
Simulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVS
Encyclopedia
Given an atomic DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors which are trajectories not to reach to illegal states. (see Behavior of DEVS
). [Zeigler84] originally introduced the algorithms that handle time variables related to lifespan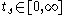 and elapsed time
and elapsed time  by introducing two other time variables, last event time,
by introducing two other time variables, last event time, 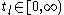 , and next event time
, and next event time  with the following relations:
with the following relations:

and
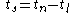
where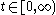 denotes the current time. And the remaining time,
denotes the current time. And the remaining time,
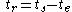
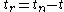
 .
.
Since the behavior of a given atomic DEVS model can be defined in two different views depending on the total state and the external transition function (refer to Behavior of DEVS
), the simulation algorithms are also introduced in two different views as below.
DEVS-simulator
variables:
parent // parent coordinator
 // time of last event
// time of last event
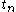 // time of next event
// time of next event
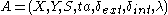 // the associated Atomic DEVS model
// the associated Atomic DEVS model
when receive init-message(Time )
)


when receive star-message(Time )
)
if then
then
error: bad synchronization;

send y-message(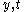 ) to parent;
) to parent;
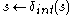
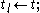
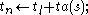
 , the last event time,
, the last event time, is set by the current time,
is set by the current time, , thus the elapsed time
, thus the elapsed time becomes zero because
becomes zero because  .
.
when receive x-message(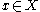 , Time
, Time  )
)
if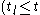 and
and 
false then
View 2: total states = states * lifespans * elapsed times
Notice that as addressed in Behavior of Atomic DEVS, depending on the value of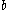 return by
return by 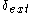 , last event time,
, last event time, , and next event time,
, and next event time,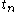 ,consequently, elapsed time,
,consequently, elapsed time,  , and lifespan
, and lifespan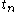 , are updated (if
, are updated (if 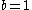 ) or preserved (if
) or preserved (if  ).
).
when receive x-message( , Time
, Time  )
)
if and
and 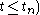 false then
false then
error: bad synchronization;
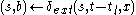
if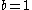 then
then

Behavior of DEVS
Behaviors of a given DEVS model is a set of sequences of timed events including null events, called event segments which make the model move one state to another within a set of legal states...
). [Zeigler84] originally introduced the algorithms that handle time variables related to lifespan
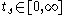 and elapsed time
and elapsed time  by introducing two other time variables, last event time,
by introducing two other time variables, last event time, 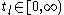 , and next event time
, and next event time  with the following relations:
with the following relations:
and
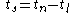
where
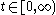 denotes the current time. And the remaining time,
denotes the current time. And the remaining time,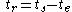
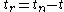
 .
.Since the behavior of a given atomic DEVS model can be defined in two different views depending on the total state and the external transition function (refer to Behavior of DEVS
Behavior of DEVS
Behaviors of a given DEVS model is a set of sequences of timed events including null events, called event segments which make the model move one state to another within a set of legal states...
), the simulation algorithms are also introduced in two different views as below.
Common parts
Regardless of two different views of total states, algorithms for initialization and internal transition cases are commonly defined as below.DEVS-simulator
variables:
parent // parent coordinator
 // time of last event
// time of last event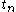 // time of next event
// time of next event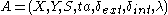 // the associated Atomic DEVS model
// the associated Atomic DEVS modelwhen receive init-message(Time
 )
)

when receive star-message(Time
 )
)if
 then
thenerror: bad synchronization;

send y-message(
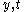 ) to parent;
) to parent;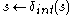
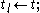
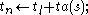
View 1: total states = states * elapsed times
As addressed in Behavior of Atomic DEVS, when DEVS receives an input event, right calling , the last event time,
, the last event time, is set by the current time,
is set by the current time, , thus the elapsed time
, thus the elapsed time becomes zero because
becomes zero because  .
.when receive x-message(
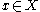 , Time
, Time  )
)if
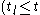 and
and 
false then
error: bad synchronization;

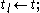
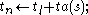
View 2: total states = states * lifespans * elapsed times Notice that as addressed in Behavior of Atomic DEVS, depending on the value of
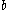 return by
return by 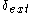 , last event time,
, last event time, , and next event time,
, and next event time,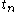 ,consequently, elapsed time,
,consequently, elapsed time,  , and lifespan
, and lifespan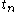 , are updated (if
, are updated (if 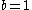 ) or preserved (if
) or preserved (if  ).
).when receive x-message(
 , Time
, Time  )
)if
 and
and 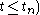 false then
false thenerror: bad synchronization;
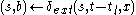
if
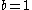 then
then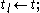

See also
- Atomic DEVS
- Behavior of atomic DEVS
- Simulation algorithms for coupled DEVSSimulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVSGiven a coupled DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors, which are a set of trajectories not to reach illegal states...

