
Bremer Straßenbahn AG
Encyclopedia
| Bremer Straßenbahn AG | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||
| Information | |||
| Head offices | Flughafendamm 12 28199 Bremen www.bsag.de |
||
| Transport association Transport association In the United Kingdom and other countries, a transport association is an association of public transport authorities in a large urban area. The modes of transport can include both private and government owned bodies.In aims of a transport association are... |
Verkehrsverbund Bremen Niedersachsen | ||
| Employees | 2150 (2004) | ||
| Gauge Rail gauge Track gauge or rail gauge is the distance between the inner sides of the heads of the two load bearing rails that make up a single railway line. Sixty percent of the world's railways use a standard gauge of . Wider gauges are called broad gauge; smaller gauges, narrow gauge. Break-of-gauge refers... |
1435 mm | ||
| Lines | |||
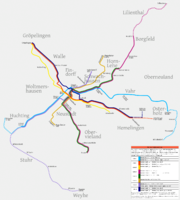
| Tramway lines | 8 (2005) 3 express lines |
||
| Bus lines | 46 (2004) | ||
| Vehicles | |||
| Tramway (2006-03) |
77 low floor trams GT8N 6 low floor trams GT8N-1 40 articulated trams 7 museal vehicles 15 work vehicles. |
||
| Omnibus (2006-03) |
72 low floor buses 140 low floor bendy buses 3 minibuses 1 coach Coach (vehicle) A coach is a large motor vehicle, a type of bus, used for conveying passengers on excursions and on longer distance express coach scheduled transport between cities - or even between countries... |
||
| Statistics | |||
| Passengers (per year) | 96,900,000 mio (2004) | ||
| Passengers (per day) | 266,000 (2004) | ||
| Transport volume (per year) | 22,100,000 km (2004) | ||
| Source: Geschäftsbericht 2004 |
|||
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
as Bremen Tramways Corporation), often abbreviated BSAG, is the public transport
Public transport
Public transport is a shared passenger transportation service which is available for use by the general public, as distinct from modes such as taxicab, car pooling or hired buses which are not shared by strangers without private arrangement.Public transport modes include buses, trolleybuses, trams...
provider for Bremen
Bremen
The City Municipality of Bremen is a Hanseatic city in northwestern Germany. A commercial and industrial city with a major port on the river Weser, Bremen is part of the Bremen-Oldenburg metropolitan area . Bremen is the second most populous city in North Germany and tenth in Germany.Bremen is...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, offering tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
way and bus
Bus
A bus is a road vehicle designed to carry passengers. Buses can have a capacity as high as 300 passengers. The most common type of bus is the single-decker bus, with larger loads carried by double-decker buses and articulated buses, and smaller loads carried by midibuses and minibuses; coaches are...
services.
Horse tramway
On March 28, 1876 the Actiengesellschaft Bremer Pferdebahn was founded. The enterprise opened a horse tramway line from Herdentor to Vahrster Brücke on June 4, 1876, extending the line to Horn in 1877. In 1883, the extension from Herdentor to the stock exchangeStock exchange
A stock exchange is an entity that provides services for stock brokers and traders to trade stocks, bonds, and other securities. Stock exchanges also provide facilities for issue and redemption of securities and other financial instruments, and capital events including the payment of income and...
in the city centre was opened.
The rival company Große Bremer Pferdebahn, which used British capital, opened a line from Hastedt to Walle on 3 November 1879; today's line 2 partly follows the trajectory of that horse line. Both companies extended their network, and lines were opened to Freihafen (1888), Hohentor (1889) and Arsterdamm (1880/1884).
