
Carotol
Encyclopedia
Carotol was first isolated by scientists Asahina and Tsukamoto in 1925. It is one of the primary components found in carrot seed oil
comprising approximately 40% of this essential oil
. This sesquiterpene
alcohol is thought to be formed in carrot seeds (Daucus carota L., Umbelliferae) during the vegetation period. Additionally, studies have shown that carotol may be involved in allelopathic interactions expressing activity as an antifungal, herbicidal and insecticidal agent.
(FPP) to the carotol (carotane backbone). This type of cyclisation is unconventional for the typical chemistry of sesquiterpenes. The only other proposed mechanism requires a complex ten-membered ring with a methyl migration. This later reaction, regardless of how plausible it may appear to be on paper, is energetically undesired and through the diligent work of M. Soucek and coworkers it was shown that the cyclization from FPP to carotol is the most probable biosynthesis route.
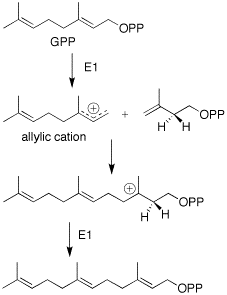
The formation of farnesyl pyrophosphate is via the mevalonate pathway. An additional five-carbon IPP unit is added in the same manner to GPP.
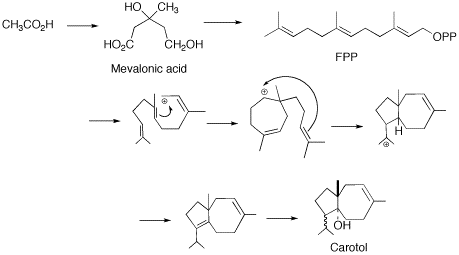
 The cyclization of FPP proceeds via a synchronous reaction of trans-antiparallel additions. This leads to the trans carbocation intermediate. Further cyclisation occurs yielding the 5 and 7-membered ring carbocation. This is followed by a 1,3-hydride shift and subsequent deprotonation to the diene. It is suggested that the carbocation elimination is directed to retain the proper structure of the isoprooyl group. Based on the work of Soucek it is then proposed that a stereospecfic hydration will then take place leading to the enzymatic introduction of the hydroxyl group.
The cyclization of FPP proceeds via a synchronous reaction of trans-antiparallel additions. This leads to the trans carbocation intermediate. Further cyclisation occurs yielding the 5 and 7-membered ring carbocation. This is followed by a 1,3-hydride shift and subsequent deprotonation to the diene. It is suggested that the carbocation elimination is directed to retain the proper structure of the isoprooyl group. Based on the work of Soucek it is then proposed that a stereospecfic hydration will then take place leading to the enzymatic introduction of the hydroxyl group.
Carrot seed oil
Carrot seed oil is the essential oil extract of the seed from the carrot plant Daucus carota. The oil has a woody, earthy sweet smell and is yellow or amber-coloured to pale orange-brown in appearance. The pharmocologically active constituents of carrot seed extract are three flavones: luteolin,...
comprising approximately 40% of this essential oil
Essential oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils or aetherolea, or simply as the "oil of" the plant from which they were extracted, such as oil of clove...
. This sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be acyclic or contain rings, including many unique combinations...
alcohol is thought to be formed in carrot seeds (Daucus carota L., Umbelliferae) during the vegetation period. Additionally, studies have shown that carotol may be involved in allelopathic interactions expressing activity as an antifungal, herbicidal and insecticidal agent.
Biosynthesis
It has been proposed that there is a direct cyclisation of farnesyl pyrophosphateFarnesyl pyrophosphate
Farnesyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes, terpenoids, and sterols...
(FPP) to the carotol (carotane backbone). This type of cyclisation is unconventional for the typical chemistry of sesquiterpenes. The only other proposed mechanism requires a complex ten-membered ring with a methyl migration. This later reaction, regardless of how plausible it may appear to be on paper, is energetically undesired and through the diligent work of M. Soucek and coworkers it was shown that the cyclization from FPP to carotol is the most probable biosynthesis route.
The formation of farnesyl pyrophosphate is via the mevalonate pathway. An additional five-carbon IPP unit is added in the same manner to GPP.



