Bimodal distribution
Overview
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
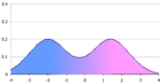
, a bimodal distribution is a continuous probability distribution with two different mode
Mode (statistics)
In statistics, the mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a data set or a probability distribution. In some fields, notably education, sample data are often called scores, and the sample mode is known as the modal score....
s. These appear as distinct peaks (local maxima) in the probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
, as shown in Figure 1.
Examples of variables with bimodal distributions include the time between eruptions of certain geyser
Geyser
A geyser is a spring characterized by intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by a vapour phase . The word geyser comes from Geysir, the name of an erupting spring at Haukadalur, Iceland; that name, in turn, comes from the Icelandic verb geysa, "to gush", the verb...
s, the color of galaxies
Galaxy color-magnitude diagram
The Galaxy color-magnitude diagram shows the relationship between absolute magnitude, luminosity, and mass of galaxies. A preliminary description of the three areas of this diagram was made in 2003 by Eric F. Bell et al...
, the size of worker weaver ants, the age of incidence of Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin's lymphoma, previously known as Hodgkin's disease, is a type of lymphoma, which is a cancer originating from white blood cells called lymphocytes...
, the speed of inactivation of the drug isoniazid
Isoniazid
Isoniazid , also known as isonicotinylhydrazine , is an organic compound that is the first-line antituberculosis medication in prevention and treatment. It was first discovered in 1912, and later in 1951 it was found to be effective against tuberculosis by inhibiting its mycolic acid...
in US adults, and the absolute magnitude of nova
Nova
A nova is a cataclysmic nuclear explosion in a star caused by the accretion of hydrogen on to the surface of a white dwarf star, which ignites and starts nuclear fusion in a runaway manner...
e.
A bimodal distribution most commonly arises as a mixture of two different unimodal distributions (i.e.

