
Canonical units
Encyclopedia
In astrodynamics
, A canonical unit is a unit of measurement defined in terms of an object's reference orbit
. In this system, a reference mass, for example the sun, is assumed to be 1 "mass unit" and the mean distance from the orbiting object to the reference object is considered the "distance unit".
Canonical units are useful when the precise distances and masses of objects in space are not available. However, by setting the mass of a given object to be 1 mass unit and the mean distance of the reference object to another object in question, many calculations can be simplified.
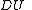 is defined to be the mean radius of the reference orbit.
is defined to be the mean radius of the reference orbit.
The time unit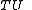 is defined by the gravitational parameter
is defined by the gravitational parameter 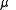 :
:
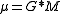
For Canonical Units, the gravitational parameter is defined as:
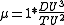
----
The quantity of the time unit (TU) can be solved in another unit system (eg. the metric system) if the mass and radius of the central body has been determined. Using the above equation and applying dimensional analysis
, set the two equations expressing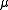 equal to each other:
equal to each other:
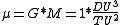
The Time unit (TU) can be converted to another unit system for a more useful qualitative solution using the following equation:
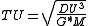
Approximate unit conversions are as follows:
Astrodynamics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It...
, A canonical unit is a unit of measurement defined in terms of an object's reference orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
. In this system, a reference mass, for example the sun, is assumed to be 1 "mass unit" and the mean distance from the orbiting object to the reference object is considered the "distance unit".
Canonical units are useful when the precise distances and masses of objects in space are not available. However, by setting the mass of a given object to be 1 mass unit and the mean distance of the reference object to another object in question, many calculations can be simplified.
Overview
The distance unit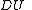 is defined to be the mean radius of the reference orbit.
is defined to be the mean radius of the reference orbit.The time unit
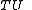 is defined by the gravitational parameter
is defined by the gravitational parameter 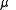 :
: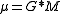
-
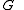 is the gravitational constantGravitational constantThe gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
is the gravitational constantGravitational constantThe gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal... -
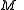 is the mass of the central reference body
is the mass of the central reference body
For Canonical Units, the gravitational parameter is defined as:
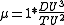
----
The quantity of the time unit (TU) can be solved in another unit system (eg. the metric system) if the mass and radius of the central body has been determined. Using the above equation and applying dimensional analysis
Dimensional analysis
In physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
, set the two equations expressing
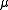 equal to each other:
equal to each other: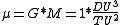
The Time unit (TU) can be converted to another unit system for a more useful qualitative solution using the following equation:
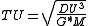
Approximate unit conversions are as follows:
- 1 DU = 6378.1 Km = 20,925,524.97 ft
- 1 DU/TU = 7.90538 Km/sec = 25,936.29 ft/sec
- 1 TU = 806.80415 sec

