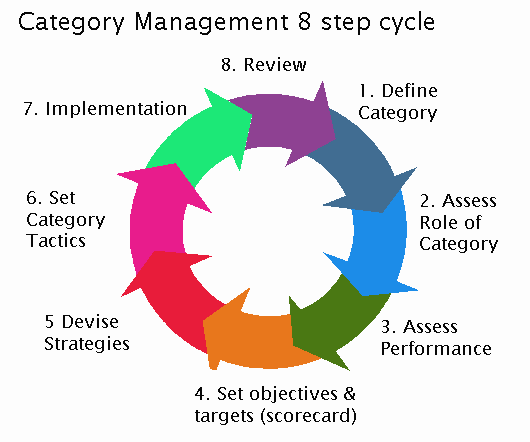
- Define the category (i.e. what products are included/excluded).
- Define the role of the category within the retailer.
- Assess the current performance.
- Set objectives and targets for the category.
- Devise an overall Strategy.
- Devise specific tactics.
- Implementation.
- The eighth step is one of review which takes us back to step 1.
The 8-step process, whilst being very comprehensive and thorough has been criticized for being rather too unwieldy and time-consuming in today's fast-moving sales environment; in one survey only 9% of supplier companies stated they used the full 8-step process. The current industry trend is for supplier companies to use the standard process as a basis to develop their own more streamlined processes, tailored to their own particular products
Market research company Nielsen has a similar process based on only 5 steps : reviewing the category, targeting consumers, planning merchandising, implementing strategy, evaluating results.
Category captains
It is commonplace for one particular supplier into a category to be nominated by the retailer as a category captain. The category captain will be expected to have the closest and most regular contact with the retailer and will also be expected to invest time, effort, and often financial investment into the strategic development of the category within the retailer.In return, the supplier will gain a more influential voice with the retailer. The category captain is often the supplier with the largest turnover in the category. Traditionally the job of category captain is given to a brand
Brand
The American Marketing Association defines a brand as a "Name, term, design, symbol, or any other feature that identifies one seller's good or service as distinct from those of other sellers."...
supplier, but in recent times the role has also gone to particularly switched-on private label
Private label
Private label products or services are typically those manufactured or provided by one company for offer under another company's brand. Private label goods and services are available in a wide range of industries from food to cosmetics to web hosting...
suppliers.
In order to do the job effectively, the supplier may be granted access to a greater wealth of data-sharing, e.g. more access to an internal sales database such as Walmart's Retail Link.
Governmental concerns about category management
Many governments have viewed increased collaboration between suppliers and retailers as a potential source of antitrustAntitrust
The United States antitrust law is a body of laws that prohibits anti-competitive behavior and unfair business practices. Antitrust laws are intended to encourage competition in the marketplace. These competition laws make illegal certain practices deemed to hurt businesses or consumers or both,...
breaches, such as price fixing
Price fixing
Price fixing is an agreement between participants on the same side in a market to buy or sell a product, service, or commodity only at a fixed price, or maintain the market conditions such that the price is maintained at a given level by controlling supply and demand...
. For example the UK Competition Commission
Competition Commission
The Competition Commission is a non-departmental public body responsible for investigating mergers, markets and other enquiries related to regulated industries under competition law in the United Kingdom...
has raised their issues on market distortion
Market distortion
In neoclassical economics, a market distortion is any event in which a market reaches a market clearing price for an item that is substantially different from the price that a market would achieve while operating under conditions of perfect competition and state enforcement of legal contracts and...
in principle. They have also acted on milk price-fixing in Britain.
Category Management Association
The Category Management Association (CMA), is a professional association formed in 2004 with members that come from a broad range of strategic insights and planning functions. It connects members with category management peers around the world, is a central resource for category management information and best practices, and is the only group certifying companies and individual category management professionals according to recognized industry standards.Modified category management
For MRPMRP
The initialism MRP or M.R.P. can stand for many things:Business, economics and management* Manufacturer's recommended price* Manufacturing resource planning * Marginal Revenue Product, see Marginal revenue productivity theory of wages...
-based manufacturing industries, the predominant cost-saving methodology in category management (CM) involves the integration of market intelligence with leveraged spending (for a given category of product or service). In industries where asset operation and preservation bear more significance to the procurement process than do product manufacturing – such as in an MRO
MRO
-Operations:* maintenance, repair, and operations -Companies:...
environment – demonstrable benefit can still be achieved with category management but is best approached with some manner of adjustment to CM’s usual processes for analysis and strategy development. The first challenge becomes incorporating analytical processes and value drivers that are largely indigenous to the MRP world in a manner that makes sense to an MRO environment. The second (and no less important) challenge becomes avoiding a trap where the CM processes are perceived to be more important than their outcome – a scenario that can result in significant analytical delay, and even complete process paralysis. An excellent example of an MRO environment warranting adjustment to classical category management is nuclear power generation in the United States, where the adjusted approach to category management has been coined MCM
MCM
-Science and technology:* Thousand circular mils or kcmil, the wire gauge is equivalent cross sectional area * Million cubic metre, the unit of volume...
