
Cartan decomposition
Encyclopedia
The Cartan decomposition is a decomposition of a semisimple Lie group
or Lie algebra
, which plays an important role in their structure theory and representation theory. It generalizes the polar decomposition of matrices.
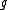 be a real semisimple Lie algebra
be a real semisimple Lie algebra
and let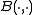 be its Killing form
be its Killing form
. An involution on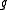 is a Lie algebra automorphism
is a Lie algebra automorphism
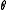 of
of 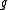 whose square is equal to the identity. Such an involution is called a Cartan involution on
whose square is equal to the identity. Such an involution is called a Cartan involution on 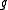 if
if 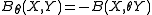 is a positive definite bilinear form.
is a positive definite bilinear form.
Two involutions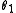 and
and 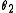 are considered equivalent if they differ only by an inner automorphism.
are considered equivalent if they differ only by an inner automorphism.
Any real semisimple Lie algebra has a Cartan involution, and any two Cartan involutions are equivalent.
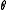 be an involution on a Lie algebra
be an involution on a Lie algebra 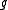 . Since
. Since 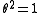 , the linear map
, the linear map 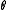 has the two eigenvalues
has the two eigenvalues 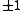 . Let
. Let 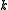 and
and 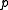 be the corresponding eigenspaces, then
be the corresponding eigenspaces, then 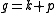 . Since
. Since 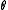 is a Lie algebra automorphism, eigenvalues are multiplicative. It follows that
is a Lie algebra automorphism, eigenvalues are multiplicative. It follows that
Thus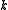 is a Lie subalgebra, while any subalgebra of
is a Lie subalgebra, while any subalgebra of 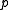 is commutative.
is commutative.
Conversely, a decomposition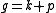 with these extra properties determines an involution
with these extra properties determines an involution 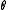 on
on 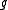 that is
that is 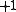 on
on 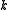 and
and 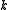 on
on 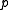 .
.
Such a pair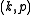 is also called a Cartan pair of
is also called a Cartan pair of 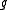 .
.
The decomposition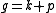 associated to a Cartan involution is called a Cartan decomposition of
associated to a Cartan involution is called a Cartan decomposition of 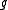 . The special feature of a Cartan decomposition is that the Killing form is negative definite on
. The special feature of a Cartan decomposition is that the Killing form is negative definite on 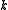 and positive definite on
and positive definite on 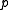 . Furthermore,
. Furthermore, 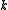 and
and 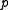 are orthogonal complements of each other with respect to the Killing form on
are orthogonal complements of each other with respect to the Killing form on 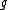 .
.
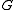 be a semisimple Lie group
be a semisimple Lie group
and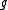 its Lie algebra
its Lie algebra
. Let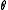 be a Cartan involution on
be a Cartan involution on 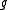 and let
and let 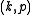 be the resulting Cartan pair. Let
be the resulting Cartan pair. Let 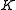 be the analytic subgroup of
be the analytic subgroup of 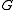 with Lie algebra
with Lie algebra 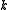 . Then
. Then
The automorphism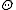 is also called global Cartan involution, and the diffeomorphism
is also called global Cartan involution, and the diffeomorphism 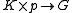 is called global Cartan decomposition.
is called global Cartan decomposition.
For the general linear group, we get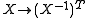 as the Cartan involution.
as the Cartan involution.
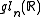 with the Cartan involution
with the Cartan involution 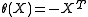 . Then
. Then 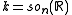 is the real Lie algebra of skew-symmetric matrices, so that
is the real Lie algebra of skew-symmetric matrices, so that 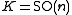 , while
, while 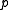 is the subspace of symmetric matrices. Thus the exponential map is a diffeomorphism from
is the subspace of symmetric matrices. Thus the exponential map is a diffeomorphism from 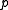 onto the space of positive definite matrices. Up to this exponential map, the global Cartan decomposition is the polar decomposition of a matrix. Notice that the polar decomposition of an invertible matrix is unique.
onto the space of positive definite matrices. Up to this exponential map, the global Cartan decomposition is the polar decomposition of a matrix. Notice that the polar decomposition of an invertible matrix is unique.
