
CPU power dissipation
Encyclopedia
Central processing unit power dissipation or CPU power dissipation is the process in which central processing unit
s (CPUs) consume electrical energy, and dissipate this energy both by the action of the switching devices contained in the CPU (such as transistor
s or vacuum tube
s) and by the energy lost in the form of heat
due to the impedance
of the electronic circuit
s. Designing CPUs that perform these tasks efficiently
without overheating
is a major consideration in nearly all CPU manufacturers to date.
Some implementations of CPUs use very little power, for example, the CPUs in mobile phone
s often use just a few hundred milliwatts
of electricity. Some Microcontrollers, used in embedded systems may use a few milliwatts. In comparison, CPUs in general purpose personal computer
s, such as desktops
and laptop
s, dissipate significantly more power because of their higher complexity and speed. These microelectronic CPUs may consume power in the order of a few watts to hundreds of watts. Historically, early CPUs implemented with vacuum tube
s consumed power in the order of many kilowatts.
CPUs for desktop computers typically use a significant portion of the power consumed by the computer
. Other major uses include fast video card
s, which contain graphics processing unit
s, and the power supply
. In laptops, the LCD back light also uses a significant portion of overall power. While energy-saving features
have been instituted in personal computers for when they are idle, the overall consumption of today's high-performance CPUs is considerable. This is in strong contrast with the much lower energy consumption of CPUs designed for low-power environments. One such CPU, the Intel XScale
, can run at 600 MHz with only half a watt of power, whereas x86 PC processors from Intel in the same performance bracket consume roughly eighty times as much energy.
There are some engineering reasons for this pattern.
Processor manufacturers usually release two power consumption numbers for a CPU:
For example, the Pentium 4 2.8 GHz has 68.4 W typical thermal power and 85 W maximum thermal power. When the CPU is idle, it will draw far less than the typical thermal power. The power consumed by a CPU, is approximately proportional to current CPU frequency, and to the square of the CPU voltage: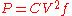
(where C is capacitance, f is frequency and V is voltage).
Datasheet
s normally contain the thermal design power
(TDP), which is the maximum amount of power the cooling system
in a computer is required to dissipate. Both Intel and Advanced Micro Devices
(AMD) have defined TDP as the maximum power consumption for thermally significant periods running worst-case non-synthetic workloads. Thus, TDP is not the actual maximum power of the processor.
In many applications, the CPU and other components are idle much of the time, so idle power contributes significantly to overall system power usage. When the CPU uses power management features to reduce energy use, other components, such as the motherboard and chipset take up a larger proportion of the computers energy. In applications where the computer is often heavily loaded, such as scientific computing, performance per watt
- how much computing the CPU does per unit of energy becomes more significant.
s and instruction-level parallelism, so that single-threaded code executed faster on newer processors with no modification. Now, to manage CPU power dissipation
, processor makers favor multi-core chip designs, and software has to be written in a multi-threaded or multi-process manner to take full advantage of the hardware. Many multi-threaded development paradigms introduce overhead, and will not see a linear increase in speed vs number of processors. This is particularly true while accessing shared or dependent resources, due to lock
contention. This effect becomes more noticeable as the number of processors increases. Recently, IBM has been exploring ways to distribute computing power more efficiently by mimicking the distributional properties of the human brain.
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
s (CPUs) consume electrical energy, and dissipate this energy both by the action of the switching devices contained in the CPU (such as transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s or vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
s) and by the energy lost in the form of heat
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
due to the impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
of the electronic circuit
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
s. Designing CPUs that perform these tasks efficiently
Energy conversion efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The useful output may be electric power, mechanical work, or heat.-Overview:...
without overheating
Thermal shock
Thermal shock is the name given to cracking as a result of rapid temperature change. Glass and ceramic objects are particularly vulnerable to this form of failure, due to their low toughness, low thermal conductivity, and high thermal expansion coefficients...
is a major consideration in nearly all CPU manufacturers to date.