Electric tramway
In 1890, the line from the stock exchange to the Bürgerweide exhibition grounds was electrified as a trial for the duration of an exhibition. After the exhibition ended, the catenary was removed, but the system had worked so well that it was decided to electrify all tramways. Electrification started in 1892, and lasted until 1913. By then the network was fully electrified, with the exception of the Freihafen line, which had since been abandoned. Meanwhile, Große Bremer Pferdebahn merged with the Bremer Pferdebahn (which had renamed itself to Bremer Straßenbahn in 1890) in 1899.In 1908, line numbers were introduced. By 1939, the network consisted of the following lines:
- 1: Ringbahn
- 2: Gröpelingen - Markt - Sebalsdsbrück
- 3: AG Weser - Markt - Hohwisch
- 4: Horn - Bahnhof - Markt - Arsterdamm
- 5: Flughafen - Markt - Bahnhof - Hemmstraße
- 6: Vulkanstraße - Brill - Bahnhof - Hemmstraße
- 7: Hartwigstraße - Bahnhof - Markt - Rablinghausen
- 8: Gröpelingen - Burg
- 10: Friedrich-Karl-Straße - Bahnhof - Waller Bahnhof
- 11: AG Weser - Norddeutsche Hütte
- 12: Sebaldsbrück - Osterholzer Friedhof
- 15: Hemmstraße - Bahnhof - Markt - Pappelstraße - Emder Straße (über Westbrücke)
- 16: Gastfeldstraße - Brill - Bahnhof - Wachmannstraße
The system suffered severe damage during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
- tramway services were abandoned on April 22, 1945. After WWII had ended, only 10% of the rolling stock were in working order, and 80% of the catenary had been damaged.
World War II aftermath
On June 13, 1945 the first tramways went into operation again. In the immediate WWII aftermath, the Bremen network consisted of two parts, as the bridges over the river Weser had been destroyed. In 1947, the connection between the two parts of the network was made, and apart from the tramway line over the Stephanibrücke, the 1950s BSAG network reached its pre-war spread.In 1953, bus traffic was taken over by the BSAG. The new workshop Flughafendamm near Bremen Airport
Bremen Airport
Bremen Airport or Flughafen Bremen serves the German city of Bremen and is located south of the city. There were 2.4 million passengers in 2008.-History:The beginnings of the airport date back to the early 20th century...
was constructed in 1959; in 1963 the head offices moved to that site also.
In 1965, the main stepover stop was moved from the marketplace to Domsheide.
Line closures
Bremen, like other cities in the world, had lines close in the 1950s and 1960s due to increased use of automobiles. On the following lines, service was abandoned:- Line 8 1949 (TrolleybusTrolleybusA trolleybus is an electric bus that draws its electricity from overhead wires using spring-loaded trolley poles. Two wires and poles are required to complete the electrical circuit...
at first, from 1961 diesel bus) - Line 12 1952
- Line 10 in St.-Jürgen-Straße
- Line 5 1964
- Line 7 1965
- Line 6 1965/67. The rails in Pappelstraße were used until 2001.
- Line 11 1970
- Line 4 1972, the section Kirchbachstraße - Arsterdamm had been taken over in 1967 by the new Line 1. The line reopens in 1998.
Lines 15 and 16 were renumberd to lines 5 and 6 in 1967.
Network extensions
However, some lines were also notably extended:- Line 3 to Gröpelingen 1949
- Line 16 to Grolland 1955, from 1976 (then line 6) to Huchting
- Line 6 to Gastfeldstraße 1955 (closed in 1967)
- Line 16 to Riensberg 1959
- Line 15 to Kulenkampffallee 1960
- Line 10 to Georg-Bitter-Straße 1963, to Sebaldsbrück and Gröpelingen 1975. The rails in Georg-Bitter-Straße continue to be used by extra trains.
- Line 1; new line Arsterdamm - Blockdiek, extended 1968 to Osterholz, from 1973 to Arsten, renamed to line 4 and extended to Arsten Süd on 7 December 1998.
- Line 4 reopened to Horn-Lehe 23 May 1998, extension to Borgfeld on 6 December 2002.
- Line 6 newly built between Flughafendamm and Flughafen, replaces old part of Line 5 on 23 May 1998.
- Line 6 extension between Riensberg and Universität, opened October 10, 1998.
