
Biexciton
Encyclopedia
Biexcitons are created from two free excitons.
The basic quantum operations can be performed on a sequence of pairs of physically distinguishable quantum bits and, therefore, can be illustrated by a simple four-level system.
In an optically driven system where the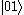 and
and 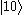 states can be directly excited, direct excitation of the upper
states can be directly excited, direct excitation of the upper 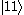 level from the ground state
level from the ground state 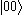 is usually forbidden and the most efficient alternative is coherent nondegenerate two-photon excitation, using
is usually forbidden and the most efficient alternative is coherent nondegenerate two-photon excitation, using 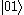 or
or 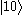 as an intermediate state.
as an intermediate state.
At high exciton
densities in some materials, the formation of exciton
molecules called biexcitons is also observed.
This is the equivalent process to the formation of an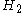 molecule from two isolated hydrogen
molecule from two isolated hydrogen
atoms.
Biexcitons have been observed in a number of compound semiconductors, including CdS, ZnSe, ZnO and especially copper chloride.
CuCl has a band gap at 3.40 eV, and the ground state exciton
is observed at 3.20 eV, implying that Rx = 0.2 eV.
At high densities, a new feature is observed in the absorption spectrum at 3.18 eV.
This is attributed to biexciton formation.
The energy difference between the two features tells us that the binding energy of the biexciton is 0.02 eV.
Attempts to observe biexcitons in materials like GaAs have been hindered by the nonlinear saturation effects described.
(a) excitation from the one-exciton
band to the biexciton band (pump-probe experiments);
(b) two-photon absorption of light from the ground state to the biexciton state;
(c) luminescence
from a biexciton state made up from two free excitons in a dense exciton
system.
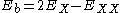
where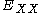 is the biexciton energy,
is the biexciton energy, 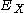 is the exciton
is the exciton
energy, and
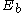 is the biexciton binding energy.
is the biexciton binding energy.
When a biexciton is annihilated, it disintegrates into a free exciton
and a photon. The energy of the photon is smaller than that of the biexciton by the biexciton binding energy,
so the biexciton luminescence
peak appears on the low-energy side of the exciton
peak. See Figure 1 in Reference 8.
The biexciton binding energy in semiconductor quantum dots has been the subject of extensive theoretical study. Because a biexciton is a composite of two electrons and two holes, we must solve a four-body problem under spatially restricted conditions. The biexciton binding energies for CuCl quantum dots, as measured by the site selective luminescence
method, increased with decreasing quantum dot
size. The data were well fitted by the function
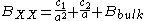
where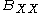 is biexciton binding energy,
is biexciton binding energy,  is the radius of the quantum dots,
is the radius of the quantum dots, 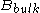 is the binding energy of bulk crystal, and
is the binding energy of bulk crystal, and 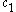 and
and 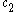 are fitting parameters.
are fitting parameters.
of the system consisting of two electrons (1, 2) and two holes (a, b) is given by
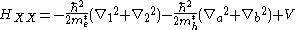
where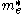 and
and 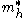 are the effective masses of electrons and holes, respectively, and
are the effective masses of electrons and holes, respectively, and
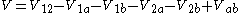
where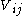 denotes the Coulomb interaction between the charged particles
denotes the Coulomb interaction between the charged particles 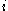 and
and 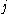 (
(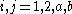 denote the two electrons and two holes in the biexciton) given by
denote the two electrons and two holes in the biexciton) given by
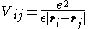
where is the dielectric constant of the material.
is the dielectric constant of the material.
Denoting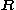 and
and  are the c.m. coordinate and the relative coordinate of the biexciton, respectively, and
are the c.m. coordinate and the relative coordinate of the biexciton, respectively, and 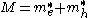 is the effective mass
is the effective mass
of the exciton
, the Hamiltonian becomes
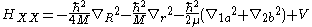
where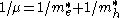 ;
; 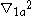 and
and 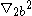 are the Laplacians with respect to relative coordinates between electron and hole, respectively.
are the Laplacians with respect to relative coordinates between electron and hole, respectively.
And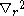 is that with respect to relative coordinate between the c. m. of excitons, and
is that with respect to relative coordinate between the c. m. of excitons, and 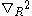 is that with respect to the c. m. coordinate
is that with respect to the c. m. coordinate 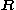 of the system.
of the system.
In the units of the exciton
Rydberg and Bohr radius
, the Hamiltonian can be written in dimensionless form
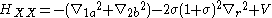
where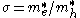 with neglecting kinetic energy operator of c. m. motion. And
with neglecting kinetic energy operator of c. m. motion. And 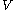 can be written as
can be written as
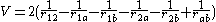
To solve the problem of the bound states of the biexciton complex, it is required to find the wave functions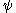 satisfying the wave equation
satisfying the wave equation
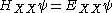
If the eigenvalue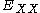 can be obtained, the binding energy of the biexciton can be also acquired
can be obtained, the binding energy of the biexciton can be also acquired
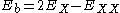
where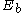 is the binding energy of the biexciton and
is the binding energy of the biexciton and 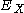 is the energy of exciton
is the energy of exciton
.
in a wide diameter range.
