
Behavior of Coupled DEVS
Encyclopedia
DEVS is closed under coupling [Zeigper84] [ZPK00]. In other words, given a coupled DEVS model  , its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model
, its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model  . For a given coupled DEVS
. For a given coupled DEVS  , once we have an equivalent atomic DEVS
, once we have an equivalent atomic DEVS  , behavior of
, behavior of 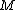 can be referred to behavior of atomic DEVS
can be referred to behavior of atomic DEVS
which is based on Timed Event System
.
Similar to behavior of atomic DEVS
, behavior of the Coupled DEVS class is described depending on definition of the total state set and its handling as follows.
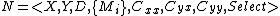 , its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model
, its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model 
where
 , its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model
, its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model  . For a given coupled DEVS
. For a given coupled DEVS  , once we have an equivalent atomic DEVS
, once we have an equivalent atomic DEVS  , behavior of
, behavior of 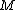 can be referred to behavior of atomic DEVS
can be referred to behavior of atomic DEVSBehavior of DEVS
Behaviors of a given DEVS model is a set of sequences of timed events including null events, called event segments which make the model move one state to another within a set of legal states...
which is based on Timed Event System
Timed event system
The General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define the time base, the admissible input segments, the system states, the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, the output for a given state....
.
Similar to behavior of atomic DEVS
Behavior of DEVS
Behaviors of a given DEVS model is a set of sequences of timed events including null events, called event segments which make the model move one state to another within a set of legal states...
, behavior of the Coupled DEVS class is described depending on definition of the total state set and its handling as follows.
View1: Total States = States * Elapsed Times
Given a coupled DEVS model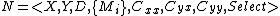 , its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model
, its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model 
where
-
 and
and 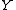 are the input event set and the output event set, respectively.
are the input event set and the output event set, respectively. -
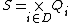 is the partial state set where
is the partial state set where 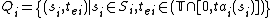 is the total state set of component
is the total state set of component 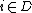 (Refer to View1 of Behavior of DEVS), where
(Refer to View1 of Behavior of DEVS), where 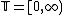 is the set of non-negative real numbers.
is the set of non-negative real numbers. -
 is the initial state set where
is the initial state set where 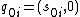 is the total initial state of component
is the total initial state of component  .
.  is the time advance function, where
is the time advance function, where 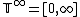 is the set of non-negative real numbers plus infinity.Given
is the set of non-negative real numbers plus infinity.Given  ,
, 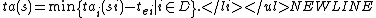
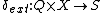 is the external state function. Given a total state
is the external state function. Given a total state 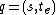 where
where  , and input event
, and input event 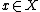 , the next state is given by
, the next state is given by 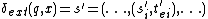
where
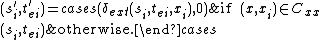
Given the partial state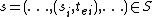 , let
, let 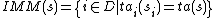 denote the set of imminent components. The firing component
denote the set of imminent components. The firing component  which triggers the internal state transition and an output event is determined by
which triggers the internal state transition and an output event is determined by 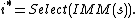
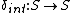 is the internal state function. Given a partial state
is the internal state function. Given a partial state  , the next state is given by
, the next state is given by 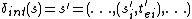
where

 is the output function. Given a partial state
is the output function. Given a partial state  ,
, 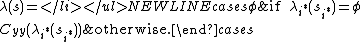
View2: Total States = States * Lifespan * Elapsed Times
Given a coupled DEVS model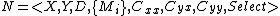 , its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model
, its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model 
where-
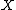 and
and 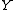 are the input event set and the output event set, respectively.
are the input event set and the output event set, respectively. -
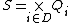 is the partial state set where
is the partial state set where  is the total state set of component
is the total state set of component 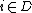 (Refer to View2 of Behavior of DEVS).
(Refer to View2 of Behavior of DEVS). -
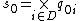 is the initial state set where
is the initial state set where 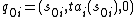 is the total initial state of component
is the total initial state of component 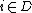 .
.
 is the time advance function. Given
is the time advance function. Given  ,
, 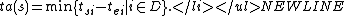
 is the external state function. Given a total state
is the external state function. Given a total state 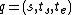 where
where 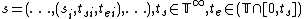 , and input event
, and input event 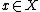 , the next state is given by
, the next state is given by 
where
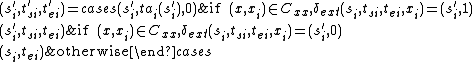
and
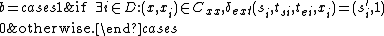
Given the partial state , let
, let 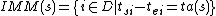 denote the set of imminent components. The firing component
denote the set of imminent components. The firing component 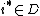 which trigers the internal state transition and an output event is determined by
which trigers the internal state transition and an output event is determined by 
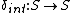 is the internal state function. Given a partial state
is the internal state function. Given a partial state  , the next state is given by
, the next state is given by 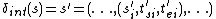
where
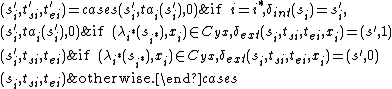
 is the output function. Given a partial state
is the output function. Given a partial state  ,
, 
Time Passage
Since in a coupled DEVS model with non-empty sub-components, i.e.,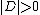 , the number of clocks which trace their elapsed times are multiple, so time passage of the model is noticeable.
, the number of clocks which trace their elapsed times are multiple, so time passage of the model is noticeable.
For View1
Given a total state where
where 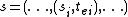
If unit event segment is the null event segment, i.e.
is the null event segment, i.e.  , the state trajectory in terms of Timed Event SystemTimed event systemThe General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define the time base, the admissible input segments, the system states, the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, the output for a given state....
, the state trajectory in terms of Timed Event SystemTimed event systemThe General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define the time base, the admissible input segments, the system states, the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, the output for a given state....
is
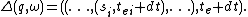
For View2
Given a total state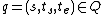 where
where 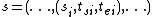
If unit event segment is the null event segment, i.e.
is the null event segment, i.e.  , the state trajectory in terms of Timed Event SystemTimed event systemThe General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define the time base, the admissible input segments, the system states, the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, the output for a given state....
, the state trajectory in terms of Timed Event SystemTimed event systemThe General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define the time base, the admissible input segments, the system states, the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, the output for a given state....
is

Remarks
- The behavior of a couple DEVS network whose all sub-components are deterministic DEVS models can be non-deterministic if
 is non-deterministic.
is non-deterministic.
See also
- DEVSDEVSDEVS abbreviating Discrete Event System Specification is a modular and hierarchical formalism for modeling and analyzing general systems that can be discrete event systems which might be described by state transition tables, and continuous state systems which might be described by differential...
- Behavior of Atomic DEVSBehavior of DEVSBehaviors of a given DEVS model is a set of sequences of timed events including null events, called event segments which make the model move one state to another within a set of legal states...
- Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVSSimulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVSGiven a coupled DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors, which are a set of trajectories not to reach illegal states...
- Simulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVSSimulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVSGiven an atomic DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors which are trajectories not to reach to illegal states....
- The behavior of a couple DEVS network whose all sub-components are deterministic DEVS models can be non-deterministic if
-

