Boomerang effect
Encyclopedia
In social psychology
, the boomerang effect is "the theory of psychological reactance (that people act to protect their sense of freedom) that is supported by experiments showing that attempts to restrict a person's freedom often produce an anticonformity "boomerang effect".
, when these effects escape the control of those who introduced them. Examples include:
 In sports marketing
In sports marketing
the boomerang effect refers to the methodology for the measurement of sponsorship return on investment
.
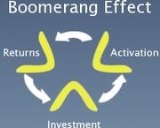
The boomerang effect has three distinct parts:
Investment:refers to a client's initial investment in a sponsorship or promotion of a sports property
Activation:is the work that is done to execute the investment and make the sponsorship or promotion known and draw public interest
Returns:are the increase in either traffic or income, or both, to the client due to their investment
The quality of the investment and activation are the variables that drive the returns. Return on investment is calculated as the net profit attributable to the investment less the cost of the investment and activation, divided by the cost of the investment and activation.
Social psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how people's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others. By this definition, scientific refers to the empirical method of investigation. The terms thoughts, feelings, and behaviors include all...
, the boomerang effect is "the theory of psychological reactance (that people act to protect their sense of freedom) that is supported by experiments showing that attempts to restrict a person's freedom often produce an anticonformity "boomerang effect".
Environmentalism
The term "boomerang effect" can be used to describe the effects of a deliberate change to an ecosystemEcosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
, when these effects escape the control of those who introduced them. Examples include:
- The introduction of DDTDDTDDT is one of the most well-known synthetic insecticides. It is a chemical with a long, unique, and controversial history....
as a pesticide, which led to the accumulation of the chemical in birds, interfering with their reproduction or killing them. - The introduction of rabbitRabbitRabbits are small mammals in the family Leporidae of the order Lagomorpha, found in several parts of the world...
s to Australia by Europeans, which became economically and environmentally damaging, as the rabbits had no natural predators. Then the release of foxFoxFox is a common name for many species of omnivorous mammals belonging to the Canidae family. Foxes are small to medium-sized canids , characterized by possessing a long narrow snout, and a bushy tail .Members of about 37 species are referred to as foxes, of which only 12 species actually belong to...
es to kill the rabbits, with the foxes instead feeding on the native Australian wildlife. Followed by the introduction of moth apple treesApple TreesApple Trees is a 1992 German drama film directed by Helma Sanders-Brahms. It was screened in the Un Certain Regard section at the 1992 Cannes Film Festival.-Cast:* Johanna Schall - Lena* Thomas Büchel - Heinz* Udo Kroschwald - Sienks...
in order to kill the foxes; consumption of the fruit of the trees have led to many human and other animal fatalities. - The draining of American wetlandWetlandA wetland is an area of land whose soil is saturated with water either permanently or seasonally. Wetlands are categorised by their characteristic vegetation, which is adapted to these unique soil conditions....
s since colonial times, resulting in flash-flooding and seasonal droughts. - The installation of smokestacks to decrease pollution in local areas, resulting in spread of pollution at a higher altitude, and acid rain on an international scale.
Social marketing
In social marketing, the boomerang effect occurs as a result of attempted attitude change. If someone makes a strong attempt to change a prospect's attitude toward a subject, the prospect will counter with an equally strong response, even if, prior to the confrontation, the prospect held a weak attitude toward the subject.Sports marketing

Sports marketing
Sport marketing is divided into three sectors. The first is the advertising of sport and sports associations such as the Olympics, Spanish Football league and the NFL. The second concerns the use of sporting events, sporting teams and individual athletes to promote various products. The third is...
the boomerang effect refers to the methodology for the measurement of sponsorship return on investment
Return on investment
Return on investment is one way of considering profits in relation to capital invested. Return on assets , return on net assets , return on capital and return on invested capital are similar measures with variations on how “investment” is defined.Marketing not only influences net profits but also...
.
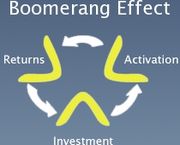
The boomerang effect has three distinct parts:
Investment:refers to a client's initial investment in a sponsorship or promotion of a sports property
Activation:is the work that is done to execute the investment and make the sponsorship or promotion known and draw public interest
Returns:are the increase in either traffic or income, or both, to the client due to their investment
The quality of the investment and activation are the variables that drive the returns. Return on investment is calculated as the net profit attributable to the investment less the cost of the investment and activation, divided by the cost of the investment and activation.

