Boomerang attack
Encyclopedia
Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties...
, the boomerang attack is a method for the cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis is the study of methods for obtaining the meaning of encrypted information, without access to the secret information that is normally required to do so. Typically, this involves knowing how the system works and finding a secret key...
of block cipher
Block cipher
In cryptography, a block cipher is a symmetric key cipher operating on fixed-length groups of bits, called blocks, with an unvarying transformation. A block cipher encryption algorithm might take a 128-bit block of plaintext as input, and output a corresponding 128-bit block of ciphertext...
s based on differential cryptanalysis
Differential cryptanalysis
Differential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable primarily to block ciphers, but also to stream ciphers and cryptographic hash functions. In the broadest sense, it is the study of how differences in an input can affect the resultant difference at the output...
. The attack was published in 1999 by David Wagner, who used it to break the COCONUT98
COCONUT98
In cryptography, COCONUT98 is a block cipher designed by Serge Vaudenay in 1998...
cipher.
The boomerang attack has allowed new avenues of attack for many ciphers previously deemed safe from differential cryptanalysis.
Refinements on the boomerang attack have been published: the amplified boomerang attack, then the rectangle attack.
The attack
The boomerang attack is based on differential cryptanalysisDifferential cryptanalysis
Differential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable primarily to block ciphers, but also to stream ciphers and cryptographic hash functions. In the broadest sense, it is the study of how differences in an input can affect the resultant difference at the output...
. In differential cryptanalysis, an attacker exploits how differences in the input to a cipher (the plaintext) can affect the resultant difference at the output (the ciphertext). A high-probability "differential" (that is, an input difference that will produce a likely output difference) is needed that covers all, or nearly all, of the cipher. The boomerang attack allows differentials to be used which cover only part of the cipher.
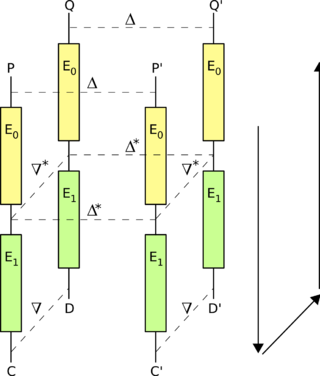
The attack attempts to generate a so-called "quartet" structure at a point halfway through the cipher. For this purpose, say that the encryption action, E, of the cipher can be split into two consecutive stages, E0 and E1, so that E(M) = E1(E0(M)), where M is some plaintext message. Suppose we have two differentials for the two stages; say,

for E0, and
 for E1-1 (the decryption action of E1).
for E1-1 (the decryption action of E1).The basic attack proceeds as follows:
- Choose a random plaintext
 and calculate
and calculate  .
. - Request the encryptions of
 and
and  to obtain
to obtain  and
and 
- Calculate
 and
and 
- Request the decryptions of
 and
and  to obtain
to obtain  and
and 
- Compare
 and
and  ; when the differentials hold,
; when the differentials hold,  .
.
Application to specific ciphers
One attack on KASUMI, a block cipher used in 3GPP3GPP
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project is a collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations, known as the Organizational Partners...
, is a related-key rectangle attack which breaks the full eight rounds of the cipher faster than exhaustive search (Biham et al., 2005). The attack requires 254.6 chosen plaintexts, each of which has been encrypted under one of four related keys, and has a time complexity equivalent to 276.1 KASUMI encryptions.
External links
- Boomerang attack — explained by John Savard
- Nathan Keller's homepage