Some implementations of CPUs use very little power, for example, the CPUs in mobile phone
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
s often use just a few hundred milliwatts
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
of electricity. Some Microcontrollers, used in embedded systems may use a few milliwatts. In comparison, CPUs in general purpose personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, such as desktops
Desktop computer
A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright...
and laptop
Laptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
s, dissipate significantly more power because of their higher complexity and speed. These microelectronic CPUs may consume power in the order of a few watts to hundreds of watts. Historically, early CPUs implemented with vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
s consumed power in the order of many kilowatts.
CPUs for desktop computers typically use a significant portion of the power consumed by the computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
. Other major uses include fast video card
Video card
A video card, Graphics Card, or Graphics adapter is an expansion card which generates output images to a display. Most video cards offer various functions such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors...
s, which contain graphics processing unit
Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit or GPU is a specialized circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory in such a way so as to accelerate the building of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display...
s, and the power supply
Power supply unit (computer)
A power supply unit converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of the computer. Modern personal computers universally use a switched-mode power supply...
. In laptops, the LCD back light also uses a significant portion of overall power. While energy-saving features
Power management
Power management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power state when inactive. In computing this is known as PC power management and is built...
have been instituted in personal computers for when they are idle, the overall consumption of today's high-performance CPUs is considerable. This is in strong contrast with the much lower energy consumption of CPUs designed for low-power environments. One such CPU, the Intel XScale
Intel XScale
The XScale, a microprocessor core, is Intel's and Marvell's implementation of the ARMv5 architecture, and consists of several distinct families: IXP, IXC, IOP, PXA and CE . Intel sold the PXA family to Marvell Technology Group in June 2006....
, can run at 600 MHz with only half a watt of power, whereas x86 PC processors from Intel in the same performance bracket consume roughly eighty times as much energy.
There are some engineering reasons for this pattern.
- For a given device, operating at a higher clock rateClock rateThe clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
always requires more power. Reducing the clock rate of the microprocessor through power managementPower managementPower management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power state when inactive. In computing this is known as PC power management and is built...
when possible reduces energy consumption. - New features generally require more transistorTransistorA transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s, each of which uses power. Turning unused areas off saves energy, such as through clock gatingClock gatingClock gating is a power-saving technique used in many synchronous circuits-Description:Clock gating is a popular technique used in many synchronous circuits for reducing dynamic power dissipation. Clock gating saves power by adding more logic to a circuit to prune the clock tree...
. - As a processor model's design matures, smaller transistors, lower-voltage structures, and design experience may reduce energy consumption.
Processor manufacturers usually release two power consumption numbers for a CPU:
- typical thermal power, which is measured under normal load. (for instance, AMD's Average CPU powerAverage CPU PowerThe average CPU power , is a scheme to characterize power consumption of new central processing units under "average" daily usage, especially server processors, the rating scheme is defined by Advanced Micro Devices for use in its line of processors based on the K10 microarchitecture...
) - maximum thermal power, which is measured under a worst-case load.
For example, the Pentium 4 2.8 GHz has 68.4 W typical thermal power and 85 W maximum thermal power. When the CPU is idle, it will draw far less than the typical thermal power. The power consumed by a CPU, is approximately proportional to current CPU frequency, and to the square of the CPU voltage:

(where C is capacitance, f is frequency and V is voltage).
Datasheet
Datasheet
thumb|A floppy disk controller datasheet.A datasheet, data sheet, or spec sheet is a document summarizing the performance and other technical characteristics of a product, machine, component , material, a subsystem or software in sufficient detail to be used by a design engineer to integrate the...
s normally contain the thermal design power
Thermal Design Power
The thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
(TDP), which is the maximum amount of power the cooling system
Computer cooling
Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within their safe operating temperature limits.Various cooling methods help to improve processor performance or reduce the noise of cooling fans....
in a computer is required to dissipate. Both Intel and Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. or AMD is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Sunnyvale, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for commercial and consumer markets...