Lie group
In mathematics, a Lie group is a group which is also a differentiable manifold, with the property that the group operations are compatible with the smooth structure...
or Lie algebra
Lie algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
, which plays an important role in their structure theory and representation theory. It generalizes the polar decomposition of matrices.
Cartan involutions on Lie algebras
Let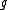 be a real semisimple Lie algebra
be a real semisimple Lie algebraLie algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
and let
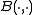 be its Killing form
be its Killing formKilling form
In mathematics, the Killing form, named after Wilhelm Killing, is a symmetric bilinear form that plays a basic role in the theories of Lie groups and Lie algebras...
. An involution on
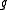 is a Lie algebra automorphism
is a Lie algebra automorphismAutomorphism
In mathematics, an automorphism is an isomorphism from a mathematical object to itself. It is, in some sense, a symmetry of the object, and a way of mapping the object to itself while preserving all of its structure. The set of all automorphisms of an object forms a group, called the automorphism...
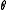 of
of 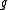 whose square is equal to the identity. Such an involution is called a Cartan involution on
whose square is equal to the identity. Such an involution is called a Cartan involution on 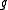 if
if 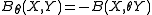 is a positive definite bilinear form.
is a positive definite bilinear form.Two involutions
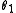 and
and 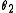 are considered equivalent if they differ only by an inner automorphism.
are considered equivalent if they differ only by an inner automorphism.Any real semisimple Lie algebra has a Cartan involution, and any two Cartan involutions are equivalent.
Examples
- A Cartan involution on
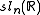 is defined by
is defined by 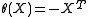 , where
, where 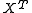 denotes the transpose matrix of
denotes the transpose matrix of 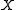 .
.
- The identity map on
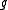 is an involution, of course. It is the unique Cartan involution of
is an involution, of course. It is the unique Cartan involution of 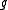 if and only if the Killing form of
if and only if the Killing form of 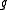 is negative definite. Equivalently,
is negative definite. Equivalently, 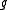 is the Lie algebra of a compact Lie group.
is the Lie algebra of a compact Lie group.
- Let
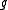 be the complexification of a real semisimple Lie algebra
be the complexification of a real semisimple Lie algebra 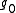 , then complex conjugation on
, then complex conjugation on 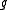 is an involution on
is an involution on 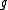 . This is the Cartan involution on
. This is the Cartan involution on 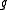 if and only if
if and only if 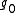 is the Lie algebra of a compact Lie group.
is the Lie algebra of a compact Lie group.
- The following maps are involutions of the Lie algebra
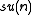 of the special unitary group SU(n):
of the special unitary group SU(n):
-
- the identity involution
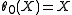 , which is the unique Cartan involution in this case;
, which is the unique Cartan involution in this case;
- the identity involution
-
-
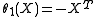 which on
which on 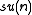 is also the complex conjugation;
is also the complex conjugation;
-
-
- if
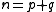 is odd,
is odd, 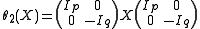 . These are all equivalent, but not equivalent to the identity involution (because the matrix
. These are all equivalent, but not equivalent to the identity involution (because the matrix 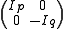 does not belong to
does not belong to 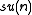 .)
.)
- if
-
- if
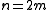 is even, we also have
is even, we also have 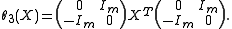
- if
Cartan pairs
Let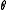 be an involution on a Lie algebra
be an involution on a Lie algebra 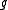 . Since
. Since 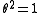 , the linear map
, the linear map 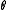 has the two eigenvalues
has the two eigenvalues 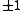 . Let
. Let 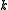 and
and 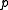 be the corresponding eigenspaces, then
be the corresponding eigenspaces, then 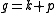 . Since
. Since 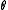 is a Lie algebra automorphism, eigenvalues are multiplicative. It follows that
is a Lie algebra automorphism, eigenvalues are multiplicative. It follows that
-
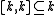 ,
, 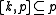 , and
, and 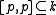 .
