Beta-secretase
Encyclopedia

Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that in humans is encoded by the BACE1 gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
.
β-Secretase is an aspartic-acid protease
Protease
A protease is any enzyme that conducts proteolysis, that is, begins protein catabolism by hydrolysis of the peptide bonds that link amino acids together in the polypeptide chain forming the protein....
important in the pathogenesis
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of a disease is the mechanism by which the disease is caused. The term can also be used to describe the origin and development of the disease and whether it is acute, chronic or recurrent...
of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
, and in the formation of myelin sheaths in peripheral nerve cells. The transmembrane protein
Transmembrane protein
A transmembrane protein is a protein that goes from one side of a membrane through to the other side of the membrane. Many TPs function as gateways or "loading docks" to deny or permit the transport of specific substances across the biological membrane, to get into the cell, or out of the cell as...
contains two active site aspartate residues in its extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
protein domain
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
and may function as a dimer
Protein dimer
In biochemistry, a dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids...
.
Role in Alzheimer's disease
Generation of the 40 or 42 amino acidAmino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
-long amyloid-β
Amyloid beta
Amyloid beta is a peptide of 36–43 amino acids that is processed from the Amyloid precursor protein. While it is most commonly known in association with Alzheimer's disease, it does not exist specifically to cause disease...
peptides that aggregate in the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
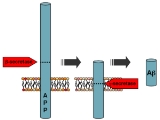
of Alzheimer's patients requires two sequential cleavages of the amyloid precursor protein
Amyloid precursor protein
Amyloid precursor protein is an integral membrane protein expressed in many tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons. Its primary function is not known, though it has been implicated as a regulator of synapse formation, neural plasticity and iron export...
(APP). Extracellular cleavage of APP by BACE creates a soluble extracellular fragment and a cell membrane-bound fragment referred to as C99. Cleavage of C99 within its transmembrane domain by γ-secretase releases the intracellular domain of APP and produces amyloid-β. Since alpha-secretase cleaves APP closer to the cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
than BACE does, it removes a fragment of the amyloid-β peptide. Initial cleavage of APP by alpha-secretase rather than BACE prevents eventual generation of amyloid-β.
Unlike APP and the presenilin
Presenilin
Presenilins are a family of related multi-pass transmembrane proteins that function as a part of the gamma-secretase intramembrane protease complex...
proteins important in γ-secretase, no known mutations in the gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
encoding BACE cause early-onset, familial Alzheimer's disease, which is a rare form of the disorder. However, levels of this enzyme have been shown to be elevated in the far more common late-onset sporadic Alzheimer's. The physiological purpose of BACE's cleavage of APP and other transmembrane proteins is unknown. BACE2
BACE2
Beta-secretase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BACE2 gene.BACE2 is a close homolog of BACE1, a protease known to be an important enzyme involved in the cellular pathways that some believe lead to Alzheimer's disease...
is a close homolog
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
of BACE1 with no reported APP cleavage in vivo.
BACE inhibitors
Drugs to block this enzyme (BACE inhibitors) in theory would prevent the build up of beta-amyloid and may help slow or stop the disease. Several companies are in the early stages of development and testing of this new potential class of treatment.Relationship to plasmepsin
Beta secretase, a vertebrate (human) aspartic-acid protease, is distantly related to the pathogenic aspartic-acid protease plasmepsinPlasmepsin
Plasmepsins are a class of at least 10 enzymes produced by the plasmodium parasite. There are ten different isoforms of these proteins and ten genes coding them respectively in plasmodium falciparum . It has been suggested that the plasmpesin family is smaller in other human plasmodium species...
, which is a potential target for future anti-malarial drugs.
External links
- The MEROPSMeropsMerops may refer to:* Merops , a genus of bee-eaters.* MEROPS, an on-line database for peptidases.It may also refer to several figures from Greek mythology:* King of Ethiopia, husband of Clymene, who lay with Helios and bore Phaethon...
online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: A01.004