Thus, a biexciton binding energy exceeding the inhomogeneous exciton
line width is predicted for a wide range of nanotubes.
The biexciton binding energy in carbon nanotube is quite accurately approximated by an inverse dependence on , except perhaps for the smallest values of
, except perhaps for the smallest values of  .
.
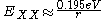
The actual biexciton binding energy is inversely proportional to the physical nanotube radius.
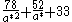 (meV)
(meV)
where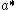 is the effective radius of microcrystallites in a unit of nm. The enhanced Coulomb interaction in microcrystallites still increase the biexciton binding energy in the large-size regime, where the quantum confinement energy of excitons is not considerable.
is the effective radius of microcrystallites in a unit of nm. The enhanced Coulomb interaction in microcrystallites still increase the biexciton binding energy in the large-size regime, where the quantum confinement energy of excitons is not considerable.
of biexcitons (XX), which can be regarded as an entity of two weakly bound excitons (X), is often discussed in a simple way of argumentation:
The recombination of any of the two excitons forming the biexciton will result in its disappearance.
Therefore one would expect that the biexciton lifetime
,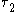 , is about half of that of the exciton
, is about half of that of the exciton
,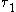 .
.
However, some elementary points of view should be taken into account.
For example, a direct radiative recombination into the ground state of the crystal, allowed for the exciton
state, is optically forbidden for singlet biexcitons.
Furthermore, the spin structure and the Coulomb interaction of the electrons and the holes forming the excitons and the biexcitons has to be considered.
In a CdSe/ZnSe quantum dot
, the lifetime of biexciton is measured as 310 ps, and that of exciton
is about 290 ps.
The ratio of the two lifetimes
is not about 2, but about 1.
The final state of the biexciton recombination is an optically allowed (bright) exciton
state.
Because of exchange interaction, the excitons are split into optically allowed states (bright,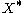 ) and optically forbidden states (dark,
) and optically forbidden states (dark, 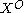 ).
).
The spin flip time between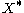 and
and 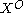 states,
states, 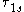 , is expected to be in the range of several ns, i.e., much longer than the bright exciton
, is expected to be in the range of several ns, i.e., much longer than the bright exciton
lifetime.
The time evolution of the probabilities for the population of the biexciton and exciton
states,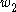 and
and 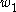 , respectively:
, respectively:
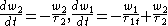
with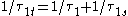 , where
, where 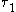 and
and 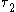 are the
are the 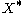 and the XX radiative recombination times, respectively.
and the XX radiative recombination times, respectively.
Solving this equation system, the X and XX dynamics can be described quantitatively.
As a result, while decay of XX is monoexponential, the onset of the X line is significantly delayed, resulting in a plateaulike characteristics of the exciton
decay curve.
Formation of biexcitons
In quantum information and computation, it is essential to construct coherent combinations of quantum states.The basic quantum operations can be performed on a sequence of pairs of physically distinguishable quantum bits and, therefore, can be illustrated by a simple four-level system.
In an optically driven system where the
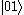 and
and 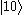 states can be directly excited, direct excitation of the upper
states can be directly excited, direct excitation of the upper 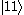 level from the ground state
level from the ground state 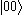 is usually forbidden and the most efficient alternative is coherent nondegenerate two-photon excitation, using
is usually forbidden and the most efficient alternative is coherent nondegenerate two-photon excitation, using 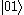 or
or 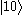 as an intermediate state.
as an intermediate state.At high exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
densities in some materials, the formation of exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
molecules called biexcitons is also observed.
This is the equivalent process to the formation of an
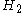 molecule from two isolated hydrogen
molecule from two isolated hydrogenHydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atoms.
Biexcitons have been observed in a number of compound semiconductors, including CdS, ZnSe, ZnO and especially copper chloride.
CuCl has a band gap at 3.40 eV, and the ground state exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
is observed at 3.20 eV, implying that Rx = 0.2 eV.
At high densities, a new feature is observed in the absorption spectrum at 3.18 eV.
This is attributed to biexciton formation.
The energy difference between the two features tells us that the binding energy of the biexciton is 0.02 eV.
Attempts to observe biexcitons in materials like GaAs have been hindered by the nonlinear saturation effects described.