.
Thus
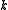 is a Lie subalgebra, while any subalgebra of
is a Lie subalgebra, while any subalgebra of 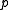 is commutative.
is commutative.Conversely, a decomposition
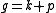 with these extra properties determines an involution
with these extra properties determines an involution 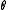 on
on 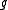 that is
that is 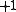 on
on 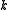 and
and 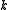 on
on 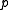 .
.Such a pair
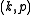 is also called a Cartan pair of
is also called a Cartan pair of 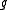 .
.The decomposition
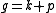 associated to a Cartan involution is called a Cartan decomposition of
associated to a Cartan involution is called a Cartan decomposition of 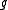 . The special feature of a Cartan decomposition is that the Killing form is negative definite on
. The special feature of a Cartan decomposition is that the Killing form is negative definite on 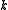 and positive definite on
and positive definite on 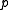 . Furthermore,
. Furthermore, 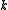 and
and 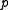 are orthogonal complements of each other with respect to the Killing form on
are orthogonal complements of each other with respect to the Killing form on 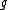 .
.Cartan decomposition on the Lie group level
Let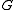 be a semisimple Lie group
be a semisimple Lie groupLie group
In mathematics, a Lie group is a group which is also a differentiable manifold, with the property that the group operations are compatible with the smooth structure...
and
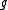 its Lie algebra
its Lie algebraLie algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
. Let
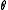 be a Cartan involution on
be a Cartan involution on 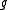 and let
and let 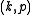 be the resulting Cartan pair. Let
be the resulting Cartan pair. Let 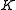 be the analytic subgroup of
be the analytic subgroup of 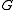 with Lie algebra
with Lie algebra 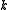 . Then
. Then
- There is a Lie group automorphism
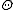 with differential
with differential 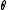 that satisfies
that satisfies 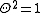 .
. - The subgroup of elements fixed by
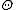 is
is 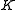 ; in particular,
; in particular, 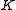 is a closed subgroup.
is a closed subgroup. - The mapping
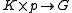 given by
given by 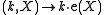 is a diffeomorphism.
is a diffeomorphism. - The subgroup
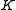 contains the center
contains the center 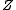 of
of 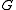 , and
, and 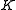 is compact modulo center, that is,
is compact modulo center, that is, 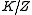 is compact.
is compact. - The subgroup
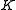 is the maximal subgroup of
is the maximal subgroup of 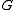 that contains the center and is compact modulo center.
that contains the center and is compact modulo center.
The automorphism
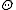 is also called global Cartan involution, and the diffeomorphism
is also called global Cartan involution, and the diffeomorphism 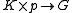 is called global Cartan decomposition.
is called global Cartan decomposition.For the general linear group, we get
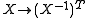 as the Cartan involution.
as the Cartan involution.Relation to polar decomposition
Consider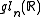 with the Cartan involution
with the Cartan involution 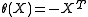 . Then
. Then 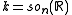 is the real Lie algebra of skew-symmetric matrices, so that
is the real Lie algebra of skew-symmetric matrices, so that 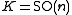 , while
, while 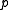 is the subspace of symmetric matrices. Thus the exponential map is a diffeomorphism from
is the subspace of symmetric matrices. Thus the exponential map is a diffeomorphism from 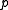 onto the space of positive definite matrices. Up to this exponential map, the global Cartan decomposition is the polar decomposition of a matrix. Notice that the polar decomposition of an invertible matrix is unique.
onto the space of positive definite matrices. Up to this exponential map, the global Cartan decomposition is the polar decomposition of a matrix. Notice that the polar decomposition of an invertible matrix is unique.