– standing for MRO-based Category Management or Modified Category Management. Not only does electricity generation epitomize an MRO-driven environment, the nuclear energy source adds numerous dimensions of supply and procurement complexity – including federal and state regulatory compliance, nuclear industry standards compliance, nuclear-unique system and component design, and a tightly-audited (and very small) supply base, amongst others. Due to the nature and quantity of discrete characteristics native to nuclear power generation, it can easily be argued that nuclear power generation, in and of itself, should be a distinct category of procurement within a category management project. The fundamental adjustment made between the classical category management approach and the nuclear MCM approach is a shift from procurement strategies focused on leveraged spending to procurement strategies embracing nuclear value drivers, technology innovation, risk management, and strategic sourcing.
Category Management in a supply context
Use of the term ‘category management’ can also be focused on an organisation’s sourcingSourcing
In business, the term word sourcing refers to a number of procurement practices, aimed at finding, evaluating and engaging suppliers of goods and services:*Global sourcing, a procurement strategy aimed at exploiting global efficiencies in production...
, acquisition
Acquisition
Acquisition may refer to:* Takeover, the acquisition of a company* Mergers and acquisitions, strategy of buying and selling of various companies to quickly grow a company...
and supply management
Supply management
The term supply management describes the methods and processes of modern corporate or institutional buying. This may be for the purchasing of supplies for internal use referred to as indirect goods and services, purchasing raw materials for the consumption during the manufacturing process, or for...
processes, and this usage has become more prominent in recent years. In this context, Category Management has been defined as “an evolving methodology that drives sourcing strategy in progressive organisations today”.
The Chartered Institute of Purchasing and Supply
Chartered Institute of Purchasing and Supply
The Chartered Institute of Purchasing & Supply is a global organisation working for the purchasing and supply professions. CIPS is the world’s largest procurement and supply professional organisation. It is the worldwide centre of excellence on purchasing and supply management issues...
defines Category Management as:
- "organising the resources of the procurement team in such a way as to focus externally onto the supply markets of an organisation (as against having a focus on the internal customers or on internal Procurement departmental functions) in order to fully leverage purchasing decisions”.
Peter Hunt, partner at ADR International, writes
- “the term category management can mean different things to different people, so a working definition is needed. A ‘category’ is the logical grouping of similar expenditure items, such as spend on advertising agency services or IT hardware. Category management is the sourcing process used to manage these categories to satisfy business needs while maximising the value delivered from the supply base”.
Large multi-site or multi-functional organisations use category management to ensure that commonly used goods and services are not separately purchased by the various functional teams but are sources through a single process able to maximise leverage in the market for the relevant category. The benefits which result are:
- better value for money through aggregation of demand;
- standardising requirements in terms of specification, quantity and purchasing authorisation;
- skilled procurement personnel are actively involved in purchasing processes;
- resources can be committed cost effectively to market watching and analysis.
Many public sector organisations have recently adopted category management as a strategic transformation tool. Sir Philip Green, in his “Efficiency Review” of UK government spending, recommended that “centralised procurement [should be] mandated for common categories to leverage this buying power and achieve best practice”.
External links
- ECR Community Platform (Category Management)
- CIPS Category Management Model, http://www.cips.org/en/resources/categorymanagementmodel/
See also
- Fast moving consumer goodsFast Moving Consumer GoodsFast moving consumer goods or Consumer Packaged Goods are products that are sold quickly and at relatively low cost. Examples include non-durable goods such as soft drinks, toiletries, and grocery items...
- Grocery
- Homestore
- MarketingMarketingMarketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
- RetailingRetailingRetail consists of the sale of physical goods or merchandise from a fixed location, such as a department store, boutique or kiosk, or by mail, in small or individual lots for direct consumption by the purchaser. Retailing may include subordinated services, such as delivery. Purchasers may be...
- SalesSalesA sale is the act of selling a product or service in return for money or other compensation. It is an act of completion of a commercial activity....
- shopper marketingShopper MarketingShopper marketing is "understanding how one's target consumers behave as shoppers, in different channels and formats, and leveraging this intelligence to the benefit of all stakeholders, defined as brands, consumers, retailers and shoppers."...
- PlanogramPlanogramA planogram is "a diagram or model that indicates the placement of retail products on shelves in order to maximize sales".Also known as plano-grams, plan-o-grams, schematics and POGs, planograms are a tool used in visual merchandising.-Overview:A planogram is often received before a product reaches...