Observation of biexcitons
Three possibilities of observing biexcitons exist:(a) excitation from the one-exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
band to the biexciton band (pump-probe experiments);
(b) two-photon absorption of light from the ground state to the biexciton state;
(c) luminescence
Luminescence
Luminescence is emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; it is thus a form of cold body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions, or stress on a crystal. This distinguishes luminescence from incandescence, which is light emitted by a...
from a biexciton state made up from two free excitons in a dense exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
system.
Binding energy of biexcitons
The biexciton is a quasi-particle formed from two excitons, and its energy is expressed as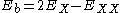
where
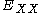 is the biexciton energy,
is the biexciton energy, 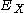 is the exciton
is the excitonExciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
energy, and
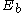 is the biexciton binding energy.
is the biexciton binding energy.When a biexciton is annihilated, it disintegrates into a free exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
and a photon. The energy of the photon is smaller than that of the biexciton by the biexciton binding energy,
so the biexciton luminescence
Luminescence
Luminescence is emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; it is thus a form of cold body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions, or stress on a crystal. This distinguishes luminescence from incandescence, which is light emitted by a...
peak appears on the low-energy side of the exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
peak. See Figure 1 in Reference 8.
The biexciton binding energy in semiconductor quantum dots has been the subject of extensive theoretical study. Because a biexciton is a composite of two electrons and two holes, we must solve a four-body problem under spatially restricted conditions. The biexciton binding energies for CuCl quantum dots, as measured by the site selective luminescence
Luminescence
Luminescence is emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; it is thus a form of cold body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions, or stress on a crystal. This distinguishes luminescence from incandescence, which is light emitted by a...
method, increased with decreasing quantum dot
Quantum dot
A quantum dot is a portion of matter whose excitons are confined in all three spatial dimensions. Consequently, such materials have electronic properties intermediate between those of bulk semiconductors and those of discrete molecules. They were discovered at the beginning of the 1980s by Alexei...
size. The data were well fitted by the function
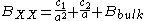
where
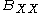 is biexciton binding energy,
is biexciton binding energy,  is the radius of the quantum dots,
is the radius of the quantum dots, 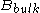 is the binding energy of bulk crystal, and
is the binding energy of bulk crystal, and 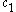 and
and 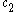 are fitting parameters.
are fitting parameters.A simple model for describing binding energy of biexcitons
In the effective-mass approximation, the HamiltonianHamiltonian (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, the Hamiltonian H, also Ȟ or Ĥ, is the operator corresponding to the total energy of the system. Its spectrum is the set of possible outcomes when one measures the total energy of a system...
of the system consisting of two electrons (1, 2) and two holes (a, b) is given by
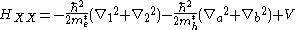
where
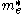 and
and 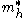 are the effective masses of electrons and holes, respectively, and
are the effective masses of electrons and holes, respectively, and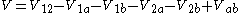
where
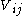 denotes the Coulomb interaction between the charged particles
denotes the Coulomb interaction between the charged particles 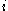 and
and 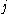 (
(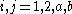 denote the two electrons and two holes in the biexciton) given by
denote the two electrons and two holes in the biexciton) given by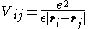
where
 is the dielectric constant of the material.
is the dielectric constant of the material.Denoting
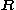 and
and  are the c.m. coordinate and the relative coordinate of the biexciton, respectively, and
are the c.m. coordinate and the relative coordinate of the biexciton, respectively, and 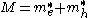 is the effective mass
is the effective massEffective mass
In solid state physics, a particle's effective mass is the mass it seems to carry in the semiclassical model of transport in a crystal. It can be shown that electrons and holes in a crystal respond to electric and magnetic fields almost as if they were particles with a mass dependence in their...
of the exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
, the Hamiltonian becomes
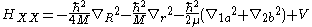
where
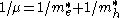 ;
; 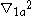 and
and 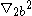 are the Laplacians with respect to relative coordinates between electron and hole, respectively.
are the Laplacians with respect to relative coordinates between electron and hole, respectively.And
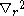 is that with respect to relative coordinate between the c. m. of excitons, and
is that with respect to relative coordinate between the c. m. of excitons, and 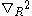 is that with respect to the c. m. coordinate
is that with respect to the c. m. coordinate 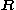 of the system.
of the system.In the units of the exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
Rydberg and Bohr radius
Bohr radius
The Bohr radius is a physical constant, approximately equal to the most probable distance between the proton and electron in a hydrogen atom in its ground state. It is named after Niels Bohr, due to its role in the Bohr model of an atom...