(AMD) have defined TDP as the maximum power consumption for thermally significant periods running worst-case non-synthetic workloads. Thus, TDP is not the actual maximum power of the processor.
In many applications, the CPU and other components are idle much of the time, so idle power contributes significantly to overall system power usage. When the CPU uses power management features to reduce energy use, other components, such as the motherboard and chipset take up a larger proportion of the computers energy. In applications where the computer is often heavily loaded, such as scientific computing, performance per watt
Performance per watt
In computing, performance per watt is a measure of the energy efficiency of a particular computer architecture or computer hardware. Literally, it measures the rate of computation that can be delivered by a computer for every watt of power consumed....
- how much computing the CPU does per unit of energy becomes more significant.
Effect on increasing speed
For years, processor makers consistently delivered increases in clock rateClock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
s and instruction-level parallelism, so that single-threaded code executed faster on newer processors with no modification. Now, to manage CPU power dissipation
CPU power dissipation
Central processing unit power dissipation or CPU power dissipation is the process in which central processing units consume electrical energy, and dissipate this energy both by the action of the switching devices contained in the CPU and by the energy lost in the form of heat due to the impedance...
, processor makers favor multi-core chip designs, and software has to be written in a multi-threaded or multi-process manner to take full advantage of the hardware. Many multi-threaded development paradigms introduce overhead, and will not see a linear increase in speed vs number of processors. This is particularly true while accessing shared or dependent resources, due to lock
Lock (computer science)
In computer science, a lock is a synchronization mechanism for enforcing limits on access to a resource in an environment where there are many threads of execution. Locks are one way of enforcing concurrency control policies.-Types:...
contention. This effect becomes more noticeable as the number of processors increases. Recently, IBM has been exploring ways to distribute computing power more efficiently by mimicking the distributional properties of the human brain.
See also
- List of CPU power dissipation
- Power managementPower managementPower management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power state when inactive. In computing this is known as PC power management and is built...
- Advanced Configuration and Power InterfaceAdvanced Configuration and Power InterfaceIn computing, the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface specification provides an open standard for device configuration and power management by the operating system....
(ACPI) - Low-power electronicsLow-power electronicsLow-power electronics means that the consumption of electric power is deliberately low, e.g. notebook processors.- Computing elements :The density and speed of integrated-circuit computing elements have increased exponentially for several decades, following a trend described by Moore's Law...
- Voltage and frequency scaling
- Overvolting
- Undervolting
- OverclockingOverclockingOverclocking is the process of operating a computer component at a higher clock rate than it was designed for or was specified by the manufacturer, but some manufacturers purposely underclock their components to improve battery life. Many people just overclock or 'rightclock' their hardware to...
- UnderclockingUnderclockingUnderclocking, also known as downclocking, is the practice of modifying a synchronous circuit's timing settings to run at a lower clock rate than it was specified to operate at. It may be said to be the computer equivalent of driving a car below the speed limit...
- Performance per wattPerformance per wattIn computing, performance per watt is a measure of the energy efficiency of a particular computer architecture or computer hardware. Literally, it measures the rate of computation that can be delivered by a computer for every watt of power consumed....
- IT energy managementIT energy managementIT energy management is the analysis and management of energy demand within the information technology arena. IT energy demand accounts for approximately 2% of global CO2 emissions, approximately the same level as aviation...
- Green computingGreen computingGreen computing or green IT, refers to environmentally sustainable computing or IT. In the article Harnessing Green IT: Principles and Practices, San Murugesan defines the field of green computing as "the study and practice of designing, manufacturing, using, and disposing of computers, servers,...
- Moore's lawMoore's LawMoore's law describes a long-term trend in the history of computing hardware: the number of transistors that can be placed inexpensively on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years....
External links
- CPU Reference for all vendors. Process node, die size, speed, power, instruction set, etc.
- Processor Electrical Specifications
- SizingLounge – Online calculation tool for server energy costs.
- For specification on Intel processors.

