
Branched-chain amino acids
Encyclopedia
A branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) is an amino acid
having aliphatic side-chains
with a branch (a carbon
atom bound to more than two other carbon atoms). Among the proteinogenic amino acid
s, there are three BCAAs: leucine
, isoleucine
and valine
.
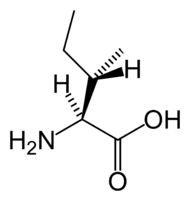
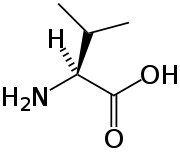 The BCAAs are among the nine essential amino acids for humans, accounting for 35% of the essential amino acids in muscle proteins and 40% of the preformed amino acids required by mammals . BCAA’s have been used clinically to aid in the recovery of burn victims . They are also used in the treatment in some cases of hepatic encephalopathy
The BCAAs are among the nine essential amino acids for humans, accounting for 35% of the essential amino acids in muscle proteins and 40% of the preformed amino acids required by mammals . BCAA’s have been used clinically to aid in the recovery of burn victims . They are also used in the treatment in some cases of hepatic encephalopathy
.
A recent study suggested that the reduction in blood BCAAs may be associated with the improvement in blood sugar regulation. The mechanism remains unknown.
(BCKDH). A deficiency of this complex leads to a buildup of the branched-chain amino acid (leucine
, isoleucine
, and valine
) and their toxic by-products in the blood and urine, giving the condition the name maple syrup urine disease
.
The BCKDH complex converts branched-chain amino acids into Acyl-CoA
derivatives, which after subsequent reactions are converted either into acetyl-CoA
or succinyl-CoA
that enter the citric acid cycle
.
Enzymes involved are branched chain aminotransferase
and 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase
.
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
having aliphatic side-chains
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
with a branch (a carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atom bound to more than two other carbon atoms). Among the proteinogenic amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acids are those amino acids that can be found in proteins and require cellular machinery coded for in the genetic code of any organism for their isolated production. There are 22 standard amino acids, but only 21 are found in eukaryotes. Of the 22, 20 are directly encoded by...
s, there are three BCAAs: leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA....
and valine
Valine
Valine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar...
.


Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is the occurrence of confusion, altered level of consciousness and coma as a result of liver failure. In the advanced stages it is called hepatic coma or coma hepaticum...
.
A recent study suggested that the reduction in blood BCAAs may be associated with the improvement in blood sugar regulation. The mechanism remains unknown.
Degradation
Degradation of branched-chain amino acids involves the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexBranched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex
The branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase complex is a combination of enzymes responsible for the degradation of the branched-chain amino acids...
(BCKDH). A deficiency of this complex leads to a buildup of the branched-chain amino acid (leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA....
, and valine
Valine
Valine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar...
) and their toxic by-products in the blood and urine, giving the condition the name maple syrup urine disease
Maple syrup urine disease
Maple syrup urine disease , also called branched-chain ketoaciduria, is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting branched-chain amino acids. It is one type of organic acidemia...
.
The BCKDH complex converts branched-chain amino acids into Acyl-CoA
Acyl-CoA
Acyl-CoA is a group of coenzymes involved in the metabolism of fatty acids. It is a temporary compound formed when coenzyme A attaches to the end of a long-chain fatty acid inside living cells. The compound undergoes beta oxidation, forming one or more molecules of acetyl-CoA...
derivatives, which after subsequent reactions are converted either into acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA is an important molecule in metabolism, used in many biochemical reactions. Its main function is to convey the carbon atoms within the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. In chemical structure, acetyl-CoA is the thioester...
or succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-Coenzyme A, abbreviated as Succinyl-CoA or SucCoA, is a combination of succinic acid and coenzyme A.-Source:It is an important intermediate in the citric acid cycle, where it is synthesized from α-Ketoglutarate by α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through decarboxylation...
that enter the citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
.
Enzymes involved are branched chain aminotransferase
Branched chain aminotransferase
Branched chain aminotransferase is an aminotransferase enzyme which acts upon branched-chain amino acids. It uses largely α-ketoglutarate in forming branched chain α-keto acids and glutamate....
and 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase
3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe 3 substrates of this enzyme are 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate, dihydrolipoyllysine-residue transferase, and lipoyllysine, whereas its 3 products are dihydrolipoyllysine-residue transferase,...
.