, the Hamiltonian can be written in dimensionless form
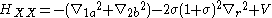
where
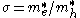 with neglecting kinetic energy operator of c. m. motion. And
with neglecting kinetic energy operator of c. m. motion. And 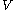 can be written as
can be written as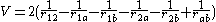
To solve the problem of the bound states of the biexciton complex, it is required to find the wave functions
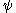 satisfying the wave equation
satisfying the wave equation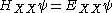
If the eigenvalue
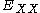 can be obtained, the binding energy of the biexciton can be also acquired
can be obtained, the binding energy of the biexciton can be also acquired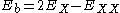
where
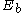 is the binding energy of the biexciton and
is the binding energy of the biexciton and 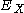 is the energy of exciton
is the energy of excitonExciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
.
Binding energy in nanotubes
Biexcitons with bound complexes formed by two excitons are surprisingly stable for carbon nanotubeCarbon nanotube
Carbon nanotubes are allotropes of carbon with a cylindrical nanostructure. Nanotubes have been constructed with length-to-diameter ratio of up to 132,000,000:1, significantly larger than for any other material...
in a wide diameter range.
Thus, a biexciton binding energy exceeding the inhomogeneous exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
line width is predicted for a wide range of nanotubes.
The biexciton binding energy in carbon nanotube is quite accurately approximated by an inverse dependence on
 , except perhaps for the smallest values of
, except perhaps for the smallest values of  .
.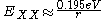
The actual biexciton binding energy is inversely proportional to the physical nanotube radius.
Binding energy in CuCl QDs
The binding energy of biexcitons increase with the decrease in their size and its size dependence and bulk value are well represented by the expression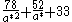 (meV)
(meV)where
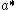 is the effective radius of microcrystallites in a unit of nm. The enhanced Coulomb interaction in microcrystallites still increase the biexciton binding energy in the large-size regime, where the quantum confinement energy of excitons is not considerable.
is the effective radius of microcrystallites in a unit of nm. The enhanced Coulomb interaction in microcrystallites still increase the biexciton binding energy in the large-size regime, where the quantum confinement energy of excitons is not considerable.Lifetime of biexcitons and excitons
In solid state physics, the recombinationCarrier generation and recombination
In the solid state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as...
of biexcitons (XX), which can be regarded as an entity of two weakly bound excitons (X), is often discussed in a simple way of argumentation:
The recombination of any of the two excitons forming the biexciton will result in its disappearance.
Therefore one would expect that the biexciton lifetime
Lifetime
Lifetime may refer to:*Life expectancy, the length of time a person is expected to remain alive*Mean lifetime, a certain number that characterizes the rate of reduction of a particle of an assembly...
,
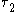 , is about half of that of the exciton
, is about half of that of the excitonExciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
,
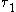 .
.However, some elementary points of view should be taken into account.
For example, a direct radiative recombination into the ground state of the crystal, allowed for the exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
state, is optically forbidden for singlet biexcitons.
Furthermore, the spin structure and the Coulomb interaction of the electrons and the holes forming the excitons and the biexcitons has to be considered.
In a CdSe/ZnSe quantum dot
Quantum dot
A quantum dot is a portion of matter whose excitons are confined in all three spatial dimensions. Consequently, such materials have electronic properties intermediate between those of bulk semiconductors and those of discrete molecules. They were discovered at the beginning of the 1980s by Alexei...
, the lifetime of biexciton is measured as 310 ps, and that of exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
is about 290 ps.
The ratio of the two lifetimes
LifeTimes
LifeTimes is an album by Diana Hubbard, released in 1979 by Waterhouse Records 8. In addition to Diana Hubbard, the album includes musical contributions from Chick Corea, Stanley Clarke, John Goodsall, Michael Boddicker, and Patrick Moraz. Diana is the daughter of Scientology founder L. Ron Hubbard...
is not about 2, but about 1.
The final state of the biexciton recombination is an optically allowed (bright) exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
state.
Because of exchange interaction, the excitons are split into optically allowed states (bright,
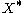 ) and optically forbidden states (dark,
) and optically forbidden states (dark, 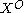 ).
).The spin flip time between
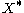 and
and 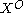 states,
states, 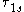 , is expected to be in the range of several ns, i.e., much longer than the bright exciton
, is expected to be in the range of several ns, i.e., much longer than the bright excitonExciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
lifetime.
The time evolution of the probabilities for the population of the biexciton and exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
states,
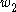 and
and 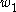 , respectively:
, respectively: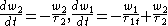
with
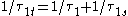 , where
, where 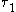 and
and 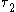 are the
are the 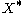 and the XX radiative recombination times, respectively.
and the XX radiative recombination times, respectively.Solving this equation system, the X and XX dynamics can be described quantitatively.
As a result, while decay of XX is monoexponential, the onset of the X line is significantly delayed, resulting in a plateaulike characteristics of the exciton
Exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids...
decay curve.

