
Cassini projection
Encyclopedia
The Cassini projection is a map projection
described by César-François Cassini de Thury
in 1745. It is the transverse
aspect of the equirectangular projection
, in that the globe is first rotated so the central meridian becomes the "equator", and then the normal equirectangular projection is applied. Composing these operations:


where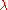 is the longitude from the central meridian and
is the longitude from the central meridian and 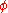 is the latitude. When programming these equations, the inverse tangent function used is actually the atan2
is the latitude. When programming these equations, the inverse tangent function used is actually the atan2
function, with the first argument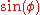 and the second
and the second 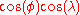 .
.
The use of the Cassini projection has largely been superseded by the Transverse Mercator projection, at least with central mapping agencies.
Due to this, the Cassini projection works best on long, narrow areas, and worst on wide areas.
Map projection
A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion...
described by César-François Cassini de Thury
César-François Cassini de Thury
César-François Cassini de Thury , also called Cassini III or Cassini de Thury, was a French astronomer and cartographer.- Biography :...
in 1745. It is the transverse
Transversality
In mathematics, transversality is a notion that describes how spaces can intersect; transversality can be seen as the "opposite" of tangency, and plays a role in general position. It formalizes the idea of a generic intersection in differential topology...
aspect of the equirectangular projection
Equirectangular projection
The equirectangular projection is a very simple map projection attributed to Marinus of Tyre, who Ptolemy claims invented the projection about AD 100...
, in that the globe is first rotated so the central meridian becomes the "equator", and then the normal equirectangular projection is applied. Composing these operations:


where
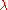 is the longitude from the central meridian and
is the longitude from the central meridian and  is the latitude. When programming these equations, the inverse tangent function used is actually the atan2
is the latitude. When programming these equations, the inverse tangent function used is actually the atan2Atan2
In trigonometry, the two-argument function atan2 is a variation of the arctangent function. For any real arguments and not both equal to zero, is the angle in radians between the positive -axis of a plane and the point given by the coordinates on it...
function, with the first argument
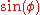 and the second
and the second 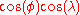 .
.The use of the Cassini projection has largely been superseded by the Transverse Mercator projection, at least with central mapping agencies.
Distortions
Things along the central meridian, and at right angles to it, are not distorted. Elsewhere, the distortion is largely in a north-south direction, and varies by the square of the central meridian. As such, the greater the longitudinal extent of the area, the worse the distortion becomes.Due to this, the Cassini projection works best on long, narrow areas, and worst on wide areas.
External links
- Table of examples and properties of all common projections, from radicalcartography.net
- Ordnance Survey GeoFacts on the Cassini Projection