GT4
The oldest vehicles still in active service are the articulated tramcars GT4d, GT4e and GT4f and the fitting trailers GB4d, GB4e and GB4f. The vehicles were built from 1973 to 1977 by Wegmann & Co. in KasselKassel
Kassel is a town located on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Kassel Regierungsbezirk and the Kreis of the same name and has approximately 195,000 inhabitants.- History :...
. Of the 61 trams and 57 trailers originally delivered, four GT4f-vehicles are still in service, though this is limited to the purposes of the tram driving school, and other special occasions. The rest has been demolished or delivered to Timişoara
Timisoara
Timișoara is the capital city of Timiș County, in western Romania. One of the largest Romanian cities, with an estimated population of 311,586 inhabitants , and considered the informal capital city of the historical region of Banat, Timișoara is the main social, economic and cultural center in the...
in Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
.
GT8N
In the late 1990s, the Hansa-built stock dating from the 1960s was scheduled for replacement. Since the BSAG had already invested in low-floor buses, low-floor tram vehicles were wanted as well. In 1990, the BSAG presented a prototypePrototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
to the public. This three-part articulated car was the world's first 100% low floor tram. From 1993 to 1996, 78 low-floor trams, called GT8N, were ordered from AEG
AEG
Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft was a German producer of electrical equipment founded in 1883 by Emil Rathenau....
. Their main difference to the prototype is that they have four parts instead of three, hence offering more space and thus more beneficial for wheelchair users. One vehicle has been taken out of service after an accident, the prototype was sold to the Norrköping
Norrköping
Norrköping is a city in the province of Östergötland in eastern Sweden and the seat of Norrköping Municipality, Östergötland County. The city has a population of 87,247 inhabitants in 2010, out of a municipal total of 130,050, making it Sweden's tenth largest city and eighth largest...
tramways in Sweden in 1999.
GT8N-1

The first car was delivered in September 2005, a total number of 20 trams is ordered from Bombardier. Furthermore an option of 23 additional vehicles can be honoured.
The GT8N-1 is the second generation of low floor tramcars in Bremen. Its task is to replace older GT4 Wegmann vehicles and to increase the comfort for BSAG passengers. Therefore in comparison to the older GT8N low floor cars several changes have been made. The width of the car has been enlarged to 2.65 m, that makes the interior more spacious and allows the introduction of four seats in wide range, altogether 106 seats are available. Also an air-condition for the passengers is installed, five low floor doorways and a lift for disabled passengers facilitate the entry for all passengers.
The vehicle has an overall length of 35,400 mm and a reaches a maximum speed of 70 km/h. It consists of three sections with a total of four bogies. Two of them carrying are the middle section of the car, the two end sections are carried by one bogie each of them. The end section bogies are driven, that's why above them it was not possible to realise a low floor like in the other parts of the car, altogether the GT8N-1 has 74 % low floor.
The car is uni-directional for the use in BSAG's tramway network. It is also possible to build a similar bi-directional, two-systems vehicle that can also be used on DB tracks and so may connect BSAG's inner-city tramway network with railway lines.
The GT8N-1 is based on Bombardier's FLEXITY Classic modular tramcar concept. Vehicles of that type run in several cities in Germany and also in Poland and Australia, the first car of this family was the 8NGTW, delivered in 1997 to KVG Kassel.
Historic BSAG cars

- car Nr. 49 from 1900 (the only car which is only allowed to operate without passengers)
- car Nr. 134 from 1904 (the only car not in original design, in the design of 1939, see picture right side)
- car Nr. 701 from 1947 (see picture left side)
- GT3-car Nr. 917 from 1957 (special construchtion with 3 axles, see middle of picture)
- T4-car Nr. 811 / 1806 from 1954
- GT4GT4 (Bremen)The Bremish GT4 is a tramcar that was built in two main versions form 1959 to the 1980s.In the 1950s and 1960s, the Bremish tram company BSAG, like many other German tram companies, changed old two-axle tramcars for modern ones on bogies. The cars could be longer, if they were articulated...
-car Nr. 446 / 1458 from 1967

